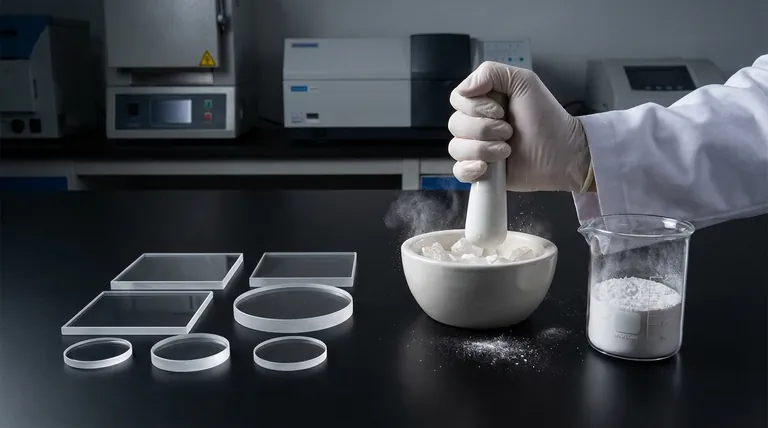
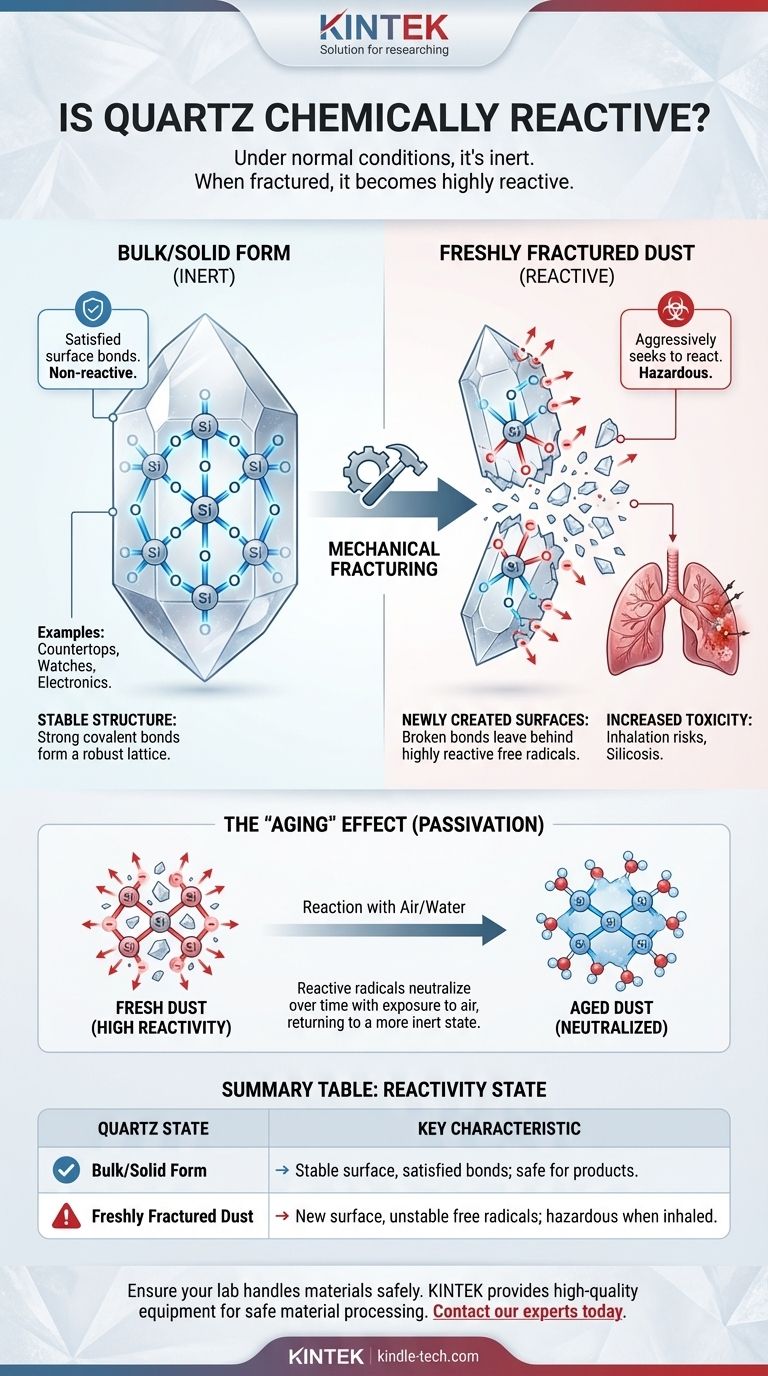
Under normal conditions, quartz is one of the most chemically inert and stable minerals on Earth. Its robust crystal structure makes it highly resistant to chemical attack. However, this inertness is conditional. When quartz is mechanically fractured or ground into fine particles, its newly created surfaces become highly reactive and can pose significant health risks.
The chemical reactivity of quartz is not a fixed property but a state-dependent one. While solid, undisturbed quartz is exceptionally stable, the act of fracturing its surface creates unstable and highly reactive sites known as mineral radicals, fundamentally changing its chemical behavior.

The Dual Nature of Quartz: Inert vs. Active
To understand the reactivity of quartz, it's essential to distinguish between its behavior as a bulk material and its behavior as a collection of fine, freshly-fractured particles.
Why Bulk Quartz is So Stable
The stability of quartz comes from its internal structure. It is composed of silicon and oxygen atoms linked by powerful covalent bonds in a repeating, three-dimensional lattice.
These bonds require a great deal of energy to break, which is why quartz is so hard and has a high melting point. In its solid, polished state (like a countertop or a large crystal), these bonds are satisfied, and the surface is stable and non-reactive.
The Trigger: Mechanical Fracturing
The situation changes dramatically when mechanical energy is applied, such as through grinding, cutting, or crushing. This process physically severs the strong silicon-oxygen bonds within the crystal lattice.
This act of breaking the crystal exposes a new, "fresh" surface that is fundamentally different from the original, stable material.
The Creation of Surface Radicals
When a silicon-oxygen bond is broken, it can leave behind atoms with unpaired electrons on the new surface. These sites are known as free radicals.
Radicals are chemically unstable and highly reactive. They will aggressively seek to react with nearby molecules—such as water, oxygen, or biological tissues—in order to regain a stable electronic state. This is the root cause of the increased reactivity of "fresh" quartz dust.
Understanding the Consequences of Reactivity
The formation of surface radicals is not just an academic concept; it has significant real-world implications, particularly in occupational health.
Increased Toxicity of Fresh Dust
The primary concern with reactive quartz surfaces is toxicity. When fine, freshly-fractured quartz dust is inhaled, these surface radicals can interact with the fluids and tissues within the lungs.
This interaction can generate oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in the development of silicosis and other lung diseases. This is why aged quartz dust, where the radicals have already been neutralized by exposure to air, is considered less hazardous than fresh dust.
The "Aging" Effect: A Temporary State
The high reactivity of a freshly fractured quartz surface is a temporary condition. These unstable radicals will quickly react with molecules in the surrounding environment, most commonly water vapor in the air.
This process, sometimes called "passivation" or "aging," neutralizes the radicals and returns the surface to a more stable, inert state. This is why the primary hazard exists at the point of dust generation—when the surfaces are at their most reactive.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Understanding the context of quartz reactivity is critical to accurately assessing its risk and behavior.
It's a Surface, Not a Bulk Phenomenon
The chemical reactivity is strictly a surface phenomenon. A solid piece of quartz, like a kitchen countertop, is not reactive in this way because its surface is stable and is not being actively fractured.
The hazard is associated with fine dust, where the ratio of reactive surface area to mass is exceptionally high.
Reactivity vs. Solubility
This radical-based reactivity is different from chemical dissolution. While quartz is famously resistant to most acids, it will dissolve in hydrofluoric acid (HF).
This is a distinct chemical process that attacks the entire crystal lattice, unlike the surface-specific reactivity caused by fracturing.
The Critical Role of Particle Size
The danger of quartz dust increases as the particle size decreases. Grinding quartz into a fine powder dramatically increases the total surface area.
A one-centimeter cube of quartz has a surface area of 6 cm². If ground into one-micrometer cubes, the total surface area of that same amount of quartz increases to 60,000 cm². This creates an exponentially larger number of reactive sites.
How to Assess Quartz Reactivity in Your Context
Your approach to quartz should be determined entirely by its physical state and your application.
- If your primary focus is occupational safety (e.g., construction, mining): Treat any process that creates fine quartz dust as a high-risk activity due to the chemical reactivity of freshly fractured surfaces.
- If your primary focus is consumer products (e.g., countertops, watches): Understand that the solid, polished form is chemically stable and non-reactive, as the surfaces are not being continuously broken.
- If your primary focus is material science or geology: Recognize that the chemical behavior of quartz in a dynamic system (like an industrial slurry or geological fault line) is dictated by its active surface chemistry, not its bulk inertness.
Ultimately, the chemical reactivity of quartz is a direct function of its physical state, transforming from a stable solid into a reactive agent only when its surface is broken.
Summary Table:
| Quartz State | Chemical Reactivity | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk/Solid Form | Very Low (Inert) | Stable surface with satisfied bonds; safe for countertops, etc. |
| Freshly Fractured Dust | Very High (Reactive) | New surface with unstable free radicals; hazardous when inhaled. |
Ensure your lab handles materials safely. The reactivity of materials like quartz is critical for both experimental outcomes and workplace safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed for safe and efficient material processing. Whether you need durable furnaces for heat treatment or safe handling tools for reactive materials, our solutions are tailored to meet rigorous laboratory standards. Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your specific needs and ensure a safer, more productive lab environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications
- What temperature does quartz glass melt at? Understanding Its Softening Point and Practical Limits
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance
- Does quartz have a high melting point? Discover Its Superior High-Temperature Performance



















