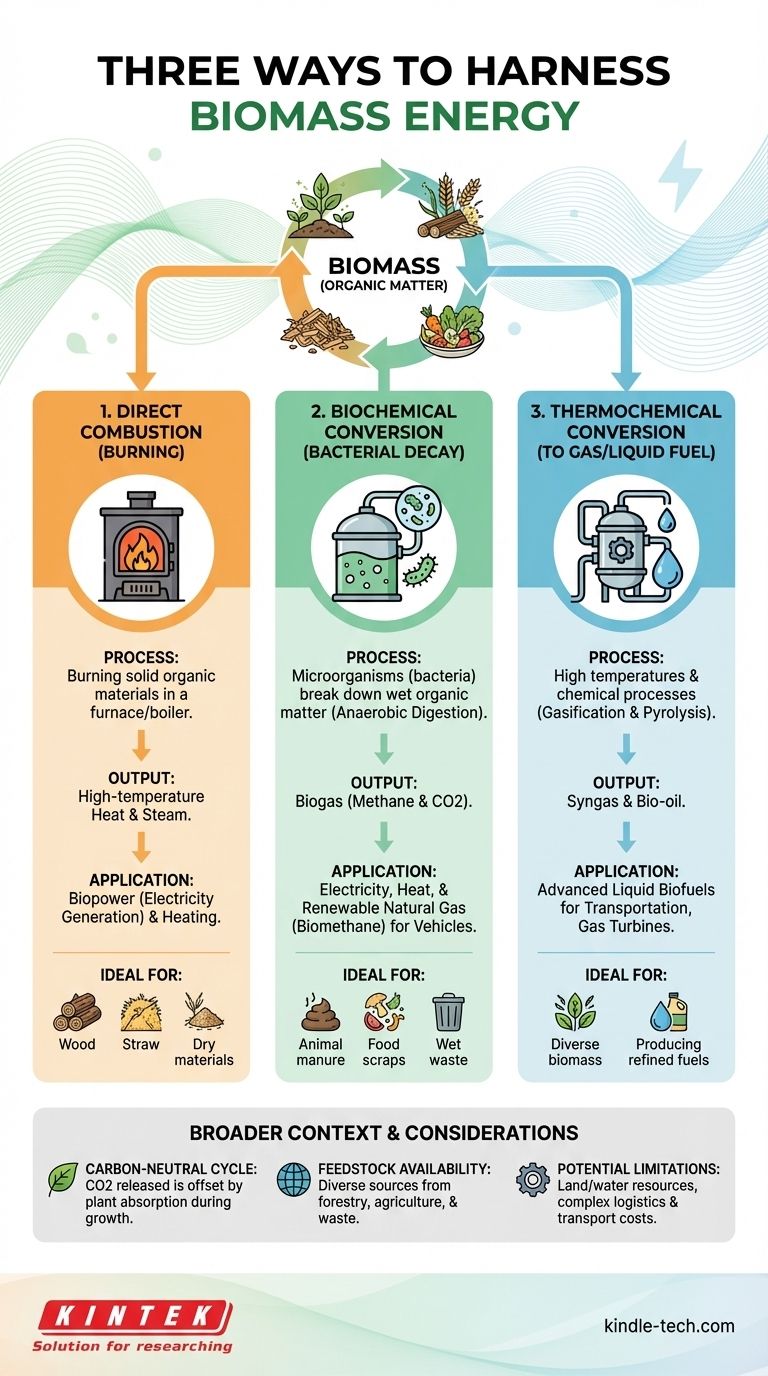
At its core, biomass can be converted into energy through three distinct pathways: direct burning, biochemical decay, and conversion into a gas or liquid fuel. These methods allow us to harness the solar energy stored in organic matter to produce heat, electricity, or advanced biofuels for transportation.
The versatility of biomass is its greatest strength. The choice between direct combustion, biochemical processes, or thermochemical conversion depends entirely on the type of organic material available and the specific form of energy you need to produce.

Method 1: Direct Combustion (Burning)
How It Works
Direct combustion is the most straightforward and traditional method for converting biomass into energy. It involves burning solid organic materials, such as wood, agricultural residue, or dedicated energy crops, in a furnace or boiler to produce high-temperature heat.
Primary Applications
This heat can be used directly for industrial processes or to warm buildings. More commonly, it is used to boil water, creating high-pressure steam that drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. This is often referred to as biopower.
Method 2: Biochemical Conversion (Bacterial Decay)
How It Works
Biochemical conversion uses microorganisms, like bacteria and enzymes, to break down wet organic matter. The most common process is anaerobic digestion, where bacteria decompose biomass in an oxygen-free environment.
The Primary Output: Biogas
This decomposition process releases biogas, a mixture composed primarily of methane (the main component of natural gas) and carbon dioxide.
Primary Applications
Biogas can be burned on-site to generate both electricity and heat. It can also be captured and purified to produce renewable natural gas (biomethane), which can be injected into existing gas pipelines or used as a vehicle fuel. This method is exceptionally effective for managing waste from sources like landfills, wastewater treatment plants, and livestock farms.
Method 3: Thermochemical Conversion (To Gas or Liquid Fuel)
How It Works
Thermochemical conversion uses high temperatures and chemical processes to transform biomass into more refined and energy-dense fuels. This is distinct from simple burning because the goal is to create a new fuel, not just release heat.
Gasification
Gasification involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen. This process doesn't burn the material completely but instead converts it into a flammable gas mixture called synthesis gas, or syngas. Syngas can then be used to power a gas turbine or be processed into liquid fuels.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis involves heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen. This thermal decomposition produces a liquid called bio-oil, which can be burned for electricity or further refined into transportation fuels. It also produces solid biochar and syngas as byproducts.
Understanding the Broader Context
A Carbon-Neutral Cycle
Biomass is considered a carbon-neutral energy source. The carbon dioxide released when biomass is converted to energy is offset by the carbon that the plants absorbed from the atmosphere during their growth, creating a balanced cycle.
Feedstock Availability
A key advantage of biomass is its wide availability from numerous sources. This includes forestry residues, agricultural crops and waste, and even municipal solid waste, making it a reliable and diverse component of a renewable energy strategy.
Potential Limitations
While powerful, biomass energy is not without challenges. It requires land and water resources, and the logistics of harvesting, collecting, and transporting bulky biomass to a processing facility can be complex and costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Each conversion pathway is suited for different types of biomass and produces a different form of energy.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity from dry materials like wood or straw: Direct combustion is the most established and efficient technology.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste like manure or food scraps: Biochemical conversion through anaerobic digestion is the ideal solution to create valuable biogas.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced liquid fuels for transportation: Thermochemical conversion via gasification or pyrolysis is the necessary pathway.
Understanding these three distinct pathways is the first step toward harnessing the versatile energy potential stored within organic matter.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Primary Output | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Burning dry biomass | Heat & Steam (for electricity/biopower) | Dry materials like wood, straw |
| Biochemical Conversion | Bacterial decay (anaerobic digestion) | Biogas (methane/CO2) | Wet waste like manure, food scraps |
| Thermochemical Conversion | High-temperature processes (gasification/pyrolysis) | Syngas, Bio-oil, Biofuels | Producing advanced liquid transportation fuels |
Ready to integrate biomass conversion into your laboratory or production process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for energy research and development. Whether you need reactors for pyrolysis, analyzers for biogas, or systems for combustion testing, our solutions help you optimize your biomass energy projects. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques












