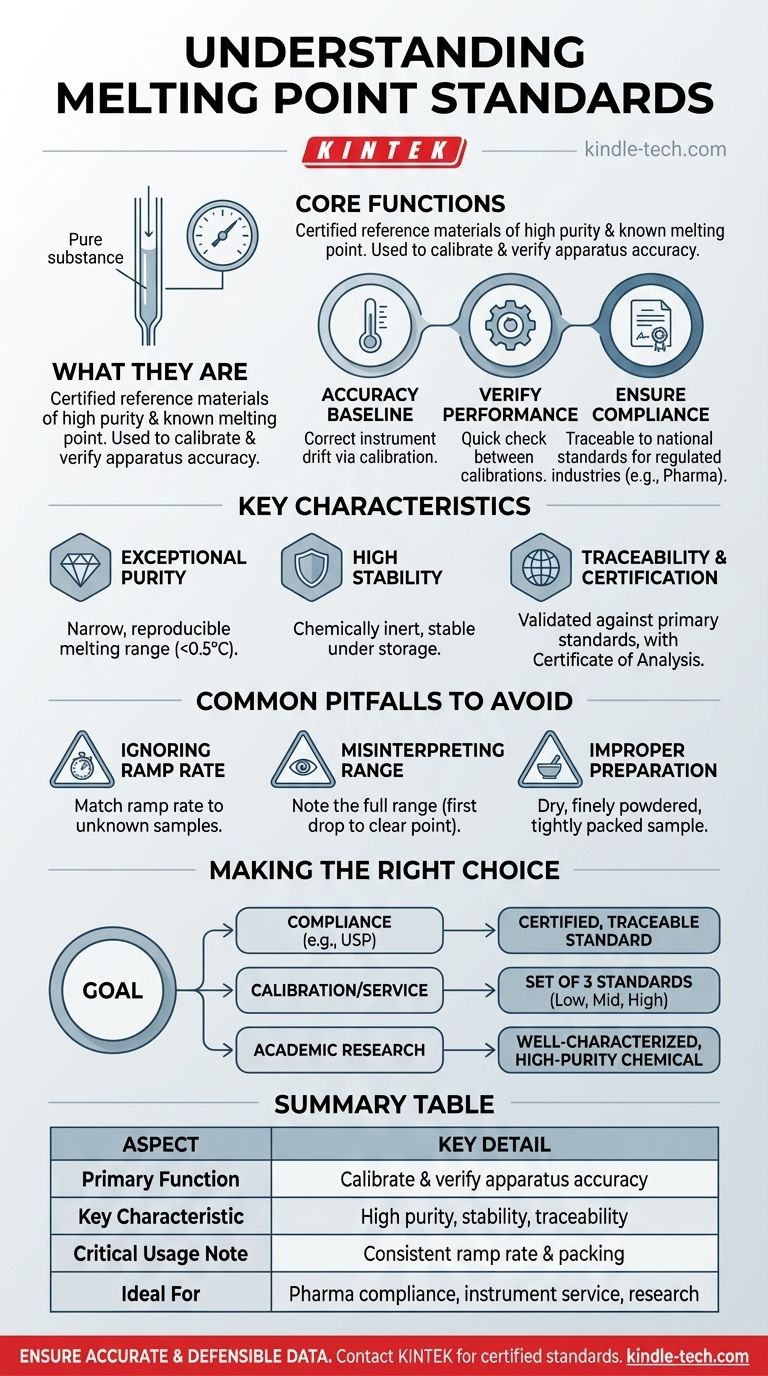
In short, melting point standards are exceptionally pure, stable substances with a precisely known and documented melting point. They serve as certified reference materials used to calibrate and verify the performance of a melting point apparatus, ensuring the temperature readings it provides are accurate and reliable.
The core purpose of a melting point standard is to anchor your experimental measurements to a known, unwavering benchmark. It transforms a simple temperature reading into a verifiable, trustworthy piece of data by confirming your instrument is functioning correctly.
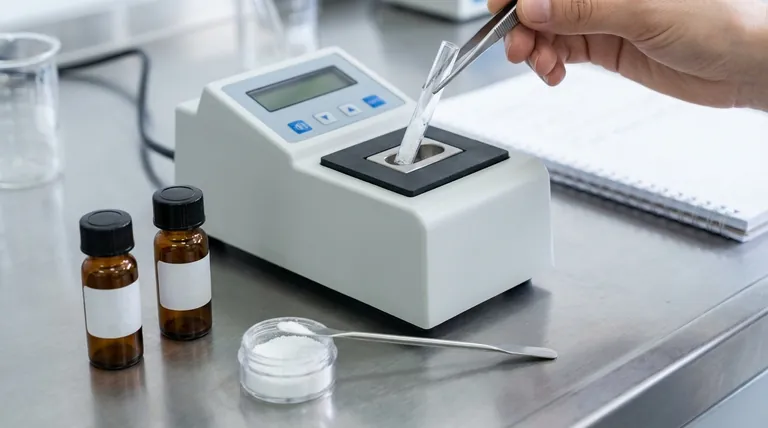

The Core Function of a Melting Point Standard
A melting point standard is not just a chemical; it's a critical tool for ensuring data integrity in any laboratory setting. Its function can be broken down into a few key areas.
Establishing a Baseline for Accuracy
The electronic components and sensors in a melting point apparatus can drift over time. Calibration using a standard with a certified melting point allows you to identify and correct for this instrumental error.
You measure the standard, compare the observed melting point to its certified value, and establish a correction factor. This ensures your measurements are accurate, not just precise.
Verifying Instrument Performance
Between formal calibrations, standards are used for performance verification or qualification. This is a quick check to confirm the instrument is still operating within specified tolerances.
Running a standard before a series of important measurements provides confidence that the results obtained for your unknown samples will be valid.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Compliance
In regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or manufacturing, data must be defensible. Using standards that are traceable to national metrology institutes (like NIST in the US or NPL in the UK) is often required.
This traceability provides an unbroken chain of comparisons, proving that your measurements conform to internationally recognized benchmarks, a key requirement for pharmacopeia (e.g., USP, EP) compliance and quality management systems.
Key Characteristics of an Ideal Standard
Not just any pure chemical can serve as a reliable standard. These reference materials are chosen for a specific set of properties that guarantee their performance.
Exceptional Purity
Impurities are the enemy of a sharp melting point; they depress and broaden the melting range. A standard must be of the highest possible purity to ensure it melts over a very narrow, reproducible temperature range (often less than 0.5°C).
High Stability
The chosen substance must be chemically inert and stable under proper storage conditions. It cannot degrade when exposed to light, air, or moderate temperature fluctuations, as this would alter its melting point over time.
Traceability and Certification
The most reliable standards come with a Certificate of Analysis that states the certified melting point and its uncertainty. This value is traceable, meaning it has been validated against primary standards maintained by a national or international metrology organization.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Using a standard correctly is just as important as choosing the right one. Simple procedural errors can invalidate the entire process and lead to inaccurate measurements for your own samples.
Ignoring the Ramp Rate
The rate at which you heat the sample (ramp rate) dramatically affects the observed melting point. A faster ramp can lead to an artificially high reading because the sample's temperature lags behind the thermometer's.
You must measure the standard using the exact same ramp rate that you will use for your unknown samples.
Misinterpreting the Melting Range
A melting "point" is actually a melting range. The process begins at the temperature where the first drop of liquid appears and is complete when the last solid crystal melts.
The certified value of the standard corresponds to a specific, defined point in this process (often the "clear point," where the sample is fully liquid). Consistency in observing this endpoint is critical.
Improper Sample Preparation and Packing
The sample, whether it's a standard or an unknown, must be completely dry and finely powdered. It should be packed tightly into a capillary tube to a consistent, small height (typically 2-3 mm).
Poor packing leads to inefficient heat transfer and results in a broad, inaccurate melting range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of certification you need depends entirely on your application. Use these guidelines to select the appropriate standard.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance (e.g., pharmaceuticals): You must use a certified, traceable standard from a recognized source like the USP or a qualified metrology vendor.
- If your primary focus is instrument calibration or service: Use a set of at least three certified standards that cover the low, middle, and high sections of your instrument's operational temperature range.
- If your primary focus is routine academic research: A well-characterized, high-purity chemical (e.g., >99.9%) from a reputable supplier is often sufficient for ensuring internal consistency and verifying instrument function.
Ultimately, proper use of a melting point standard elevates your work from estimation to metrology, ensuring every result is built on a foundation of accuracy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Calibrate and verify melting point apparatus accuracy |
| Key Characteristic | High purity, stability, and traceable certification |
| Critical Usage Note | Must use consistent ramp rate and proper sample packing |
| Ideal For | Pharmaceutical compliance, instrument service, academic research |
Ensure your lab's melting point data is accurate and defensible. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables. Let our experts help you select the right certified standards for your compliance and research needs. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your laboratory's measurement integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- How does an alumina tube furnace with a controlled atmosphere simulate conditions in CSP environments? Master Accuracy.
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning



















