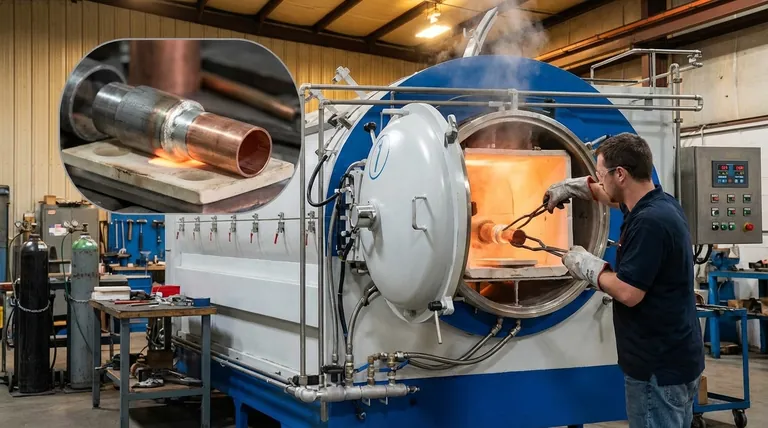
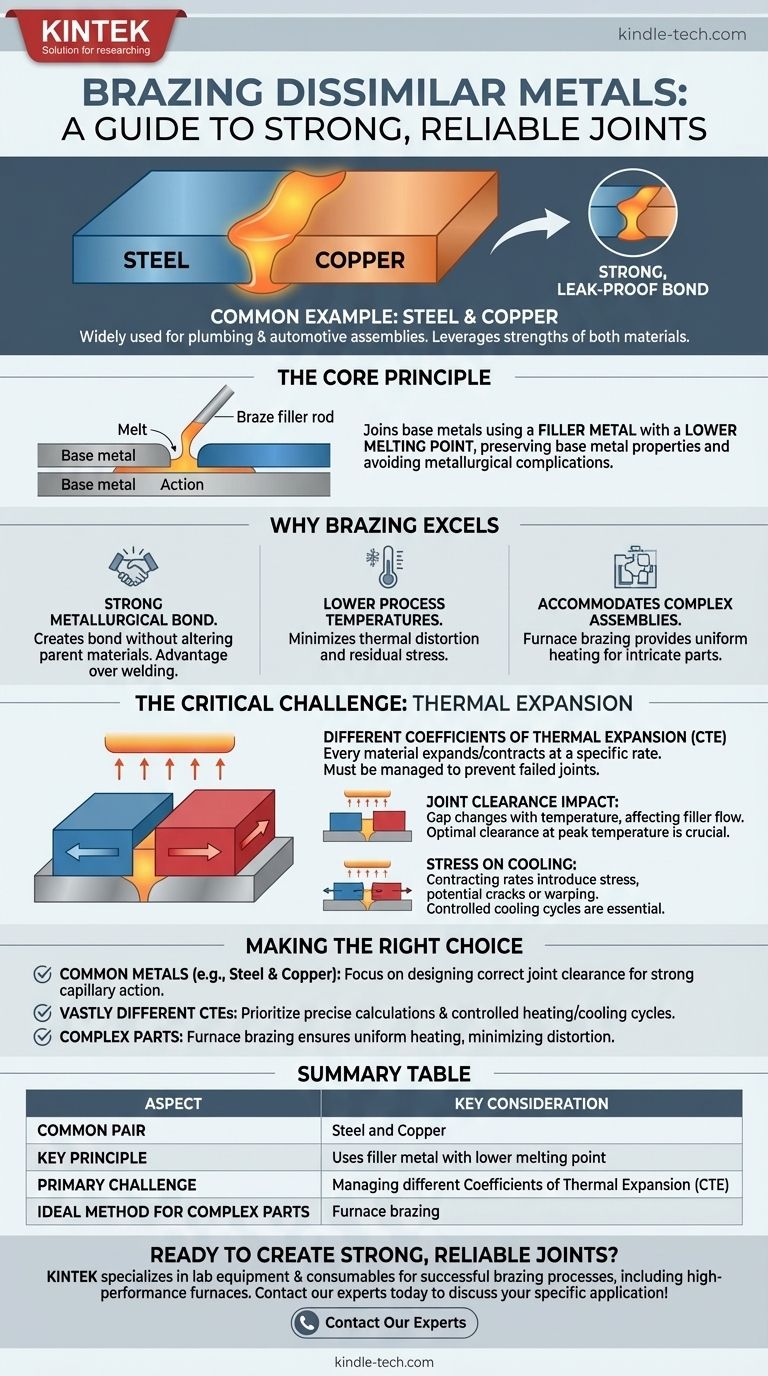
A common and effective example is the joining of steel and copper through brazing. This process is widely used because it leverages the strengths of both materials, creating a strong, leak-proof bond suitable for applications ranging from plumbing to automotive assemblies. Brazing is an exceptional method for joining a vast array of dissimilar metals, including stainless steel, nickel, aluminum, and silver.
The core principle that makes brazing so effective for dissimilar metals is that it joins them using a filler metal with a lower melting point. This process avoids melting the base metals, preserving their individual properties and preventing the metallurgical complications that often arise when trying to fuse two different materials.

Why Brazing Excels at Joining Dissimilar Metals
Brazing creates a strong metallurgical bond without fundamentally altering the parent materials. This is a critical advantage over welding, which involves melting and mixing the base metals, a process that is often impossible or creates brittle results with dissimilar materials.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The braze filler metal is the key. It is designed to melt at a temperature lower than the melting points of the two metals being joined. This molten filler is then drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the parts by capillary action, creating the joint upon cooling.
Lower Process Temperatures
Because the base metals do not melt, the overall process temperatures are significantly lower than in welding. This minimizes the risk of thermal distortion and residual stress, which are major concerns when joining materials that expand and contract at different rates.
Accommodating Complex Assemblies
Methods like furnace brazing provide uniform, controlled heating across an entire assembly. This makes it ideal for joining intricate parts or components with varying thicknesses, ensuring the braze joint is consistent and reliable throughout.
The Critical Challenge: Thermal Expansion
The single most important factor to manage when brazing dissimilar metals is their different rates of thermal expansion. Ignoring this can lead to a failed joint.
The Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
Every material expands when heated and contracts when cooled at a specific rate, known as its Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). When you join two metals with different CTEs, one will expand more than the other as they reach brazing temperature.
Impact on Joint Clearance
This difference in expansion directly affects the gap, or joint clearance, between the parts. A joint that fits perfectly at room temperature might become too tight or too loose at brazing temperature, preventing the filler metal from flowing correctly. Engineers must calculate and design the initial clearance to be optimal at the peak temperature.
Mitigating Stress on Cooling
As the assembly cools, the metals will also contract at different rates. This can introduce significant stress into the joint, potentially causing cracks or warping. Proper design and controlled cooling cycles are essential to manage these stresses and ensure a durable bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The success of your brazed joint depends on accommodating the specific properties of the metals you are joining.
- If your primary focus is joining common metals like steel and copper: Your main concern will be designing the correct joint clearance to facilitate strong capillary action with a standard silver or copper-based filler alloy.
- If your primary focus is joining metals with vastly different expansion rates: You must prioritize precise calculations for thermal expansion and implement controlled heating and cooling cycles to prevent stress fractures.
- If your primary focus is joining complex parts with varied thicknesses: Furnace brazing is likely the best method, as its uniform heating minimizes the risk of distortion across the assembly.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently use brazing to create strong, reliable joints between a wide range of dissimilar metals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Common Pair | Steel and Copper |
| Key Principle | Uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base metals |
| Primary Challenge | Managing different Coefficients of Thermal Expansion (CTE) |
| Ideal Method for Complex Parts | Furnace Brazing |
Ready to create strong, reliable joints for your assemblies?
Brazing dissimilar metals like steel and copper requires precision and the right equipment to manage thermal expansion and ensure a perfect bond. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for successful brazing processes, including high-performance furnaces for uniform heating.
Let our expertise help you achieve leak-proof, durable joints for your most complex projects. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect brazing solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















