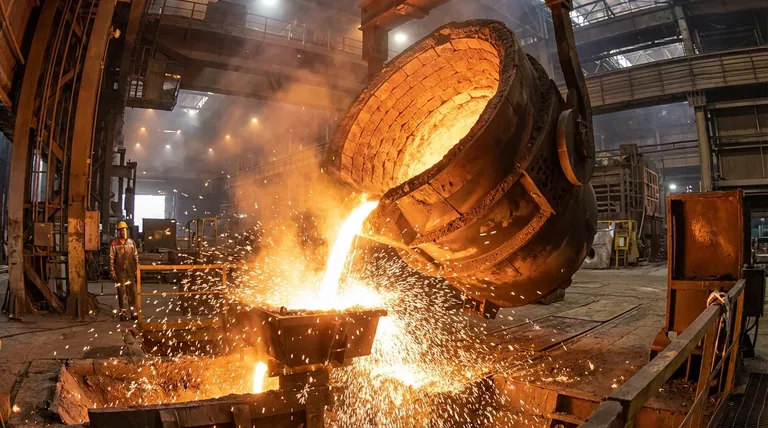
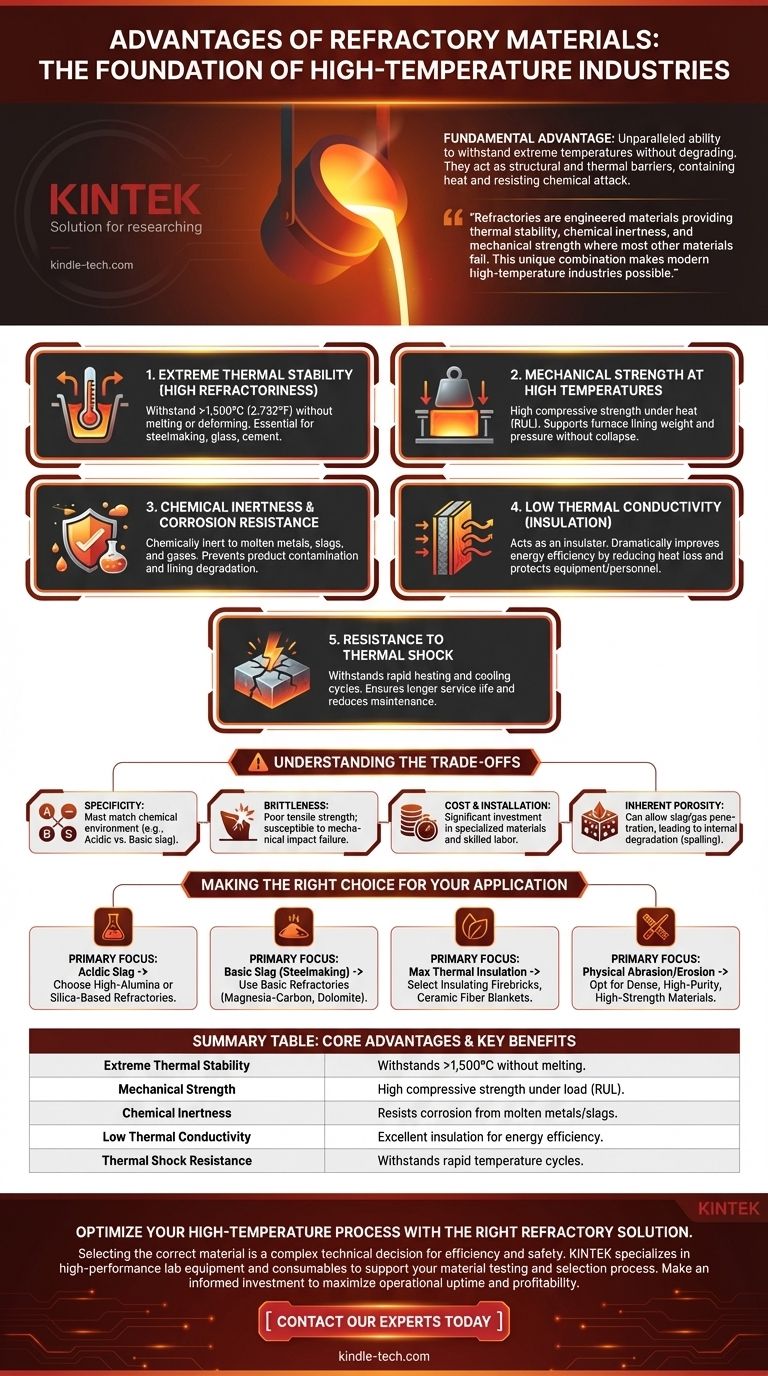
The fundamental advantage of refractory materials is their unparalleled ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading. This core property allows them to act as structural and thermal barriers in high-temperature industrial processes, containing heat and resisting chemical attack from molten substances, which would destroy ordinary materials like steel or concrete.
Refractories are more than just heat-resistant; they are engineered materials that provide a combination of thermal stability, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength at temperatures where most other materials fail. This unique combination is what makes modern high-temperature industries possible.

The Core Properties Defining Refractory Advantage
The value of refractory materials stems from a specific set of physical and chemical properties that they are engineered to possess. These properties work in concert to ensure reliability in extreme environments.
Extreme Thermal Stability (High Refractoriness)
The defining characteristic is refractoriness, the ability to withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming. By definition, refractories maintain their integrity at temperatures well above 1,500°C (2,732°F).
This allows for the containment of processes like steelmaking, glass manufacturing, and cement production, which operate at these extreme temperatures.
Mechanical Strength at High Temperatures
It is not enough for a material to simply resist melting; it must also bear physical loads. Refractories are designed to have high compressive strength even when heated.
This property, often measured as Refractoriness Under Load (RUL), ensures that the lining of a furnace or kiln can support its own weight and the pressure from its contents without collapsing.
Chemical Inertness and Corrosion Resistance
Many high-temperature processes involve highly corrosive materials like molten metals, chemical slags, and acidic or basic gases.
Refractories are formulated to be chemically inert in their specific operating environment. This prevents them from reacting with and contaminating the product, while also resisting the degradation that would otherwise dissolve the furnace lining.
Low Thermal Conductivity (Insulation)
A critical advantage of many refractories is their ability to act as an insulator. By having low thermal conductivity, they keep heat contained within the furnace or vessel.
This has two major benefits: it dramatically improves energy efficiency by reducing heat loss to the outside, and it protects the outer steel shell of the equipment and ensures personnel safety.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Industrial processes often involve rapid heating and cooling cycles. This can cause most brittle materials to crack and fail, a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
Refractories are specifically engineered to have a high resistance to thermal shock, ensuring a longer service life and reducing the frequency of maintenance and costly relining projects.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
While their advantages are clear, refractories are highly specialized materials with important limitations that must be understood to ensure proper application.
The Specificity Problem
There is no "universal" refractory. A material designed to resist acidic slag (like a silica refractory) will be rapidly destroyed by a basic slag (from steelmaking), and vice versa.
The chemical composition of the refractory must be precisely matched to the chemical environment of the process. An incorrect choice will lead to rapid failure.
Brittleness and Mechanical Limitations
Like most ceramic materials, refractories are brittle. While they have excellent compressive strength, they have poor resistance to tensile (pulling) forces and can fail easily under mechanical impact.
Care must be taken during installation and operation to avoid subjecting the refractory lining to mechanical abuse.
Cost and Installation
High-performance refractories are advanced materials and can be expensive. The total cost includes not just the material but also the highly specialized labor required for proper installation, curing, and initial heat-up.
These factors make lining a major piece of industrial equipment a significant capital investment.
Inherent Porosity
Most refractory bricks and castables have a certain degree of porosity. While sometimes beneficial for thermal shock resistance, this porosity can also be a weakness.
It can allow for the penetration of molten slag or gases, which can lead to internal degradation of the material over time, a process known as spalling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct refractory is a technical decision based on a careful analysis of the operational environment. Your choice determines the efficiency, safety, and profitability of your process.
- If your primary focus is containing molten metal with acidic slag: Choose high-alumina or silica-based refractories known for their stability in acidic environments.
- If your primary focus is resisting the basic slags found in steelmaking: Use basic refractories such as magnesia-carbon, dolomite, or magnesia-chrome bricks.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal insulation to save energy: Select lightweight insulating firebricks, ceramic fiber blankets, or insulating castables for backup linings.
- If your primary focus is withstanding intense physical abrasion and erosion: Opt for dense, high-purity, and high-strength materials like tabular alumina or silicon carbide castables.
Ultimately, understanding these core advantages and their associated trade-offs empowers you to select the precise material that guarantees the success of your high-temperature operation.
Summary Table:
| Core Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures >1,500°C without melting or deforming. |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength, even under load at high temperatures (RUL). |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from molten metals, slags, and gases. |
| Low Thermal Conductivity | Provides excellent insulation, improving energy efficiency and safety. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles, extending service life. |
Optimize your high-temperature process with the right refractory solution.
The advantages of refractory materials are critical for the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your industrial equipment. Selecting the correct material for your specific application—whether it's steelmaking, glass production, or cement manufacturing—is a complex technical decision.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables to support your material testing and selection process. Our products help you accurately characterize refractory properties, ensuring you make an informed investment that maximizes your operational uptime and profitability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory needs and help you select the ideal materials for your demanding applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
People Also Ask
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project
- What is titanium used for in manufacturing? Leveraging High-Performance Properties for Critical Applications



















