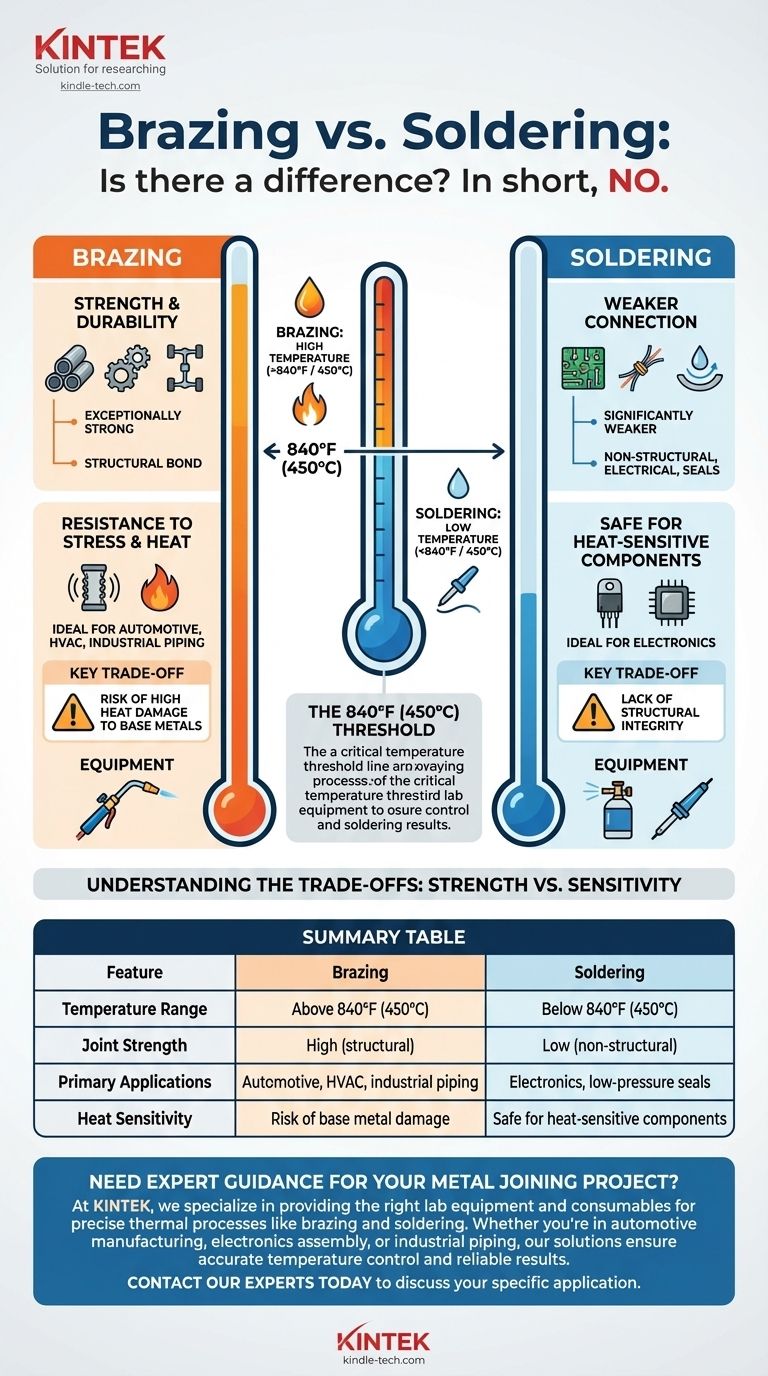
In short, no. While both brazing and soldering join metals using a molten filler material, they are fundamentally different processes. The key distinction is the temperature at which they operate, which directly determines the strength and application of the resulting joint. Brazing occurs at high temperatures (above 840°F / 450°C), creating exceptionally strong bonds, while soldering is a low-temperature process used for weaker, more delicate applications.
The choice between brazing and soldering comes down to one critical factor: strength versus sensitivity. Brazing provides a powerful structural bond at the cost of high heat, while soldering offers a weaker connection that protects heat-sensitive components.

The Defining Difference: Temperature and Filler Metal
The core distinction between these two methods is the liquid temperature of the filler metal used. This single variable dictates everything else, from the strength of the joint to the equipment required.
The 840°F (450°C) Threshold
By industry definition, any process that joins metals using a filler that melts below 840°F (450°C) is considered soldering.
Any process using a filler metal that melts above 840°F (450°C) without melting the base metals is defined as brazing.
How the Process Works
In both methods, the base metals being joined are heated to a temperature high enough to melt the filler metal but not high enough to melt the base metals themselves.
The molten filler is then drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the parts through a phenomenon called capillary action, creating a permanent bond as it cools and solidifies.
How Temperature Translates to Performance
The higher temperatures used in brazing enable the use of stronger filler alloys, resulting in joints with vastly different mechanical properties than those created by soldering.
Joint Strength and Durability
Brazed joints are exceptionally strong. The filler alloys (often brass or silver-based) form a metallurgical bond with the base metals, creating a connection that can be as strong as the materials being joined.
Soldered joints are significantly weaker. They are not intended for structural or load-bearing applications. Their primary purpose is typically for electrical conductivity or creating a low-pressure seal.
Resistance to Stress and Heat
Brazing is the preferred method for parts that will be exposed to high temperatures, vibration, or shock. This makes it ideal for applications in the automotive, HVAC, and industrial piping industries.
Soldering is used where heat input must be minimized. Its most common application is in electronics, where the high heat of brazing would destroy sensitive components like transistors and circuit boards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong process can lead to component failure or damage to your workpiece. Understanding their respective limitations is critical.
The Risk of High Heat
The primary drawback of brazing is its intense heat requirement. This high temperature can anneal (soften), warp, or otherwise damage the base metals if not applied with skill and control.
The Limitation of Low Strength
Soldering's key limitation is its lack of structural integrity. A soldered joint will fail quickly under significant mechanical load or stress. It should never be used to join critical structural components.
Equipment and Skill
Brazing almost always requires a torch, typically an oxy-acetylene torch, to generate sufficient heat. Soldering can be done with a much wider range of tools, from simple propane torches to low-power soldering irons for electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your method based on the non-negotiable requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is structural strength and durability: Brazing is the correct choice, as it creates a joint nearly as strong as the parent materials.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive components like electronics: Soldering is the only safe option due to its low application temperature.
- If your primary focus is creating a simple, leak-proof seal on low-pressure pipes: Soldering is often the faster and easier method.
Ultimately, understanding that temperature dictates strength is the key to selecting the right process for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Above 840°F (450°C) | Below 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | High (structural) | Low (non-structural) |
| Primary Applications | Automotive, HVAC, industrial piping | Electronics, low-pressure seals |
| Heat Sensitivity | Risk of base metal damage | Safe for heat-sensitive components |
Need expert guidance for your metal joining project? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processes like brazing and soldering. Whether you're in automotive manufacturing, electronics assembly, or industrial piping, our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum high-temperature furnace essential for XTO silicification? Ensure Pure Coating for Refractory Metals
- Why is a high vacuum furnace necessary for post-bond heat treatment (PBHT)? Enhance Your Diffusion-Bonded Joint Integrity
- What is sintering in a furnace? A Guide to Creating Strong, Dense Parts from Powder
- How long do you anneal steel? Master the Time, Temperature, and Cooling for Perfect Softness
- Is calcination done in a blast furnace? Clarifying the Purpose of Industrial Furnaces
- Which method of heat transfer can work through vacuum? Unlock the Power of Thermal Radiation
- What does sintering do in powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Strong, Solid Parts
- What is meant by physical Vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating



















