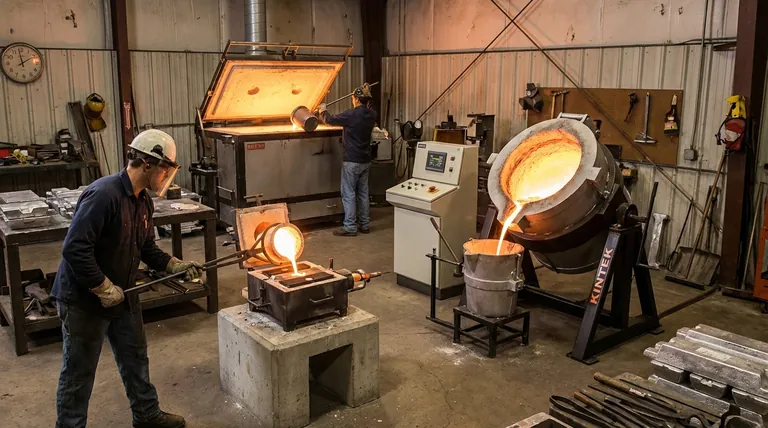
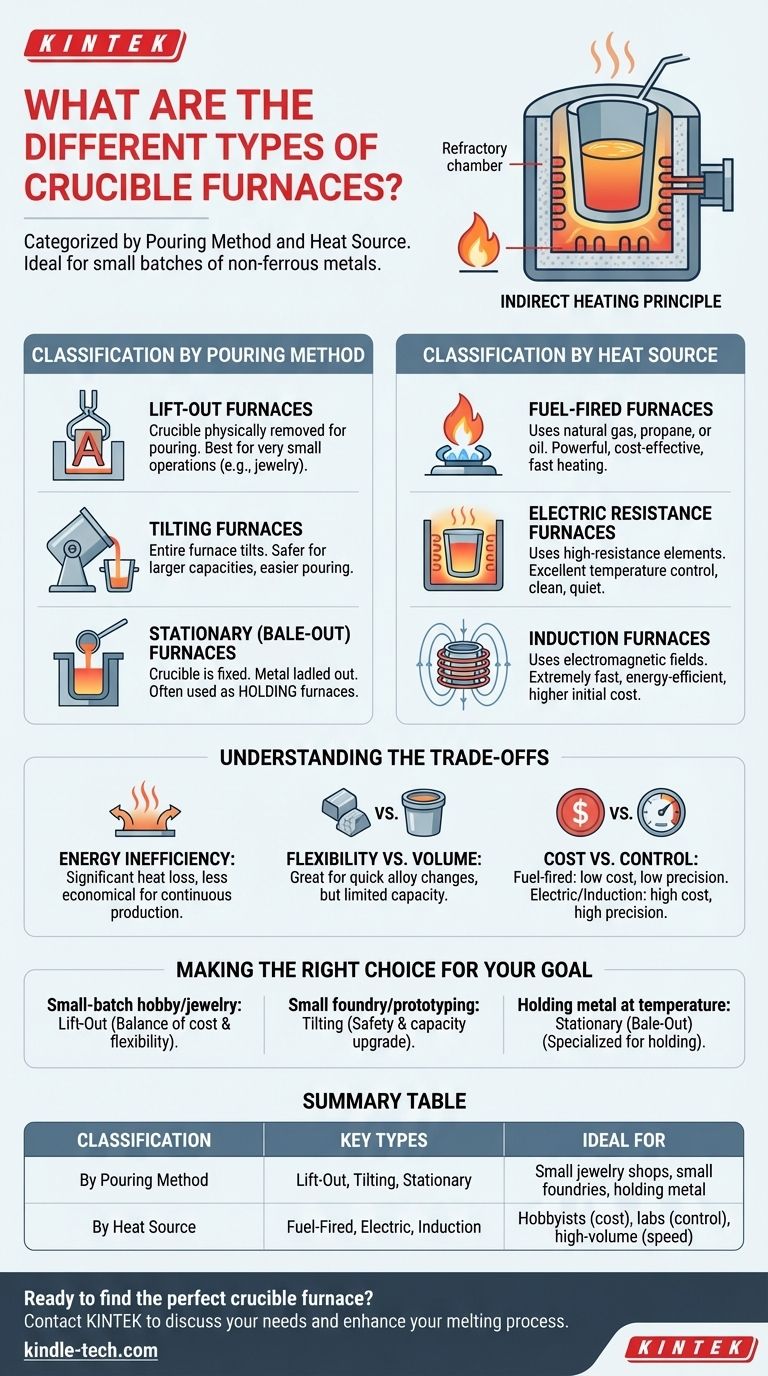
At their core, crucible furnaces are categorized based on two key factors: how the molten metal is poured and the type of heat source used. These simple, high-temperature furnaces consist of a refractory chamber that heats a separate pot, or crucible, containing the metal, making them ideal for melting smaller batches of non-ferrous metals.
The choice of a crucible furnace is not about finding the "best" type, but about matching the furnace's design—specifically its pouring mechanism and heat source—to the scale of your work, your budget, and the specific metals you intend to melt.

Understanding the Crucible Furnace
Before diving into the specific types, it's essential to grasp the fundamental principle. A crucible furnace is an indirect-heating system.
How They Work
The furnace's heat source—be it gas, oil, or electricity—heats the chamber around the crucible. The heat then transfers through the crucible wall to melt the metal inside. This prevents direct contact between the flame or heating elements and the metal, ensuring a cleaner melt.
Common Applications
Crucible furnaces are valued for their simplicity and flexibility. They are commonly found in settings where quick changes between different alloys are needed or where batch sizes are relatively small, such as:
- Jewelry making
- Small-scale foundries and art casting
- Prototyping and R&D labs
- Vocational schools and educational workshops
Classification by Pouring Method
The most significant distinction between crucible furnaces lies in how the molten metal is removed from the furnace for pouring.
Lift-Out Furnaces
In a lift-out furnace, the crucible is physically removed from the furnace using a set of specialized tongs. The operator then carries the crucible to the mold for pouring. These are sometimes called removable crucible furnaces.
The crucibles are often A-shaped or bilge-shaped to provide a secure grip for the tongs. This design is best suited for very small operations where the weight of the molten metal is manageable for one or two people.
Tilting Furnaces
For larger capacities, tilting furnaces are the standard. The crucible remains inside the furnace, and the entire furnace assembly is tilted on a pivot—either manually with a hand crank or via a hydraulic system—to pour the metal directly into a ladle or mold.
This method is significantly safer and more practical for volumes that are too heavy to lift by hand.
Stationary (Bale-Out) Furnaces
In a stationary or bale-out furnace, the crucible is fixed in place and does not tilt or get removed. Instead, molten metal is ladled out from the top as needed.
These furnaces are less common for primary melting and are more often used as holding furnaces, where they keep a large batch of metal at a constant temperature for repeated casting operations.
Classification by Heat Source
The method used to generate heat is another critical differentiator, impacting efficiency, control, and cost.
Fuel-Fired Furnaces
These furnaces use a burner to combust fuel like natural gas, propane, or oil. They are powerful and can reach high temperatures quickly. They represent a common and often cost-effective option for melting.
Electric Resistance Furnaces
These furnaces use high-resistance heating elements surrounding the crucible, similar to an electric kiln. They offer excellent temperature control and a clean, quiet operating environment free from combustion byproducts.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use powerful electromagnetic fields to heat the crucible (if conductive) or the metal itself. This method is extremely fast and energy-efficient but represents a significantly higher initial investment and level of complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Crucible furnaces are a versatile tool, but they come with important limitations to consider.
Energy Inefficiency
A defining characteristic of most crucible furnaces, particularly fuel-fired models, is their relatively poor energy efficiency. A significant amount of heat is lost through the furnace body and exhaust. This makes them less economical for large-scale, continuous production compared to direct-melting furnaces.
Flexibility vs. Volume
The primary strength of a crucible furnace is its flexibility. Because the metal is contained, you can switch from melting aluminum to bronze in the next batch with minimal contamination. However, this advantage is tied to their smaller capacity. They are not designed for high-volume melting.
Cost vs. Control
Fuel-fired lift-out furnaces offer the lowest barrier to entry, making them popular with hobbyists. However, they provide the least precise temperature control. In contrast, electric and induction furnaces offer superior precision at a higher upfront cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace type based on the primary requirements of your work.
- If your primary focus is small-batch hobby work or jewelry: A simple lift-out furnace, either gas-fired or electric, offers the best balance of low cost and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is running a small foundry or frequent prototyping: A tilting furnace provides a major safety and capacity upgrade for handling larger, safer pours.
- If your primary focus is holding metal at a consistent temperature for casting: A stationary (bale-out) furnace is the specialized tool designed specifically for this purpose.
Ultimately, understanding these core types empowers you to select a furnace that serves as an effective and appropriate tool for your specific metal-working objectives.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| By Pouring Method | Lift-Out, Tilting, Stationary (Bale-Out) | Small jewelry shops, small foundries, holding metal |
| By Heat Source | Fuel-Fired, Electric Resistance, Induction | Hobbyists (cost), labs (control), high-volume (speed) |
Ready to find the perfect crucible furnace for your workshop or lab? The right equipment is crucial for safety, efficiency, and achieving high-quality results. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying reliable lab equipment, including crucible furnaces tailored for jewelers, foundries, and R&D laboratories. Our experts can help you select the ideal model based on your metal, batch size, and budget.
Contact KINTELK today to discuss your specific needs and let us provide a solution that enhances your melting process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- What is the difference between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What are the classification of refractory materials? A Guide to Chemical and Thermal Selection



















