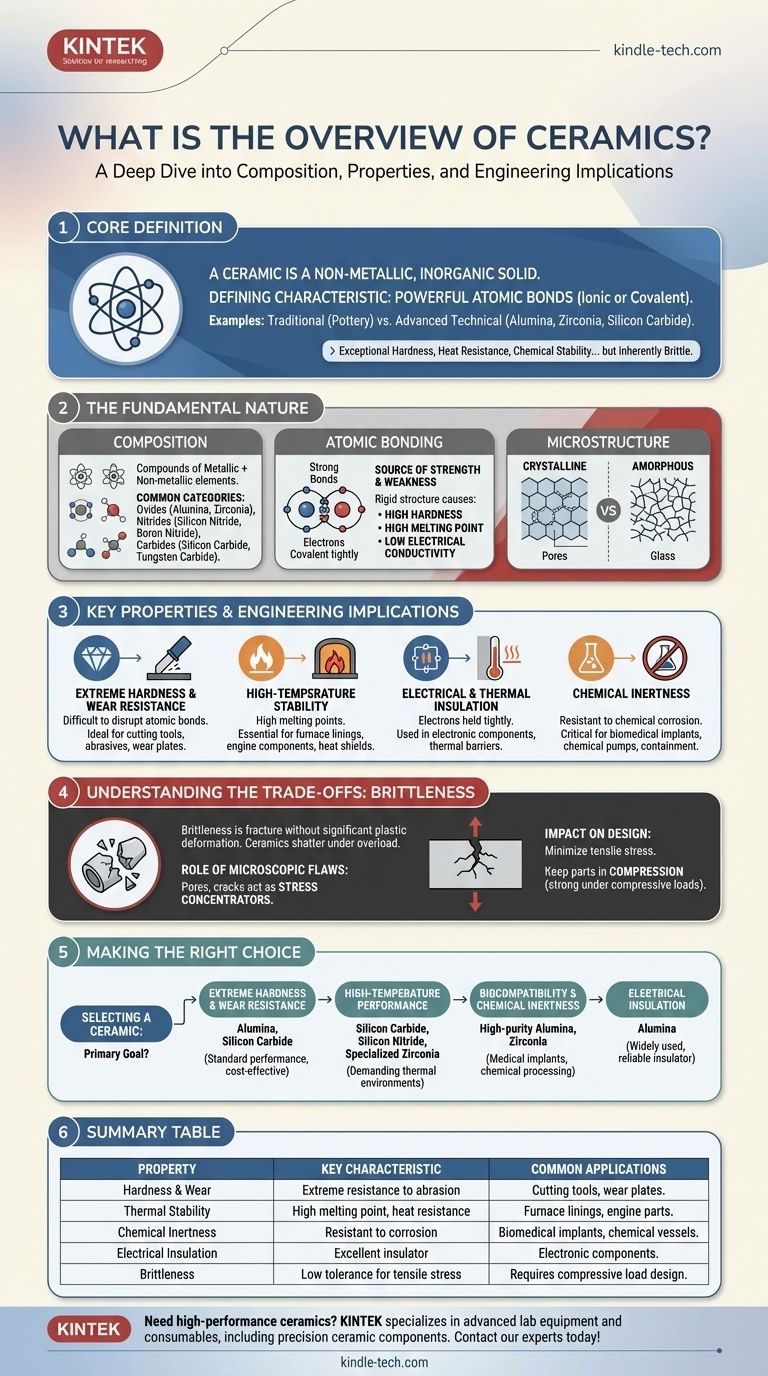
At its core, a ceramic is a non-metallic, inorganic solid. This broad class of materials is defined by its powerful atomic bonds, which are typically ionic or covalent in nature. While traditional ceramics like pottery and porcelain are well-known, the field is dominated by advanced technical ceramics—like alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide—that are engineered for extreme performance in aerospace, electronics, and biomedical applications.
The defining characteristic of ceramics is their powerful atomic structure, which grants them exceptional hardness, heat resistance, and chemical stability. However, this same rigid atomic bonding is also their greatest liability, making them inherently brittle and susceptible to fracture from microscopic flaws.
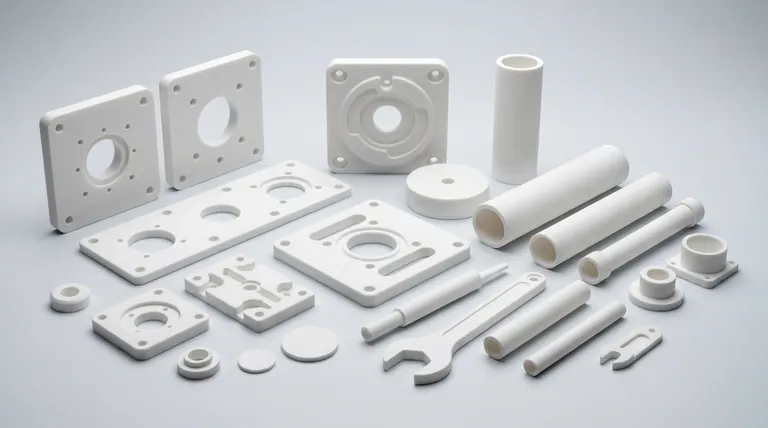

The Fundamental Nature of Ceramics
To understand why ceramics are chosen for certain applications, we must first look at their atomic composition and structure. Unlike metals with their delocalized electrons, ceramics are defined by rigid, stable bonds.
Composition: More Than Just Clay
The term "ceramic" encompasses a vast range of chemical compositions. They are compounds formed between metallic and non-metallic elements.
The most common categories include:
- Oxides: Aluminum oxide (alumina), zirconium oxide (zirconia).
- Nitrides: Silicon nitride, boron nitride.
- Carbides: Silicon carbide, tungsten carbide.
Atomic Bonding: The Source of Strength and Weakness
The properties of a ceramic are a direct result of its strong ionic and covalent bonds. These bonds hold electrons tightly in place between atoms.
This rigid structure is responsible for most of a ceramic's signature traits: high hardness, high melting points, and low electrical conductivity. It is also the direct cause of their primary weakness: brittleness.
Microstructure: Crystalline vs. Amorphous
Ceramics can be categorized by their internal structure.
Crystalline ceramics, like alumina, have atoms arranged in a highly ordered, repeating three-dimensional pattern. The size of these crystal grains and the porosity (tiny voids) between them are critical factors that control the material's final strength.
Amorphous ceramics, most notably glass, lack this long-range ordered structure. Their atoms are arranged in a disordered, random network, which is why they are often transparent.
Key Properties and Engineering Implications
Engineers select ceramics when the operating conditions are too extreme for metals or polymers. Their properties solve some of the most difficult engineering challenges.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
The strong atomic bonds are extremely difficult to disrupt, making ceramics incredibly hard and resistant to abrasion and wear. This makes them ideal for cutting tools, abrasive powders, and industrial wear plates.
High-Temperature Stability
A tremendous amount of thermal energy is required to break the bonds in a ceramic, giving them exceptionally high melting points. This property makes them essential for applications like furnace linings (refractories), engine components, and spacecraft heat shields.
Electrical and Thermal Insulation
Because electrons are held so tightly within their atomic bonds, they cannot move freely. This makes most ceramics excellent electrical and thermal insulators, used widely in electronic components and thermal barriers.
Chemical Inertness
The stable, low-energy state of the atoms in a ceramic makes the material highly resistant to chemical corrosion. This is critical for applications like biomedical implants, chemical pumps, and containment vessels.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Brittleness
The single most important design consideration for any ceramic component is managing its inherent brittleness. This property is not a flaw, but a direct consequence of the same atomic structure that provides its strengths.
What is Brittleness?
Brittleness is the tendency of a material to fracture without significant plastic deformation. When a metal is overloaded, it typically bends or stretches first. When a ceramic is overloaded, it shatters.
The Role of Microscopic Flaws
All ceramic materials contain tiny, microscopic flaws such as pores, micro-cracks, or grain boundaries. Under a tensile (pulling) load, these tiny flaws act as stress concentrators.
Because the rigid atomic lattice cannot deform and "blunt" the sharp tip of a growing crack, the crack propagates rapidly through the material, leading to sudden, catastrophic failure.
The Impact on Engineering Design
Engineers must design ceramic components to minimize or eliminate tensile stress. Parts are often kept in a state of compression, as ceramics are exceptionally strong under compressive loads that push cracks closed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a ceramic requires a clear understanding of your primary performance goal, as you are always managing a trade-off between exceptional properties and brittleness.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: Alumina and silicon carbide are standard choices for their proven performance and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: Look to silicon carbide, silicon nitride, or specialized zirconia grades for demanding thermal environments.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and chemical inertness: High-purity alumina and zirconia are the leading materials for medical implants and chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Alumina is one of the most widely used and reliable electrical insulators available.
Understanding the interplay between a ceramic's rigid atomic structure and its resulting properties is the key to unlocking its potential in demanding engineering applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear | Extreme resistance to abrasion | Cutting tools, wear plates |
| Thermal Stability | High melting point, heat resistance | Furnace linings, engine parts |
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to corrosion | Biomedical implants, chemical vessels |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator | Electronic components |
| Brittleness | Low tolerance for tensile stress | Requires compressive load design |
Need high-performance ceramics for your lab or industrial application? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including precision ceramic components made from alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide. Our materials are engineered for superior hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance—perfect for demanding environments in aerospace, electronics, and biomedical research. Contact our experts today to find the ideal ceramic solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
People Also Ask
- What ceramics are sintered? The Essential Process for Creating Strong, Durable Ceramics
- Is ceramic a good material? A Guide to Its Extreme Strengths and Trade-offs
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- Why is silicon carbide so important? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Are ceramics good electrical insulators? Discover Their Role in High-Performance Applications
- What is the role of polycrystalline alumina (Al2O3) substrates in YSZ thin film preparation? Enhance Film Integrity
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Master Dimensional Control for Your Parts
- Does sintering increase hardness? Master the Process for Superior Material Strength



















