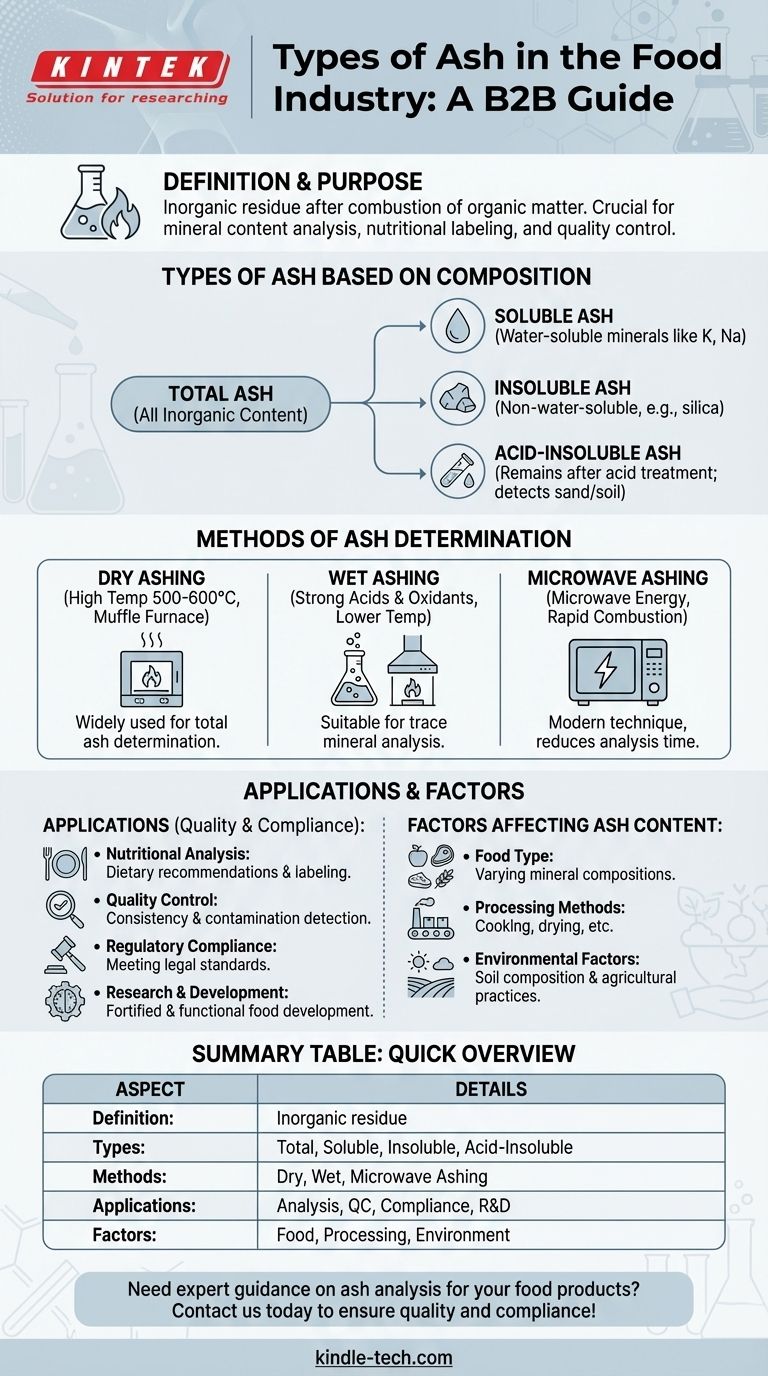
In the food industry, ash refers to the inorganic residue remaining after the organic matter in food has been burned off. This residue primarily consists of minerals, which are essential for nutritional analysis and quality control. The types of ash in the food industry are categorized based on their composition and the methods used to determine them. Understanding these types is crucial for evaluating the mineral content and ensuring the quality and safety of food products.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition and Purpose of Ash in the Food Industry
- Ash is the inorganic residue left after the combustion of organic matter in food.
- It is used to determine the mineral content of food products, which is critical for nutritional labeling, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
- The analysis of ash helps in identifying the presence of essential minerals like calcium, potassium, magnesium, and trace elements.
-
Types of Ash Based on Composition
- Total Ash: Represents the total inorganic content of a food product. It includes all minerals present in the sample.
- Soluble Ash: Refers to the portion of ash that is soluble in water. This typically includes minerals like potassium and sodium.
- Insoluble Ash: The portion of ash that is not soluble in water, often consisting of silica and other insoluble minerals.
- Acid-Insoluble Ash: A subset of insoluble ash that remains after treatment with acid. It is used to detect contaminants like sand or soil in food products.
-
Methods of Ash Determination
- Dry Ashing: Involves heating the food sample at high temperatures (500–600°C) in a muffle furnace to burn off organic matter. This method is widely used for total ash determination.
- Wet Ashing: Uses strong acids and oxidants to digest the organic matter at lower temperatures. This method is suitable for trace mineral analysis.
- Microwave Ashing: A modern technique that uses microwave energy to rapidly combust the sample, reducing analysis time.
-
Applications of Ash Analysis in the Food Industry
- Nutritional Analysis: Determines the mineral content of food, which is essential for dietary recommendations and labeling.
- Quality Control: Ensures consistency in mineral content and detects contamination or adulteration.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet legal requirements for mineral content in food products.
- Research and Development: Supports the development of fortified foods and functional foods with enhanced mineral profiles.
-
Factors Affecting Ash Content
- Food Type: Different foods have varying mineral compositions, affecting their ash content.
- Processing Methods: Cooking, drying, and other processes can alter the mineral content and ash composition.
- Environmental Factors: Soil composition and agricultural practices influence the mineral content of raw materials.
By understanding the types of ash and their significance, food industry professionals can ensure accurate mineral analysis, maintain product quality, and comply with regulatory standards.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Inorganic residue after burning organic matter in food. |
| Types of Ash | - Total Ash: All inorganic content. |
| - Soluble Ash: Water-soluble minerals like potassium and sodium. | |
| - Insoluble Ash: Silica and other insoluble minerals. | |
| - Acid-Insoluble Ash: Detects contaminants like sand or soil. | |
| Methods | - Dry Ashing: High-temperature combustion in a muffle furnace. |
| - Wet Ashing: Uses acids for trace mineral analysis. | |
| - Microwave Ashing: Rapid combustion using microwave energy. | |
| Applications | - Nutritional analysis, quality control, regulatory compliance, R&D. |
| Factors Affecting Ash | - Food type, processing methods, environmental factors like soil composition. |
Need expert guidance on ash analysis for your food products? Contact us today to ensure quality and compliance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a box furnace in LLZO synthesis? Master the Key to High-Performance Solid-State Electrolytes
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in determining the VS content? Precision in Compost Analysis
- What is the use of burnout furnace? Create Flawless Castings with Precision Mold Preparation
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the role of high-temperature furnaces in the conversion of waste shells into biodiesel catalysts? - KINTEK
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve High-Temperature Processing with Purity
- How does a vacuum drying oven benefit the preparation of CuFe12O19 magnetic nanoparticles? Enhance Purity and Structure



















