To put it directly: vacuum casting is a "middle-ground" manufacturing technology. It is more expensive per part than a single 3D print but is vastly cheaper than the steel tooling required for injection molding. Its cost-effectiveness is revealed when you need a small batch of production-quality parts, not just a single prototype.
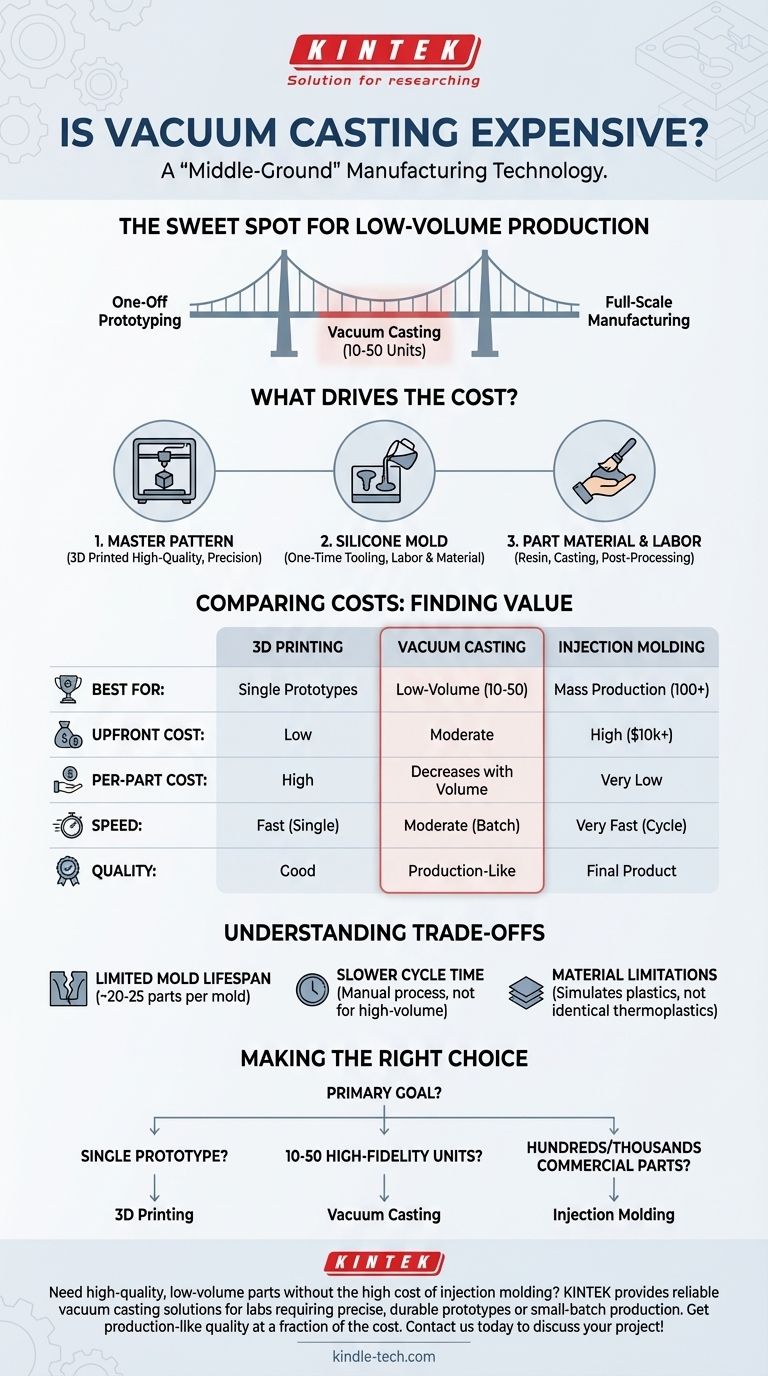
The question isn't simply whether vacuum casting is expensive, but rather at what quantity it becomes the most economical choice. It excels in low-volume production, bridging the gap between one-off prototyping and full-scale manufacturing.

What Drives the Cost of Vacuum Casting?
To understand its price, you must first understand the process. Vacuum casting is fundamentally a copying method. The costs are distributed across creating a master pattern, making a mold, and then casting the final parts.
The Master Pattern
The process begins with a high-quality master pattern, which is typically created using a precise 3D printing method like Stereolithography (SLA). The quality, size, and complexity of this initial part are the first cost factors.
The Silicone Mold
This master pattern is used to create a silicone mold. The amount of silicone required—determined by the part's size—and the labor to create the mold form the primary "tooling" cost. This cost is a one-time investment for each mold.
Part Material and Labor
Each part is cast by mixing and pouring a liquid polyurethane resin into the mold within a vacuum chamber. The cost of the specific resin, the skilled labor for the casting process, and any post-processing or finishing (like painting or sanding) add to the per-part price.
Comparing Costs: Vacuum Casting vs. Alternatives
The value of vacuum casting becomes clear only when compared to other methods. Its "sweet spot" is for low-volume production where other technologies are either too slow or too expensive.
Versus 3D Printing
For a single part, 3D printing is almost always cheaper and faster. However, if you need 10 identical parts, 3D printing them one-by-one can become more expensive and time-consuming than creating one mold and casting them. Vacuum casting's per-part cost drops with each copy made from a single mold.
Versus Injection Molding
Injection molding is the standard for mass production. It has an extremely low per-part cost but requires an enormous upfront investment ($10,000 to $100,000+) in a hard steel mold. Vacuum casting tooling is a fraction of this price, making it ideal for runs that don't justify a massive tooling budget.
The Breakeven Point
Vacuum casting is typically the most cost-effective option for quantities between 10 and 50 units per mold. It provides parts with material properties and surface finishes that are far superior to most 3D prints, closely simulating a final injection-molded product.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
No process is perfect. Being objective means acknowledging the limitations that influence when vacuum casting is the right financial decision.
Limited Mold Lifespan
A single silicone mold has a finite life. It will begin to degrade from thermal and chemical stress after producing approximately 20-25 parts. For runs of 100 parts, you would need to budget for creating about four separate molds.
Slower Per-Part Cycle Time
Compared to the seconds-long cycle time of injection molding, vacuum casting is a manual, methodical process. Mixing resins, casting, and curing takes significantly longer per part, making it unsuitable for high-volume needs.
Material Limitations
While the available polyurethane resins can simulate a wide range of production plastics (from rigid ABS to flexible rubber), they are not the exact same thermoplastic materials used in injection molding. This can be a critical distinction for end-use parts requiring specific thermal or chemical resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your production volume and quality requirements are the most critical factors in determining if vacuum casting is an "expensive" or a "cost-effective" choice for you.
- If your primary focus is a single, early-stage prototype: Stick with 3D printing for its speed and low initial cost.
- If your primary focus is creating 10-50 high-fidelity units for testing, marketing, or a pilot run: Vacuum casting is almost certainly your most economical option for achieving production-like quality.
- If your primary focus is producing hundreds or thousands of parts for a commercial product: The upfront investment in injection molding tooling is the only way to achieve a viable per-part cost.
Choosing the right manufacturing process is about aligning the method's cost structure with your specific production volume and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Master Pattern | Quality, size, and complexity of the 3D-printed master |
| Silicone Mold | One-time tooling cost based on part size and labor |
| Part Material & Labor | Per-part cost from resin, casting, and post-processing |
| Ideal Quantity | 10-50 units per mold for optimal cost-effectiveness |
| Mold Lifespan | ~20-25 parts per mold; multiple molds needed for larger runs |
Need high-quality, low-volume parts without the high cost of injection molding? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable vacuum casting solutions for laboratories requiring precise, durable prototypes or small-batch production parts. Our expertise ensures you get production-like quality at a fraction of the cost—perfect for testing, pilot runs, or market validation. Contact us today to discuss your project and receive a tailored quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
People Also Ask
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity



















