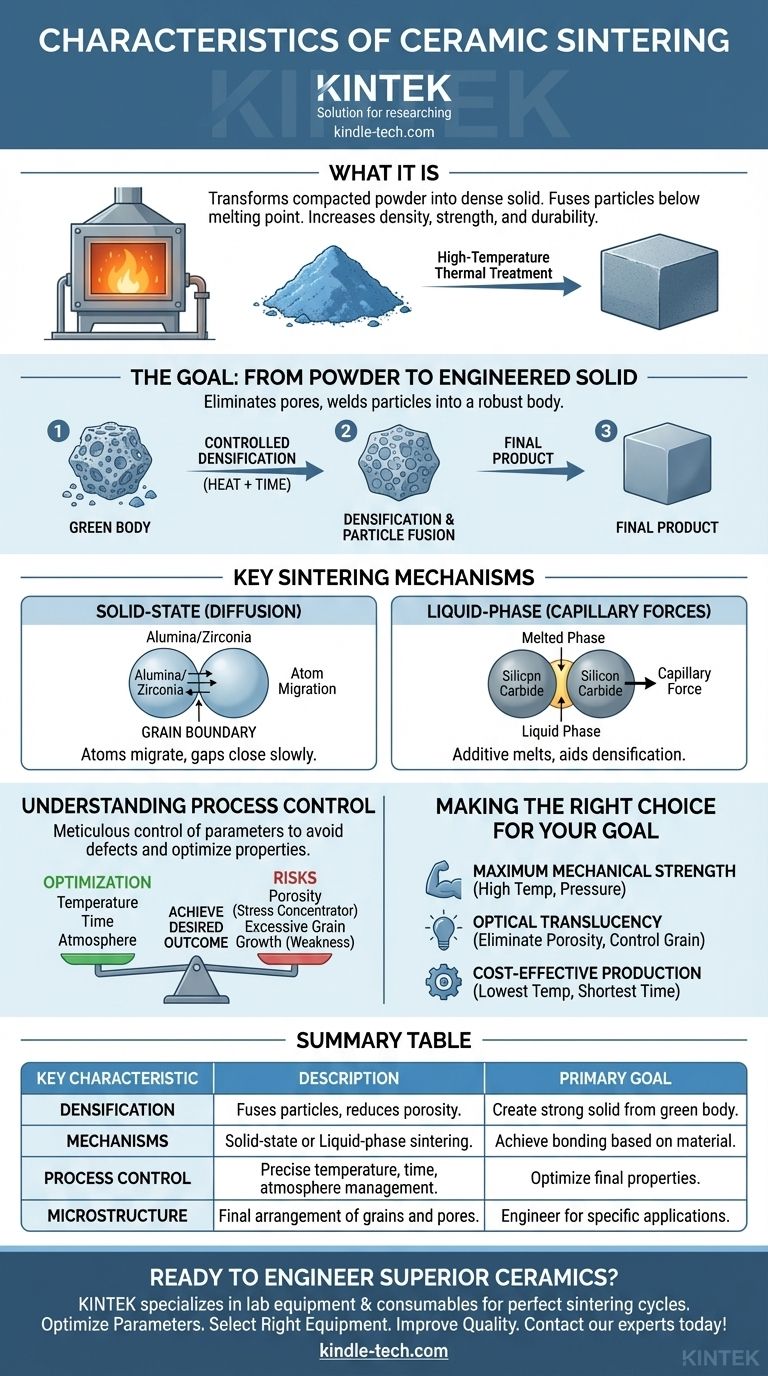
At its core, ceramic sintering is a high-temperature thermal treatment that transforms a compacted ceramic powder into a dense, solid object. This process occurs below the material's melting point and works by fusing individual particles together, dramatically reducing porosity and increasing the material's density, strength, and overall durability.
Sintering is not merely a heating process; it is a controlled microstructural transformation. Its fundamental purpose is to eliminate the empty spaces between powder particles, creating a solid, monolithic body with engineered properties far superior to the original loose material.

The Goal: From Powder to Engineered Solid
Sintering is the critical step that converts a fragile, loosely-packed form into a robust final product. The entire process is designed to achieve a controlled densification.
The Starting Point: The "Green Body"
Before sintering, ceramic powder is mixed with a binder and pressed into a desired shape. This initial, fragile object is known as a "green body." It has the right shape but lacks any significant mechanical strength.
The Primary Transformation: Densification
During sintering, the high temperature provides the energy for atoms to move between particles. This material migration fills the pores (empty spaces) between the particles, causing the entire object to shrink and become denser.
The Mechanism: Fusing Particles Together
As particles fuse, the boundaries between them (grain boundaries) shift and grow. This process welds the powder into a solid mass, forming a dense polycrystalline body with a certain strength and the desired final properties.
Key Sintering Mechanisms
The way particles fuse is not universal; it depends on the ceramic material and the manufacturing goal. The two primary methods are solid-state and liquid-phase sintering.
Solid-State Sintering: Diffusion in Action
In materials like zirconia and alumina, sintering occurs entirely in the solid state. Atoms migrate across the boundaries of touching particles through a process called diffusion, slowly closing the gaps between them.
Liquid-Phase Sintering: Aiding the Process
For harder-to-densify ceramics like silicon carbide, a small amount of an additive is used. At sintering temperature, this additive melts and forms a liquid phase that wets the ceramic particles, pulling them together through capillary forces and accelerating densification.
The Resulting Microstructure
The final arrangement of grains and pores is the material's microstructure, which dictates its properties. For example, sintering transforms zirconia's crystal structure into an extremely hard and dense state, making it ideal for cutting tools and dental implants.
Understanding the Process Control
Achieving the desired outcome is not guaranteed. Sintering is a balancing act where process parameters must be meticulously controlled to avoid defects.
The Importance of Optimization
The final physical properties of any ceramic product are a direct result of an optimized sintering cycle. Key parameters like temperature, heating rate, hold time, and atmosphere are carefully managed to achieve the target density and grain size.
The Problem of Porosity
While the main goal is often to eliminate porosity for maximum strength, some applications may require a specific level of controlled porosity. Uncontrolled or residual porosity acts as a stress concentrator and is a common source of mechanical failure.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
If the temperature is too high or the sintering time is too long, the ceramic grains can grow too large. While this reduces porosity, excessively large grains can sometimes weaken the final material, creating a critical trade-off between density and strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific approach to sintering is always dictated by the desired properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength: You will use conditions designed to achieve near-full densification, often requiring high temperatures and sometimes external pressure.
- If your primary focus is optical translucency: You must achieve near-total elimination of porosity and control grain size with extreme precision, as any pore will scatter light.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: You will optimize for the lowest temperature and shortest time that reliably meets the minimum performance specifications for products like ceramic tiles or sanitaryware.
By controlling these factors, sintering becomes a powerful tool for engineering ceramic materials to meet precise performance demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Densification | Fuses powder particles, reduces porosity, and increases density. | Create a strong, solid object from a fragile "green body." |
| Mechanisms | Solid-state (diffusion) or Liquid-phase (capillary forces) sintering. | Achieve bonding based on material (e.g., Alumina vs. Silicon Carbide). |
| Process Control | Precise management of temperature, time, and atmosphere. | Optimize final properties like strength, translucency, or porosity. |
| Microstructure | Final arrangement of grains and pores dictates material properties. | Engineer ceramics for specific applications (e.g., dental implants, cutting tools). |
Ready to Engineer Superior Ceramics?
The precise control of the sintering process is critical to achieving your material's target properties, whether it's maximum strength, optical translucency, or cost-effective production. At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your ceramic sintering cycles.
Our expertise helps you:
- Optimize Sintering Parameters: Achieve the perfect balance of density and grain size.
- Select the Right Equipment: From furnaces to atmosphere control systems.
- Improve Product Quality: Minimize defects like uncontrolled porosity or excessive grain growth.
Let KINTEK be your partner in developing high-performance ceramic components. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right solutions for your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses



















