In essence, heat treatment is an engineering process that alters a material's internal structure to enhance its physical and mechanical properties. The primary benefits include increasing strength, improving ductility, relieving internal stresses for easier machining, and introducing superior wear resistance to a finished part.
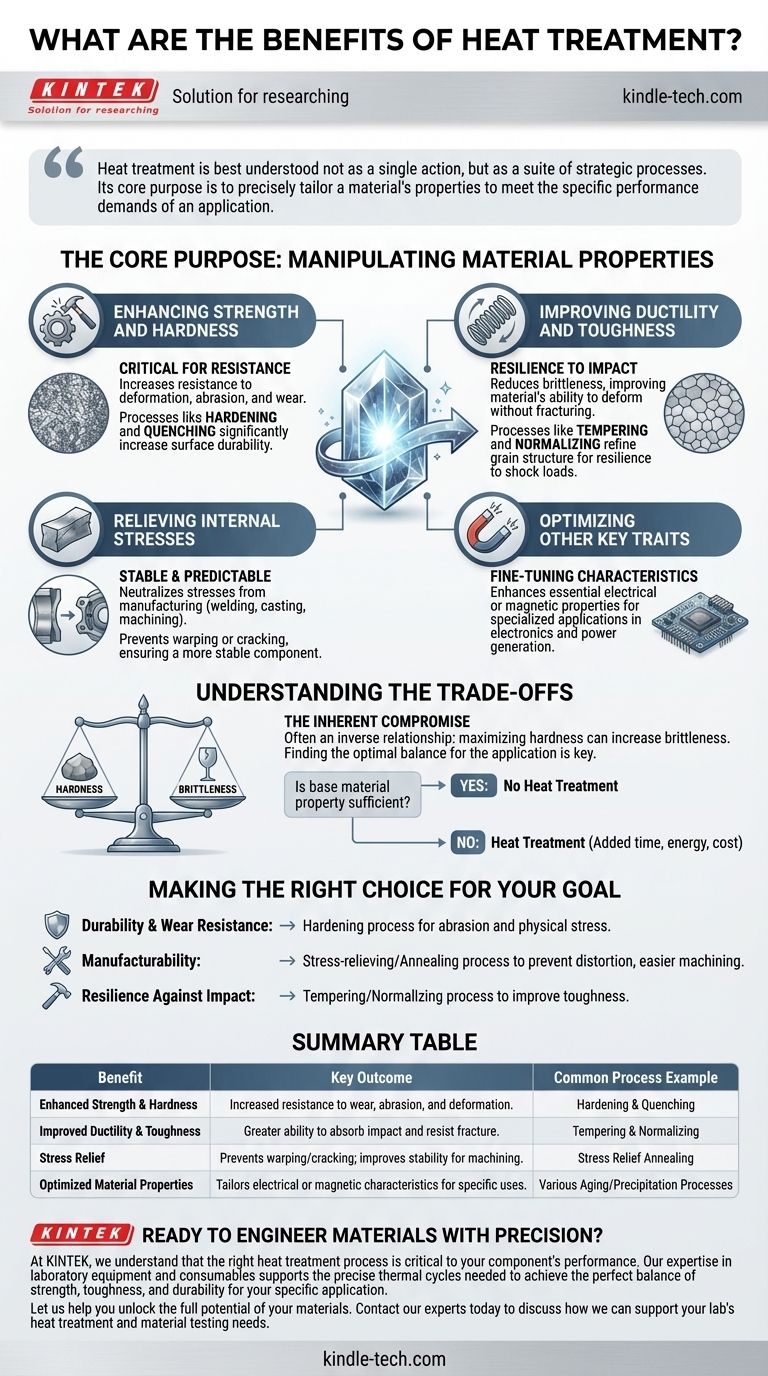
Heat treatment is best understood not as a single action, but as a suite of strategic processes. Its core purpose is to precisely tailor a material's properties to meet the specific performance demands of an application.

The Core Purpose: Manipulating Material Properties
Heat treatment works by carefully controlling heating and cooling cycles to change the microscopic crystal structure, or "microstructure," of a material. This manipulation unlocks specific, desirable characteristics.
Enhancing Strength and Hardness
One of the most common goals of heat treatment is to make a material stronger and harder.
This is critical for components that must resist deformation, abrasion, or wear over their service life. Processes like hardening and quenching create a microstructure that significantly increases surface durability.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
While hardness is crucial, so is the ability to deform without fracturing. Heat treatment can also reduce brittleness.
Certain processes refine the grain structure of a material, improving its toughness and making it more resilient to impact and shock loads.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, and heavy machining introduce significant stress into a material.
These internal stresses can cause parts to warp or crack over time or during subsequent manufacturing steps. A stress-relief heat treatment neutralizes these forces, creating a more stable and predictable component.
Optimizing Other Key Traits
Beyond pure mechanics, heat treatment can also be used to fine-tune other material characteristics.
For certain alloys, specific thermal cycles can enhance essential electrical or magnetic properties, making them suitable for specialized applications in electronics and power generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While immensely beneficial, heat treatment is a precise science that involves important considerations and potential compromises.
The Inherent Compromise: Hardness vs. Brittleness
There is often an inverse relationship between hardness and toughness.
Increasing a material's hardness to its maximum potential can also make it more brittle and susceptible to fracture. The key is to find the optimal balance for the specific application's needs.
Not Every Part Requires It
Heat treatment adds time, energy, and cost to the manufacturing process.
For applications where the material's base properties are already sufficient, subjecting it to heat treatment is an unnecessary expense. It should be specified only when its benefits solve a clear performance or manufacturing challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying heat treatment effectively requires matching the process to the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is durability and wear resistance: A hardening process is necessary to create a component that can withstand significant abrasion and physical stress.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability: A stress-relieving or annealing process is key to preventing distortion and making the material easier to machine or weld.
- If your primary focus is resilience against impact: A tempering or normalizing process will improve the material's toughness and reduce the risk of brittle failure.
Ultimately, viewing heat treatment as a deliberate design choice allows you to engineer materials to meet the precise demands of any application.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Outcome | Common Process Example |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Strength & Hardness | Increased resistance to wear, abrasion, and deformation. | Hardening & Quenching |
| Improved Ductility & Toughness | Greater ability to absorb impact and resist fracture. | Tempering & Normalizing |
| Stress Relief | Prevents warping/cracking; improves stability for machining. | Stress Relief Annealing |
| Optimized Material Properties | Tailors electrical or magnetic characteristics for specific uses. | Various Aging/Precipitation Processes |
Ready to engineer materials with precision?
At KINTEK, we understand that the right heat treatment process is critical to your component's performance. Our expertise in laboratory equipment and consumables supports the precise thermal cycles needed to achieve the perfect balance of strength, toughness, and durability for your specific application.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your lab's heat treatment and material testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum high-temperature furnace required for C/C-SiC siliconization? Ensure Perfect Composite Integrity
- Which method of heat transfer occur in a vacuum? Unlocking the Power of Thermal Radiation
- Why is a high vacuum annealing furnace typically used for Ni-Cr-Si joints? Ensure Ductile and Strong Brazed Connections
- What are the types of filler metal in brazing? Select the Right Alloy for a Strong, Durable Joint
- How does a high-temperature laboratory furnace modify Li–Al LDH during catalyst pretreatment? Enhance Catalytic Activity
- What is the process of particle sintering? A Step-by-Step Guide to Powder Metallurgy
- Why must zirconium-niobium alloy sponges undergo vacuum heat treatment? Master the Key to High-Purity Alloy Production
- What is the benefits of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Quality and Process Control



















