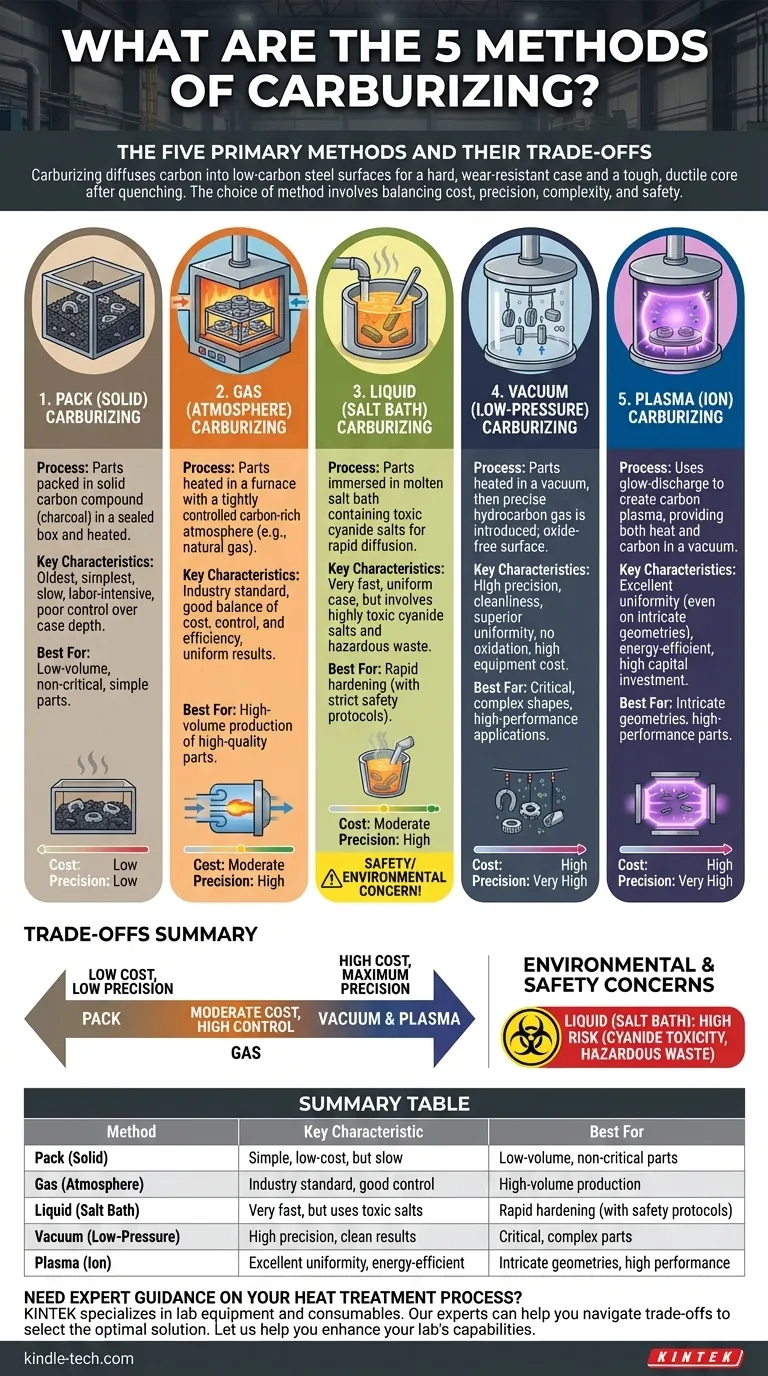
The five primary methods of carburizing are Pack (Solid), Gas (Atmosphere), Liquid (Salt Bath), Vacuum (Low-Pressure), and Plasma (Ion) Carburizing. These techniques all achieve the same fundamental goal—diffusing carbon into the surface of low-carbon steel to allow for a hard, wear-resistant case with a tough, ductile core after quenching.
While each of the five methods has its place, the choice is not arbitrary. The selection process involves a critical trade-off between processing cost, the level of precision required, part complexity, and significant environmental or safety considerations.

What is Carburizing and Why Is It Used?
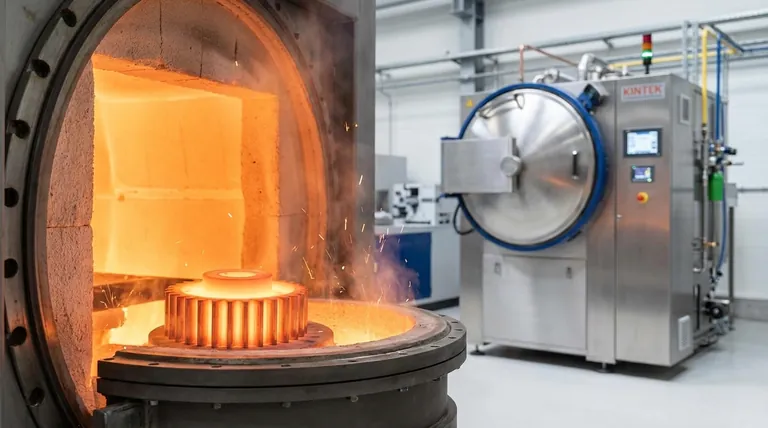
Carburizing is a heat treatment process that increases the carbon content on the surface of a metal part. It is one of the most common methods for case-hardening steel.
The Core Principle
The process involves heating a low-carbon steel component in a carbon-rich environment. At elevated temperatures, carbon atoms diffuse into the surface, creating a "case" with a higher carbon concentration than the inner "core."
The Final Hardening Step
The carburizing process itself does not harden the steel. The actual hardening occurs during a subsequent quenching (rapid cooling) step. This locks the carbon atoms into the steel's crystal structure, creating an exceptionally hard surface layer.
Key Benefits
The primary result of carburizing is a component with a dual nature. It has a very hard surface that provides excellent wear resistance and improved fatigue strength, while the low-carbon core remains soft and tough, allowing it to absorb shock and impact without fracturing.
A Breakdown of the Five Carburizing Methods
Each method uses a different medium to introduce carbon to the steel's surface.
1. Pack (Solid) Carburizing
This is the oldest and simplest method. Parts are packed into a steel box surrounded by a solid carbon-rich compound, typically charcoal mixed with an energizer like barium carbonate. The box is sealed and heated, allowing carbon to diffuse into the parts over a long period.
It is a slow, labor-intensive process with poor control over case depth, making it suitable mostly for low-volume or non-critical applications where precision is not a priority.
2. Gas (Atmosphere) Carburizing
This is the current industry standard due to its balance of cost, control, and efficiency. Parts are heated in a sealed furnace with a tightly controlled atmosphere containing carbon-rich gases, such as natural gas or propane.
This method allows for precise control over temperature and carbon potential, resulting in uniform and repeatable case depths. It is highly suitable for mass production of high-quality parts.
3. Liquid (Salt Bath) Carburizing
In this method, parts are immersed in a molten salt bath containing sodium cyanide and other salts. The cyanide compounds provide a source of carbon that diffuses rapidly into the steel.
Liquid carburizing is very fast and produces a uniform case. However, the cyanide salts are extremely toxic and pose significant safety and environmental disposal hazards, making this method far less common today.
4. Vacuum (Low-Pressure) Carburizing
This is a modern, high-performance variant of gas carburizing. Parts are heated in a vacuum, after which a small, precise amount of a hydrocarbon gas is introduced. The absence of oxygen ensures an exceptionally clean, oxide-free surface.
Vacuum carburizing offers superior control, uniformity, and metallurgical results, especially for complex shapes and high-performance applications. The main drawback is the high cost of the equipment.
5. Plasma (Ion) Carburizing
This advanced method uses glow-discharge technology. Parts are placed in a vacuum chamber and a high voltage is applied, creating a plasma of ionized carbon-rich gas around the component. The ions are accelerated and strike the part's surface, providing both heat and carbon.
Plasma carburizing allows for outstanding control over case uniformity, even on intricate geometries, and is more energy-efficient than other methods. Like vacuum carburizing, it requires a significant capital investment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method requires balancing technical requirements against practical limitations.
Cost vs. Precision
The older methods like pack carburizing are the cheapest but offer the least control. In contrast, vacuum and plasma carburizing provide exceptional precision and cleanliness but demand the highest capital investment. Gas carburizing sits in the middle, offering good control for a moderate cost, which explains its widespread adoption.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
The primary concern here is liquid carburizing. The use of cyanide salts requires stringent safety protocols and creates hazardous waste, making it an undesirable choice for modern manufacturing environments. Gas and vacuum processes are significantly cleaner and safer.
Part Complexity and Selective Hardening
For parts with complex shapes, vacuum and plasma carburizing offer the most uniform case. If only specific areas of a part need to be hardened, the process can become complicated. Copper plating or special "stop-off" paints are often used to mask areas, which adds cost and complexity to any of the methods.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the part's requirements and your operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with good process control: Gas (Atmosphere) carburizing is the well-established industry standard for a reason.
- If your primary focus is maximum precision for critical, complex parts: Vacuum or Plasma carburizing will deliver the best metallurgical quality and surface finish.
- If your primary focus is low-cost hardening for non-critical, simple parts: Pack carburizing can be a viable option, but accept its inherent lack of control.
- If your primary focus is extremely rapid case hardening: Liquid carburizing is fast, but you must be fully prepared to manage its significant safety and environmental risks.
Ultimately, aligning the method's capabilities with your component's specific performance, volume, and budget requirements will lead to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Pack (Solid) | Simple, low-cost, but slow | Low-volume, non-critical parts |
| Gas (Atmosphere) | Industry standard, good control | High-volume production |
| Liquid (Salt Bath) | Very fast, but uses toxic salts | Rapid hardening (with safety protocols) |
| Vacuum (Low-Pressure) | High precision, clean results | Critical, complex parts |
| Plasma (Ion) | Excellent uniformity, energy-efficient | Intricate geometries, high performance |
Need Expert Guidance on Your Heat Treatment Process?
Choosing the right carburizing method is critical for achieving the desired hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength in your components. The wrong choice can lead to inconsistent results, higher costs, or safety issues.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts understand the nuances of heat treatment processes and the equipment required to support them. We can help you navigate the trade-offs between cost, precision, and safety to select the optimal solution for your specific application.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure your processes are efficient, safe, and effective.
Contact our specialists today for a consultation and let's discuss how we can support your material science and heat treatment goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance



















