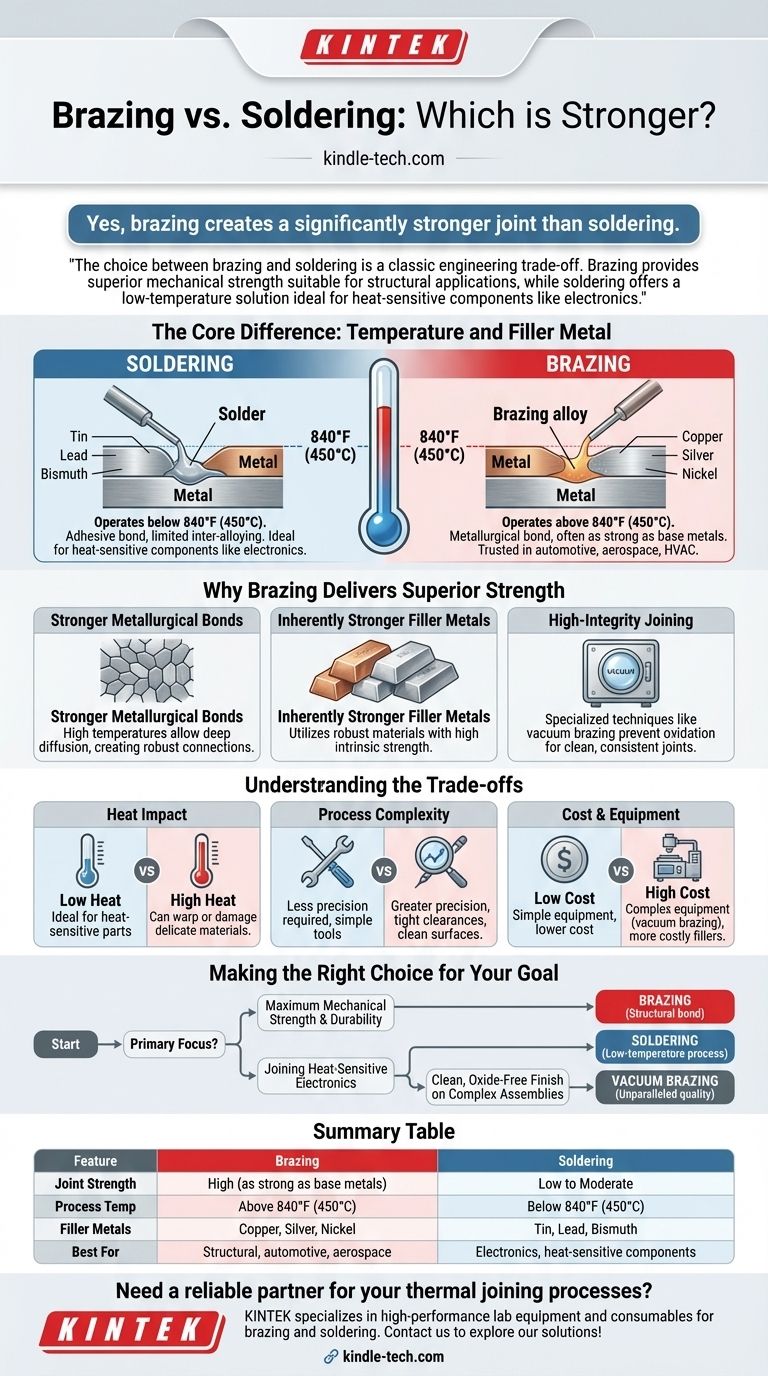
Yes, brazing creates a significantly stronger joint than soldering. The fundamental difference lies in the temperature at which each process occurs and the filler metals used. Brazing takes place at temperatures above 840°F (450°C), allowing for metallurgical bonds that are often as strong as the base metals being joined.
The choice between brazing and soldering is a classic engineering trade-off. Brazing provides superior mechanical strength suitable for structural applications, while soldering offers a low-temperature solution ideal for heat-sensitive components like electronics.
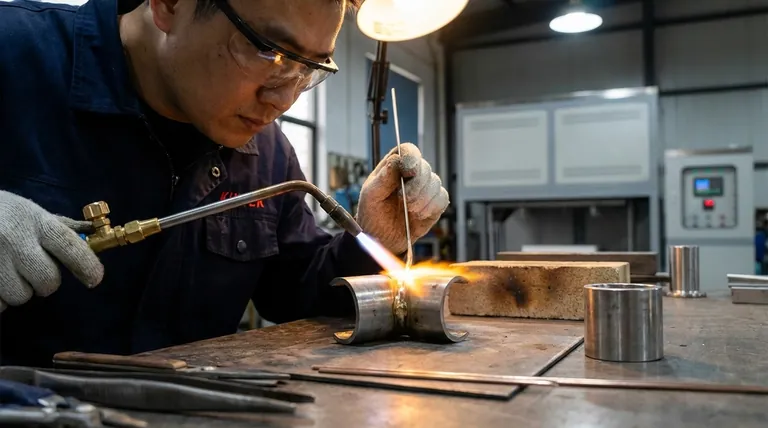

The Core Difference: Temperature and Filler Metal
The strength of a joint is directly tied to the process used to create it. While both brazing and soldering join metals without melting them, their operating temperatures dictate their capabilities.
How Brazing Works
Brazing uses a filler metal that melts above 840°F (450°C) but below the melting point of the base materials. This high heat facilitates a strong metallurgical reaction between the filler and the parent metals, creating a powerful, permanent bond.
This process is trusted in demanding industries like automotive, aerospace, and HVAC systems where joint integrity is critical.
How Soldering Works
Soldering operates at much lower temperatures, always below 840°F (450°C). The filler metal, or solder, melts and flows into the joint via capillary action, but the resulting bond is primarily adhesive with limited inter-alloying.
This makes soldering ideal for applications where mechanical strength is secondary to other factors, such as electrical conductivity in electronics.
Why Brazing Delivers Superior Strength
The strength advantage of brazing is not marginal; it's a defining characteristic that stems from the physics of the process.
Stronger Metallurgical Bonds
The high temperatures in brazing allow the filler metal to diffuse more deeply into the crystalline structure of the base metals. This creates a robust connection that can withstand significant stress, vibration, and thermal cycling.
As a result, a properly brazed joint is often as strong as, or even stronger than, the materials it connects.
Inherently Stronger Filler Metals
Brazing alloys are typically composed of robust materials like copper, silver, and nickel. These metals have high intrinsic strength, which is transferred to the final joint.
In contrast, solders are based on lower-strength, low-melting-point metals like tin, lead, or bismuth.
High-Integrity Joining
Specialized techniques like vacuum brazing prevent oxidation during the heating process. This results in an exceptionally clean, strong, and consistent joint, which is crucial for high-performance and complex geometric applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While brazing is stronger, it is not always the superior choice. The right process depends entirely on the application's specific requirements.
The Impact of High Heat
The primary drawback of brazing is its high temperature requirement. This intense heat can damage or warp delicate or heat-treated base materials, making soldering the only viable option for sensitive electronic components.
Process Complexity
Brazing generally demands greater precision than soldering. It requires exceptionally clean surfaces and very tight clearances between the parts to ensure proper capillary action and a strong bond.
Cost and Equipment
Brazing equipment, especially for advanced processes like vacuum brazing, is more complex and expensive than a simple soldering iron. The filler materials themselves are also often more costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your joining method based on the primary requirement of the finished part, not on strength alone.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength and durability: Brazing is the clear choice, as it creates a structural bond comparable to the parent materials.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive electronics or components: Soldering is the correct and necessary method due to its low-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is a clean, oxide-free finish on complex assemblies: An advanced method like vacuum brazing provides unparalleled joint quality and consistency.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal joining process is about matching the method's capabilities to your application's unique demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Strength | High (as strong as base metals) | Low to Moderate |
| Process Temp | Above 840°F (450°C) | Below 840°F (450°C) |
| Filler Metals | Copper, Silver, Nickel | Tin, Lead, Bismuth |
| Best For | Structural, automotive, aerospace | Electronics, heat-sensitive components |
Need a reliable partner for your thermal joining processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including brazing and soldering solutions tailored for laboratories and industrial R&D. Whether you're developing robust structural components or delicate electronic assemblies, our expertise ensures you achieve precise, consistent, and strong joints. Contact us today to explore how our solutions can enhance your joining applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Do different liquids melt at different rates? Unlock the Science of Melting Points and Material Properties
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- What hazard is involved when using a furnace? Protect Your Home from the Silent Killer
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- What affects the melting point of a substance? Uncover the Key Factors & Forces



















