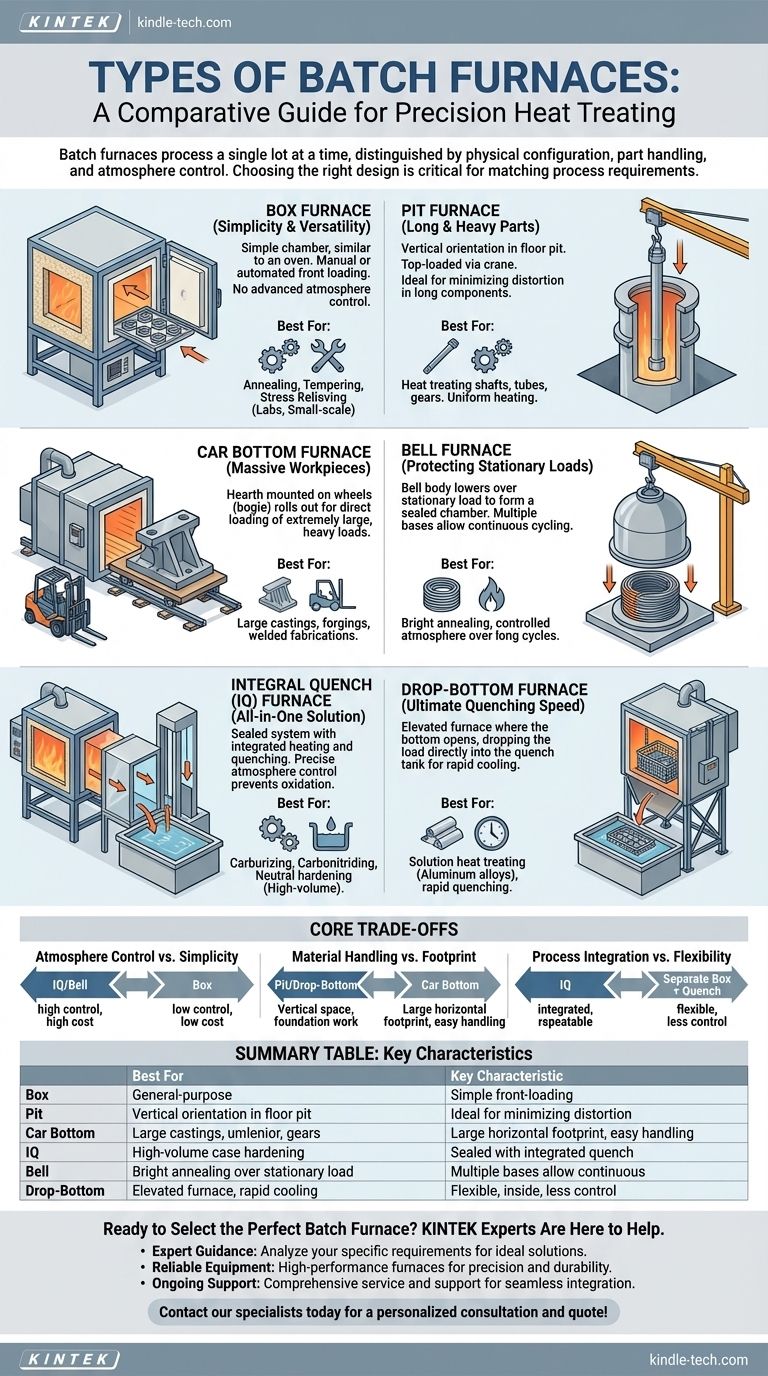
At its core, a batch furnace processes a single lot, or "batch," of material at a time, distinct from continuous furnaces that process a constant flow. The primary types are defined by their physical configuration, how parts are loaded and unloaded, and their capability for controlling the internal atmosphere. Key examples include the simple Box Furnace, the vertical Pit Furnace, the heavy-duty Car Bottom Furnace, and the highly integrated Integral Quench Furnace.
The most critical distinction between batch furnace types is not their heating method, but how their design facilitates part handling, atmosphere control, and quenching. Choosing the right furnace means matching its specific architecture to your process requirements, part geometry, and production volume.

Foundational Designs: Box and Pit Furnaces
These furnaces represent the simplest and most common configurations, forming the basis for many heat-treating operations.
The Box Furnace: Simplicity and Versatility
A box furnace is the most straightforward design, functionally similar to a conventional oven. It consists of an insulated chamber with a single door at the front for manual or automated loading and unloading.
Their simple design makes them highly versatile for a wide range of processes like annealing, tempering, and stress relieving, where complex atmosphere control or rapid quenching is not the primary requirement. They are common in labs, tool rooms, and small-scale production environments.
The Pit Furnace: Handling Long and Heavy Parts
A pit furnace is a cylindrical chamber installed vertically in a pit in the facility floor. Parts are loaded from the top using an overhead crane, making it ideal for long, heavy, or dense loads that are difficult to handle otherwise.
This vertical orientation is excellent for treating long components like shafts, tubes, and gears, as it minimizes distortion and ensures more uniform heating. Many pit furnaces use an internal sealed container, known as a retort, to provide precise atmosphere control for processes like nitriding or carburizing.
Furnaces for Large and Specialized Loads
When dealing with exceptionally large workpieces or requiring specific atmosphere conditions for stationary loads, more specialized designs are necessary.
The Car Bottom Furnace: For Massive Workpieces
Also known as a bogie hearth furnace, this design features a hearth that is mounted on wheels and can be rolled out of the furnace chamber on a track. This "car" allows for the direct loading of extremely large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped parts (like large castings, forgings, or welded fabrications) with a crane or forklift.
Once loaded, the car is moved back into the insulated chamber for the heating cycle. This design decouples the loading process from the furnace, improving safety and efficiency for massive loads.
The Bell Furnace: Protecting Stationary Loads
In a bell furnace, the workload is stacked on a stationary base. The furnace body, shaped like a bell, is then lowered over the load to form a sealed chamber. Multiple bases can be used with a single bell, allowing one load to be heated while another is cooling and a third is being prepared.
This design is excellent for processes requiring a tightly controlled atmosphere over a long cycle, such as the bright annealing of steel coils or copper wire. The seal at the base effectively contains the process atmosphere.
High-Performance Atmosphere and Quenching
For advanced thermal processes that demand precise control over both surface chemistry and cooling rates, integrated furnace systems are the standard.
The Integral Quench (IQ) Furnace: The All-in-One Solution
The Integral Quench (IQ) furnace, also called a sealed quench furnace, is a workhorse of the commercial heat-treating industry. It consists of a heated chamber connected to a sealed vestibule that houses an elevator and an integrated quench tank (typically oil).
The entire process—heating, soaking, and quenching—occurs within a sealed, controlled atmosphere. This prevents oxidation and allows for precise surface chemistry modifications, making it the standard for processes like carburizing, carbonitriding, and neutral hardening where both a hard surface and a ductile core are required.
The Drop-Bottom Furnace: For Ultimate Quenching Speed
A drop-bottom furnace is a high-performance solution designed for the fastest possible quench. The furnace is elevated, and parts are placed in a basket or on a rack inside. At the end of the heating cycle, the entire bottom of the furnace opens, dropping the load directly into a quench tank positioned below.
This extremely short delay between heating and quenching (often just a few seconds) is critical for solution heat treating aluminum alloys and other precipitation-hardening materials, where a rapid quench is necessary to lock in the desired metallurgical properties.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing capability, cost, and operational complexity. No single design is universally superior.
Atmosphere Control vs. Simplicity
A simple air-fired box furnace is inexpensive and easy to operate but offers no protection against oxidation. An Integral Quench or Bell furnace provides precise atmosphere control for superior metallurgical results but comes with higher capital cost, more complex operation, and the need for gas-generating systems.
Material Handling vs. Footprint
Pit and drop-bottom furnaces leverage vertical space, making them efficient for certain part geometries but requiring significant foundation work and overhead clearance. Car bottom furnaces demand a large horizontal footprint to accommodate the track system but make handling massive parts straightforward.
Process Integration vs. Flexibility
An IQ furnace integrates heating and quenching, ensuring process repeatability and high throughput for specific part families. A setup with a separate box furnace and open quench tank is more flexible for one-off jobs but sacrifices process control, consistency, and operator safety.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by the metallurgical outcome you need to achieve and the physical nature of your parts.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating or lab work: A box furnace offers the best combination of versatility and low initial cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume case hardening with minimal oxidation: An Integral Quench (IQ) furnace is the industry standard for its process control and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is processing extremely large or heavy fabrications: A car bottom furnace is the only practical solution for safe and effective material handling.
- If your primary focus is heat treating long, cylindrical parts like shafts: A pit furnace minimizes distortion and provides excellent temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is solution heat treating aluminum with a mandatory rapid quench: A drop-bottom furnace provides the quench speed necessary to achieve critical mechanical properties.
Ultimately, the right batch furnace is an extension of your manufacturing process, chosen to deliver a specific and repeatable result.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Box Furnace | General-purpose heat treating, labs | Simple, versatile, front-loading |
| Pit Furnace | Long/heavy parts (shafts, tubes) | Vertical, top-loading, minimizes distortion |
| Car Bottom Furnace | Massive, heavy workpieces | Hearth rolls out for easy loading |
| Integral Quench (IQ) | High-volume case hardening | Sealed chamber with integrated quench tank |
| Bell Furnace | Bright annealing, controlled atmosphere | Bell lowers over stationary load |
| Drop-Bottom Furnace | Rapid quenching (e.g., aluminum) | Load drops directly into quench tank |
Ready to Select the Perfect Batch Furnace?
Choosing the right furnace is critical for achieving consistent, high-quality results in your heat treatment process. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate the options.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our team will analyze your specific requirements—including part geometry, production volume, and desired metallurgical outcomes—to recommend the ideal batch furnace solution.
- Reliable Equipment: KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a range of batch furnaces designed for precision, durability, and efficiency.
- Ongoing Support: We ensure your furnace integrates seamlessly into your operation, backed by comprehensive service and support.
Don't leave your heat treating results to chance. Let KINTEK, your partner in laboratory excellence, help you make the right investment.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4



















