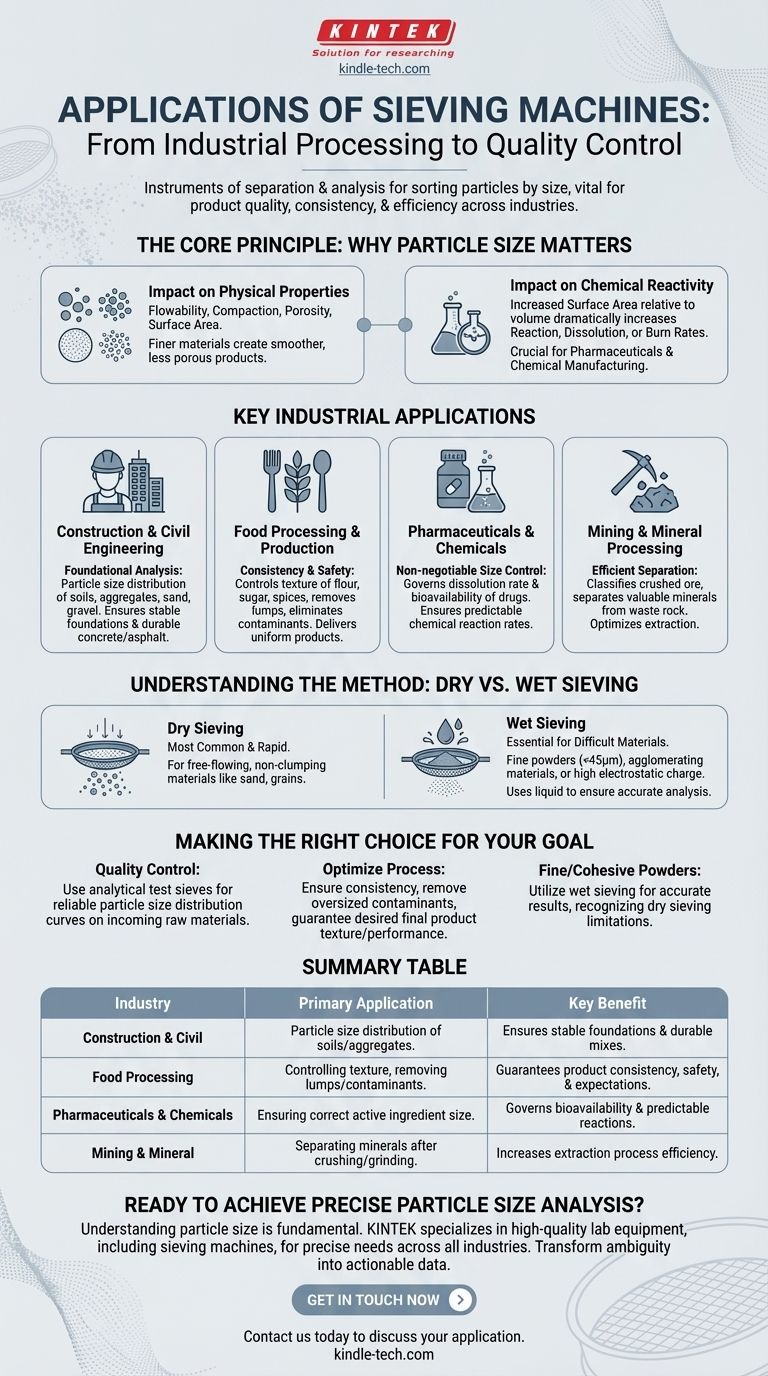
At their core, sieving machines are instruments of separation and analysis. They are used across a vast range of industries to sort particles based on size by passing them through a woven wire mesh or screen. Their applications span from heavy industrial processing in construction and mining to fine-tuned quality control in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical sectors.
The true value of a sieving machine lies not just in sorting materials, but in providing the critical data needed to ensure product quality, consistency, and process efficiency. Understanding and controlling particle size is fundamental to the performance of countless products.
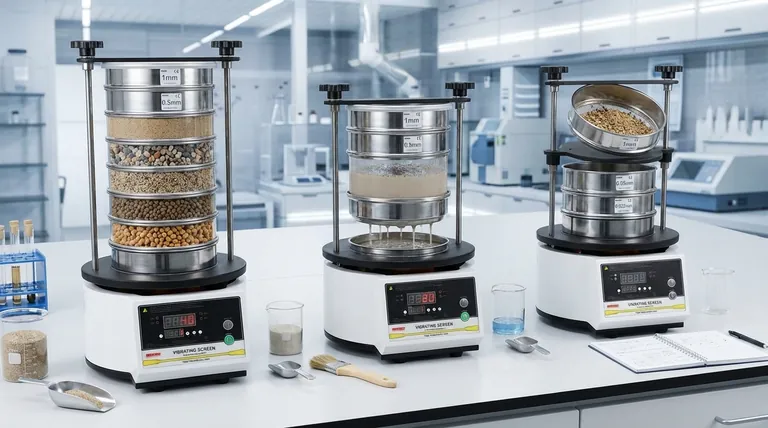

The Core Principle: Why Particle Size Matters
Before listing applications, it is essential to understand why particle size is so critical. The size and distribution of particles in a material directly influence its physical and chemical properties.
Impact on Physical Properties
Controlling particle size is the key to dictating a material's behavior. This includes properties like flowability, compaction, porosity, and surface area. For example, finer sand creates a smoother, less porous mortar than coarse sand.
Impact on Chemical Reactivity
Smaller particles have a much larger surface area relative to their volume. This dramatically increases the rate at which they can react, dissolve, or burn. This principle is vital in pharmaceuticals for drug delivery and in chemical manufacturing for process efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications
The fundamental importance of particle size control makes sieving machines indispensable in numerous fields. Their use is not merely for sorting, but for rigorous analysis and quality assurance.
Construction and Civil Engineering
Sieving is a foundational analytical technique in this sector. It is used to determine the particle size distribution of soils, aggregates, sand, and gravel. This data is critical for designing stable foundations and creating durable concrete and asphalt mixes with specific strength characteristics.
Food Processing and Production
In the food industry, sieving ensures product consistency and safety. It is used to control the texture of flour, sugar, and spices, remove lumps from powdered mixes, and eliminate foreign contaminants. The result is a uniform product that meets consumer expectations.
Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals
Particle size is non-negotiable in pharmaceuticals. It directly governs the dissolution rate and bioavailability of a drug. Sieving is used in both research and manufacturing to ensure that active ingredients will be absorbed by the body correctly and consistently. In the chemical industry, it ensures predictable reaction rates.
Mining and Mineral Processing
On a much larger scale, sieving and screening are used to separate valuable minerals from waste rock. After crushing and grinding ore, sieves help classify particles for different stages of refinement, making the entire extraction process more efficient.
Understanding the Method: Dry vs. Wet Sieving
Modern sieving machines support different methods to accommodate the vast range of materials being analyzed. The choice between dry and wet sieving depends entirely on the material's properties.
When to Use Dry Sieving
Dry sieving is the most common, straightforward, and rapid method. It is the default choice for materials that are free-flowing and do not clump or hold a static charge, such as dried sand, grains, or plastic pellets.
The Role of Wet Sieving
Wet sieving is essential for materials that are difficult to analyze dry. This includes very fine powders (typically below 45 microns), materials that tend to agglomerate, or those with high electrostatic charges. Adding a liquid like water helps break up clumps and wash fine particles through the mesh, ensuring an accurate analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application determines your sieving strategy. The goal is always to achieve an accurate and repeatable analysis that informs your process.
- If your primary focus is quality control of raw materials: Use analytical test sieves with certified mesh sizes to create a reliable particle size distribution curve for every incoming batch.
- If your primary focus is optimizing a production process: Employ sieving to ensure product consistency, remove oversized contaminants, and guarantee the final product has the desired texture or performance.
- If you are working with fine or cohesive powders: Recognize the limitations of dry sieving and utilize wet sieving to achieve an accurate and meaningful result.
Ultimately, a sieving machine is a tool for transforming ambiguity into precise, actionable data about your material.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application of Sieving | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Construction & Civil Engineering | Particle size distribution of soils, aggregates, sand, and gravel. | Ensures stable foundations and durable concrete/asphalt mixes. |
| Food Processing | Controlling texture of flour/sugar, removing lumps, eliminating contaminants. | Guarantees product consistency, safety, and meets consumer expectations. |
| Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals | Ensuring correct particle size of active ingredients and chemical powders. | Governs drug bioavailability and predictable chemical reaction rates. |
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Separating valuable minerals from waste rock after crushing/grinding. | Increases the efficiency of the entire mineral extraction process. |
Ready to Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis?
Understanding your material's particle size is fundamental to product quality, consistency, and process efficiency. Whether your goal is rigorous quality control, optimizing production, or analyzing challenging fine powders, having the right sieving equipment is critical.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including sieving machines, to meet the precise needs of laboratories across all industries. We provide the reliable tools you need to transform material ambiguity into actionable data.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application, and let our experts help you select the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the precautions of sieve shaker? Ensure Accurate Particle Analysis & Protect Your Equipment
- What are the principles of a sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- How is a vibrating sieve shaker used to classify atomized Al-Fe-Ni powders? Expert Guide to Particle Size Control
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy



















