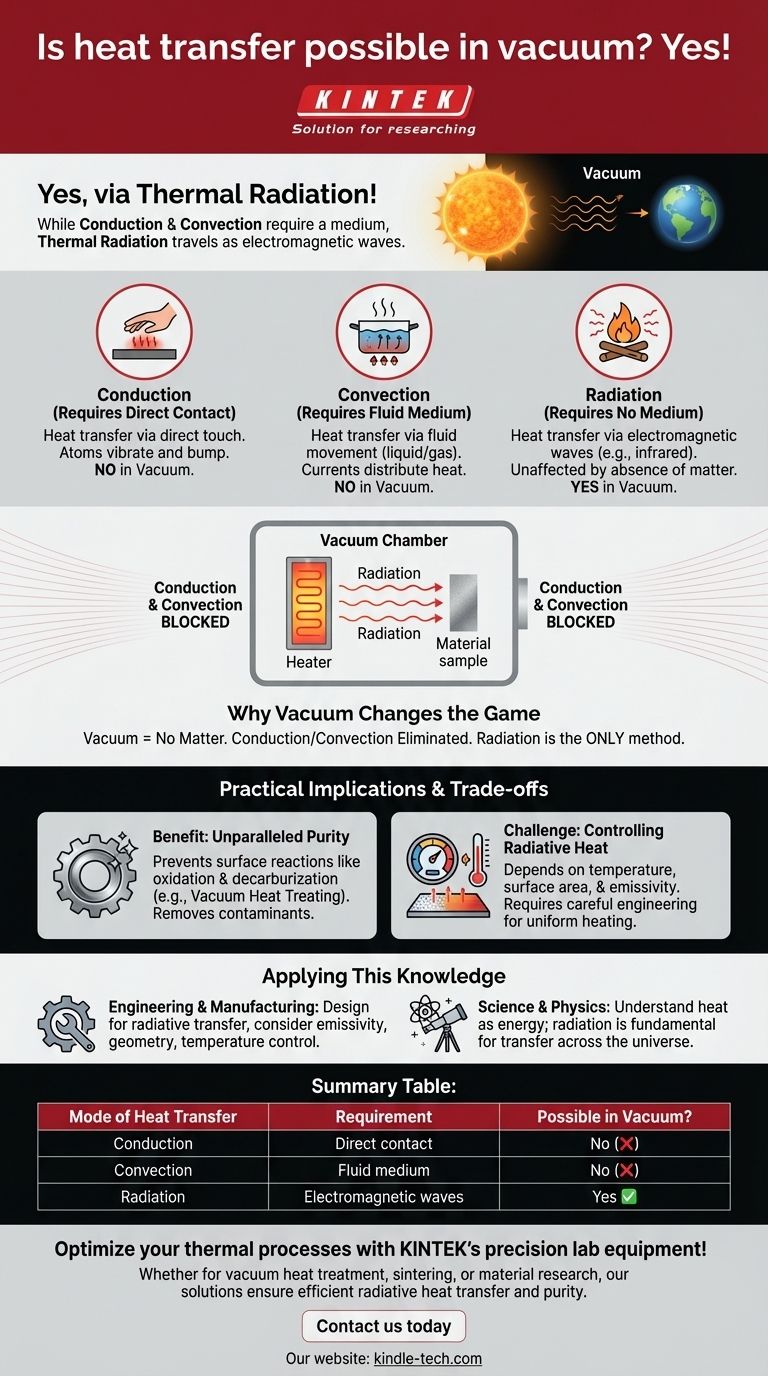
Yes, heat transfer is absolutely possible in a vacuum. While the familiar methods of heat transfer—conduction and convection—require a medium, the vacuum of space is filled with energy traveling as electromagnetic waves. This process, known as thermal radiation, is how the sun's warmth travels 93 million miles through the void to reach Earth.
In the absence of matter, conduction and convection become impossible, leaving thermal radiation as the sole method for transferring heat. Understanding this principle is fundamental to fields ranging from astrophysics to industrial manufacturing.

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer
To understand why a vacuum changes the rules, we must first be clear on the three distinct ways heat energy moves from one place to another.
Conduction (Requires Direct Contact)
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical touch. When you touch a hot stovetop, heat is conducted directly to your hand.
The atoms in the hotter object vibrate vigorously, bumping into the atoms of the colder object and transferring their energy. This process requires a medium; it cannot happen across empty space.
Convection (Requires a Fluid Medium)
Convection is heat transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). A common example is a convection oven, where a fan circulates hot air to cook food more evenly.
Warmer, less dense fluid rises, and cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a current that distributes heat. This, by definition, requires a medium to flow.
Radiation (Requires No Medium)
Radiation is the transfer of heat via electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. Unlike conduction or convection, it does not require any matter to travel.
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The hotter the object, the more energy it radiates. This is the energy you feel from a distant campfire or a glowing heating element.
Why Vacuum Changes the Game
A vacuum is, by definition, a space devoid of matter. This has a profound impact on how heat can be transferred.
Eliminating Conduction and Convection
Without atoms to touch each other (conduction) or a fluid to circulate (convection), these two modes of heat transfer are effectively stopped in a vacuum. This is the principle behind a thermos, which uses a vacuum layer to keep liquids hot or cold.
Radiation Becomes the Only Method
Because thermal radiation travels as electromagnetic waves, it is completely unaffected by the absence of matter. It is the only form of heat transfer that can operate in a vacuum.
In practical applications like vacuum induction sintering, heat is transferred from a heating module to a material's surface almost entirely through radiation. Conduction and convection are minimized due to the low gas content.
Practical Implications and Trade-offs
Operating in a vacuum isn't just a theoretical concept; it's a critical tool in modern engineering and science with distinct advantages and challenges.
The Benefit: Unparalleled Purity
Heating materials in a vacuum prevents surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization, which would normally occur in the presence of air.
This process is used in vacuum heat treating to create highly pure, clean metal parts. It can also remove contaminants and dissolved gases from the material itself, a process known as degassing.
The Challenge: Controlling Radiative Heat
Relying solely on radiation for heat transfer requires careful engineering. The rate of transfer depends on the temperature of the heat source, its surface area, and the surface properties (color and texture) of both the emitter and the receiver.
Designing a system for efficient and uniform heating in a vacuum is a complex task. Engineers must select appropriate heating modules and consider the geometry of the setup to ensure the target receives energy as intended.
Applying This Knowledge
Understanding how heat behaves in a vacuum is crucial for specific goals, whether you are designing a satellite or simply studying physics.
- If your primary focus is engineering or manufacturing: You must design systems specifically for radiative heat transfer, focusing on factors like surface emissivity, geometry, and temperature control to achieve desired outcomes.
- If your primary focus is science and physics: The key takeaway is that heat is a form of energy, and radiation is a fundamental mechanism for its transfer across the universe, entirely independent of matter.
Ultimately, recognizing that heat can travel through a void fundamentally changes our understanding of energy itself.
Summary Table:
| Mode of Heat Transfer | Requirement | Possible in Vacuum? |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct contact between materials | No |
| Convection | Fluid medium (gas or liquid) | No |
| Radiation | Electromagnetic waves | Yes |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's precision lab equipment! Whether you're conducting vacuum heat treatment, sintering, or advanced material research, our specialized solutions ensure efficient radiative heat transfer and unparalleled purity. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's performance and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.



















