Fluidized bed systems are renowned for their exceptional heat and mass transfer capabilities. They achieve this by suspending solid particles in an upward-flowing stream of gas or liquid, forcing the solids to behave like a fluid. This unique state offers uniform temperatures and efficient mixing but also introduces challenges related to particle erosion, energy consumption, and material loss.
The core trade-off of a fluidized bed system is clear: it offers unparalleled process uniformity and efficiency in exchange for higher operational complexity and the energy cost required to maintain the fluidized state.
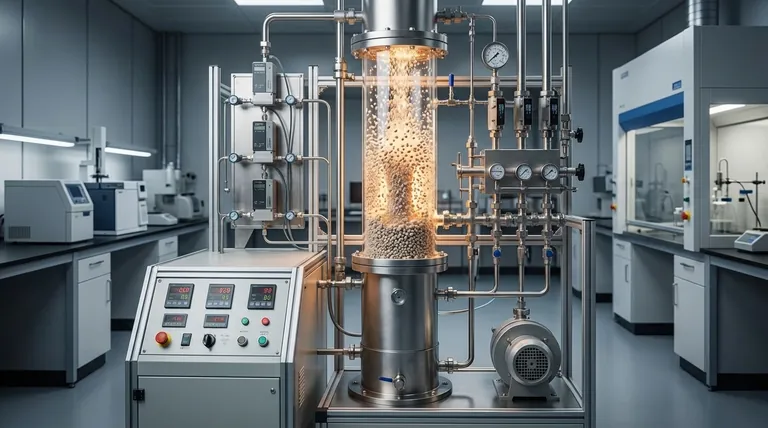

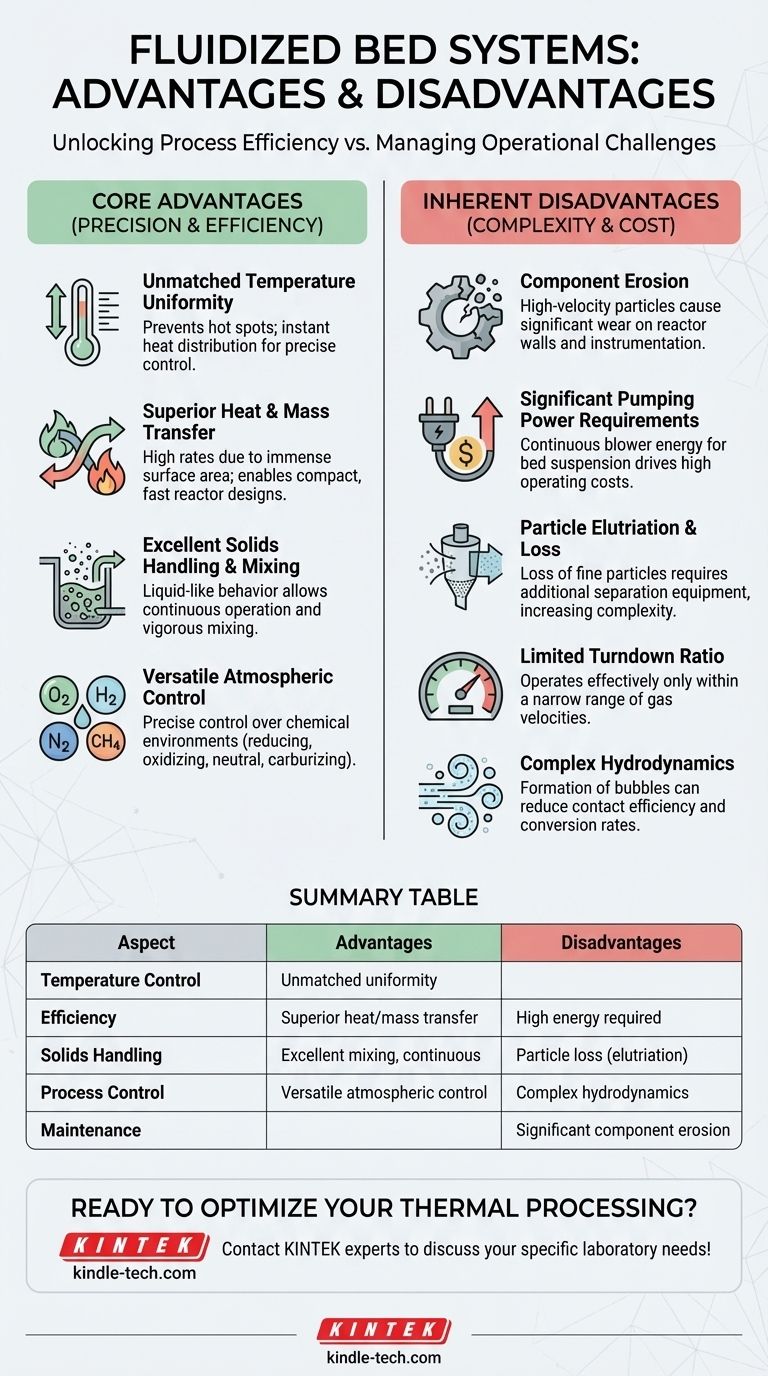
The Core Advantages of Fluidization
Fluidized beds are chosen for demanding applications where precise control and high throughput are critical. Their primary benefits stem directly from the fluid-like behavior of the solid particles.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The rapid and constant motion of particles ensures that heat is distributed almost instantaneously throughout the bed. This prevents the formation of hot spots, which is critical for controlling temperature-sensitive chemical reactions or achieving uniform heat treatment of materials.
Superior Heat and Mass Transfer
The immense surface area of the suspended particles exposed to the fluidizing gas results in extremely high rates of heat and mass transfer. This allows for more compact reactor designs and faster processing times compared to packed bed or moving bed systems.
Excellent Solids Handling and Mixing
Because the solid bed behaves like a liquid, it can be easily drained, and fresh material can be added continuously. The inherent turbulence also provides vigorous mixing of solids, which is ideal for processes requiring consistent blend quality or catalytic reactions.
Versatile Atmospheric Control
The fluidizing gas is also the process atmosphere. This gives operators precise control over the chemical environment within the system, allowing for reducing, oxidizing, neutral, and carburizing atmospheres as required by the specific application.
Understanding the Inherent Disadvantages
While powerful, the dynamic nature of fluidized beds introduces significant operational and maintenance challenges that must be carefully considered.
Component Erosion
The constant movement and collision of hard particles at high velocities create a highly abrasive environment. This leads to significant wear and tear on the reactor walls, internal pipes, and instrumentation, making material selection and maintenance critical concerns.
Significant Pumping Power Requirements
Suspending the entire bed of particles requires a blower or pump to overcome the pressure drop across the bed. This continuous energy demand can represent a substantial portion of the system's total operating cost, especially for dense or deep beds.
Particle Elutriation and Loss
Fine particles can be easily carried out of the reactor by the upward-flowing gas stream, a phenomenon known as elutriation. This necessitates the use of downstream separation equipment, such as cyclones, to capture and often recycle these lost particles, adding to system cost and complexity.
Limited Turndown Ratio
Fluidized beds operate effectively only within a specific range of gas velocities—above the minimum fluidization velocity and below the velocity that causes excessive elutriation. This narrow operating window, or limited turndown ratio, can make them less flexible for processes with widely varying production rates.
Complex Hydrodynamics
The fluid dynamics within the bed, particularly the formation of bubbles, can be complex and difficult to predict. Large bubbles can allow gas to bypass the solid particles, reducing contact efficiency and lowering the conversion rate in chemical reactors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing whether to use a fluidized bed system requires balancing its unique process advantages against its operational demands.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control and high reaction rates: A fluidized bed is an exceptional choice, especially for highly exothermic or temperature-sensitive processes where uniformity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs and maintenance: The high energy consumption and erosion rates may make simpler technologies like rotary kilns or packed beds a more suitable option.
- If your primary focus is handling solids with a wide particle size distribution: The tendency for fine particles to be lost and coarse particles to segregate requires careful design and may favor a different type of reactor.
Ultimately, selecting a fluidized bed system is a strategic decision that balances its superior process intensity against its demanding operational requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Unmatched uniformity, prevents hot spots | - |
| Efficiency | Superior heat/mass transfer, compact design | High energy/pumping power required |
| Solids Handling | Excellent mixing, continuous operation | Particle elutriation (loss of fines) |
| Process Control | Versatile atmospheric control (oxidizing, reducing, etc.) | Complex hydrodynamics, limited turndown ratio |
| Maintenance | - | Significant component erosion, wear and tear |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with a fluidized bed system?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including robust fluidized bed reactors designed to maximize your process efficiency while managing operational challenges. Our systems are engineered with durable materials to combat erosion and are optimized for energy efficiency.
Whether you are in R&D, chemicals, or materials science, let KINTEK's expertise help you achieve precise temperature control and superior reaction rates.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK fluidized bed system can meet your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures









