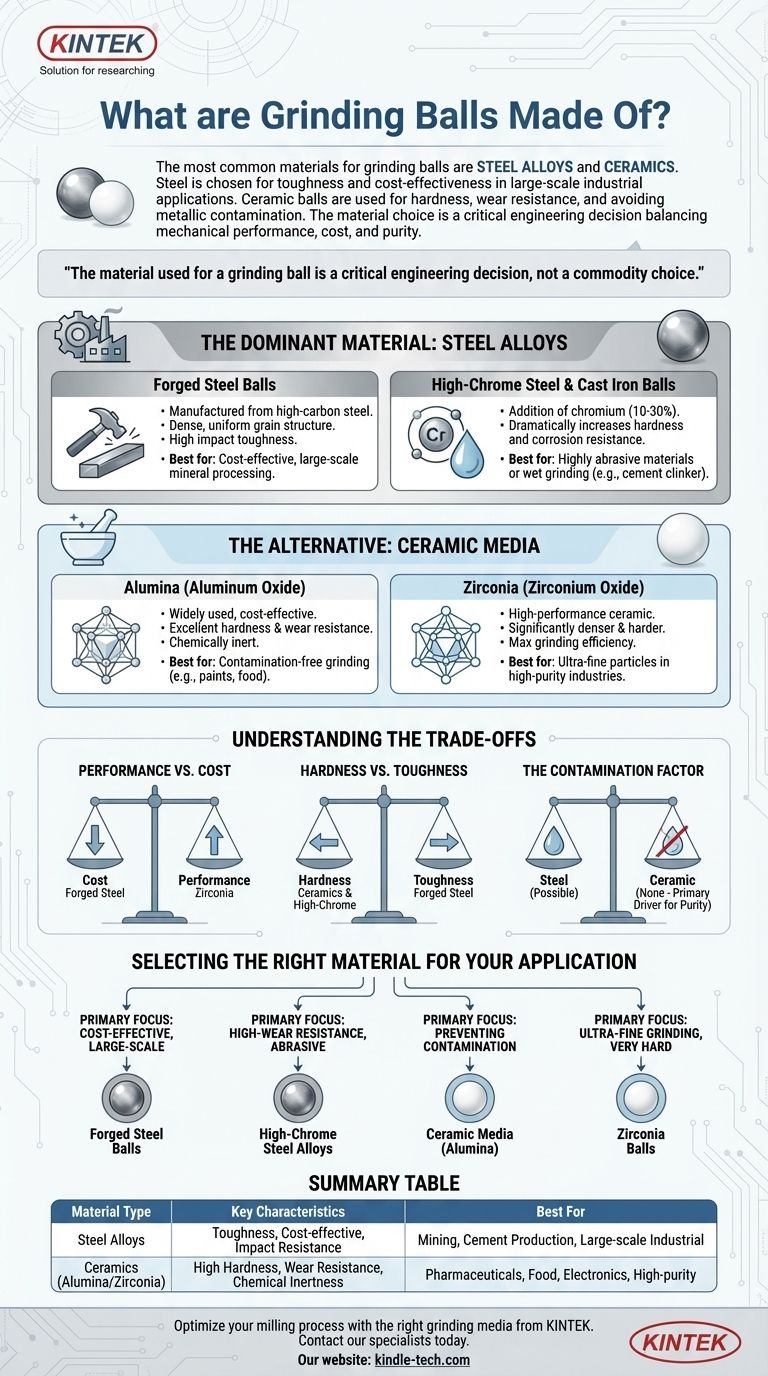
The most common materials for grinding balls are steel alloys and ceramics. Steel, particularly high-carbon and high-chromium steel, is chosen for its toughness and cost-effectiveness in large-scale industrial applications like mining and cement production. Ceramic balls, such as those made from alumina or zirconia, are used when hardness, wear resistance, and avoiding metallic contamination are the primary concerns.
The material used for a grinding ball is a critical engineering decision, not a commodity choice. It represents a fundamental trade-off between mechanical performance (hardness and wear resistance), operational cost, and the chemical purity of the final ground product.
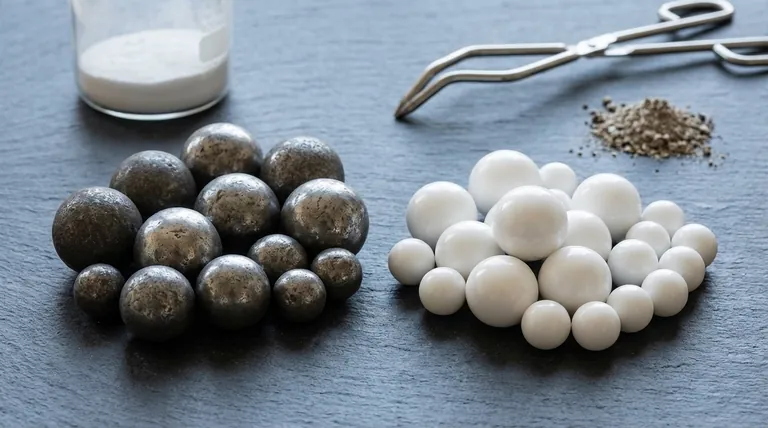

The Dominant Material: Steel Alloys
For most heavy industrial applications, steel is the default choice due to its excellent combination of toughness and affordability. The specific alloy is tuned to balance hardness and impact resistance.
Forged Steel Balls
Forged steel balls are manufactured from high-carbon steel bars. The forging process creates a dense, uniform grain structure that provides high impact toughness, making them resistant to fracturing in large, high-impact mills.
These are often the most cost-effective option for applications like mineral processing and raw grinding where sheer force is more critical than extreme wear resistance.
High-Chrome Steel & Cast Iron Balls
The addition of chromium (typically 10-30%) to the steel or iron alloy dramatically increases its hardness and resistance to both abrasive wear and corrosion.
High-chromium media is the standard for applications involving highly abrasive materials or wet grinding processes where corrosion can significantly accelerate wear on standard steel balls. This makes them essential in industries like cement manufacturing.
The Alternative: Ceramic Media
Ceramic grinding media is used when the prevention of iron contamination is non-negotiable or when extreme hardness is required for grinding very hard materials.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
Alumina is a widely used and relatively cost-effective ceramic. It offers excellent hardness and wear resistance, far exceeding that of most steel alloys.
Its primary advantage is being chemically inert, making it essential for grinding materials like paints, pharmaceuticals, white cement, and food products where iron contamination would ruin the final product.
Zirconia (Zirconium Oxide)
Zirconia represents the high-performance tier of ceramic media. It is significantly denser and harder than alumina, providing maximum grinding efficiency and minimal media wear.
This higher density allows for smaller balls to be used while maintaining high grinding energy, which is ideal for creating ultra-fine particles in advanced materials science, electronics, and high-purity chemical manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right grinding media involves navigating a few key compromises. Understanding these factors is critical to optimizing your process.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between the performance of a grinding ball and its cost. Forged steel is the most economical, while high-performance ceramics like zirconia carry a significant price premium that is only justified by strict purity requirements or the need for extreme grinding efficiency.
Hardness vs. Toughness
Hardness is the resistance to scratching and wear, while toughness is the ability to absorb impact without fracturing. High-chromium alloys and ceramics are extremely hard but can be more brittle than forged steel. In very high-impact ball mills, a tougher, less-hard ball may be preferable to prevent media shattering.
The Contamination Factor
This is often the single most important deciding factor. If your process cannot tolerate even trace amounts of iron, steel media is immediately disqualified. This is the primary driver for the adoption of ceramic media in high-purity industries.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your final choice should be dictated entirely by the specific goals and constraints of your milling process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale grinding (e.g., mineral ore): Forged or low-chromium steel balls offer the best balance of impact toughness and affordability.
- If your primary focus is high-wear resistance in an abrasive environment (e.g., cement clinker): High-chromium steel alloys are the industry standard for their superior hardness and durability.
- If your primary focus is preventing any metallic contamination (e.g., pharmaceuticals, white pigments): Ceramic media, typically alumina, is the only acceptable choice to ensure product purity.
- If your primary focus is ultra-fine grinding of very hard materials: High-density zirconia balls provide the maximum grinding efficiency and minimal media wear.
Choosing the correct grinding media is a foundational decision that directly impacts your process efficiency, product purity, and operational costs.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Alloys | Toughness, cost-effectiveness, impact resistance | Mining, cement production, large-scale industrial grinding |
| Ceramics (Alumina/Zirconia) | High hardness, wear resistance, chemical inertness | Pharmaceuticals, food products, electronics, high-purity applications |
Optimize your milling process with the right grinding media from KINTEK.
Selecting the correct grinding balls is crucial for your lab's efficiency, product purity, and cost management. Whether you need durable steel alloys for heavy-duty grinding or contamination-free ceramics for high-purity applications, KINTEK provides expert solutions tailored to your needs.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our lab equipment and consumables can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What is the strongest zirconia phase? Tetragonal Zirconia Offers Unmatched Toughness
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What are the disadvantages of ceramics? Understanding Brittleness, Cost, and Design Challenges
- What is a ball mill used for in ceramics? Achieve Ultimate Control Over Glaze and Clay Quality
- What is the overview of ceramics? Unlocking the Potential of Advanced Materials












