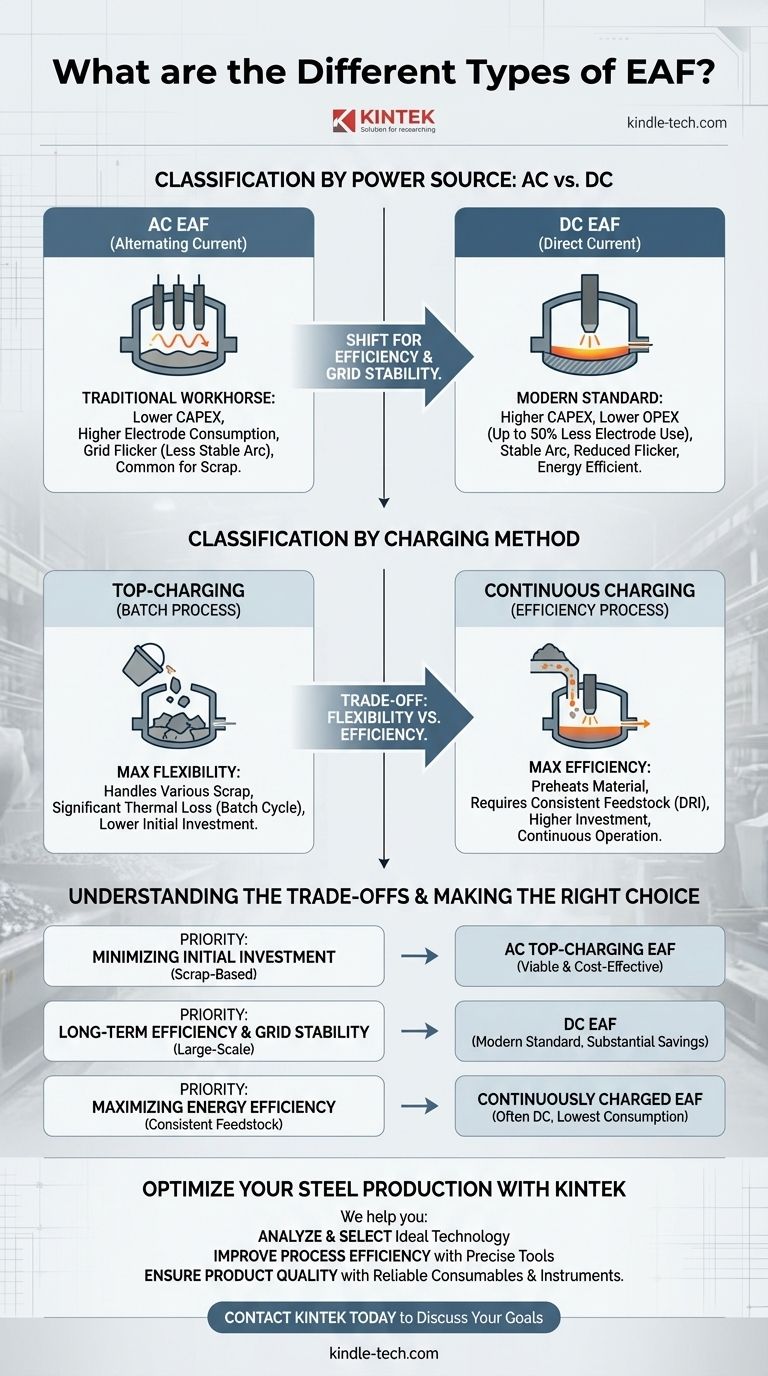
The primary types of Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) are classified by two fundamental characteristics: their electrical power source and their method for charging raw materials. While other variations exist, the most significant distinction is between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) furnaces, which dictates everything from operational efficiency to environmental impact.
The core evolution in EAF technology has been the shift from traditional AC furnaces to more modern DC furnaces. This change reflects a strategic move towards greater energy efficiency, lower operating costs, and reduced impact on the electrical grid.

Classification by Power Source: AC vs. DC
The choice between an AC and DC power supply is the most critical differentiator in EAF design. It fundamentally changes the furnace's operation, cost structure, and performance.
The Traditional Workhorse: AC EAF
An Alternating Current (AC) EAF is the classic design and historically the most common type. It operates using a three-phase AC power supply connected to three separate graphite electrodes.
These electrodes are lowered into the furnace, and the powerful current arcs between the electrodes and through the metallic charge, generating intense heat for melting.
The nature of AC power creates a less stable arc, leading to more electrical noise, or "flicker," on the power grid. This can be a significant issue for local utility providers.
The Modern Standard: DC EAF
A Direct Current (DC) EAF represents a major technological advancement. It typically uses a single, large graphite electrode as the cathode.
The circuit is completed through a conductive furnace bottom, which acts as the anode. This setup creates a single, highly stable, and focused arc between the central electrode and the molten bath.
This stability results in significant advantages, including up to 50% lower graphite electrode consumption, reduced electrical flicker, and often lower energy consumption per ton of steel produced.
Classification by Charging Method
How raw materials are introduced into the furnace defines its process flow and has a major impact on energy efficiency.
Top-Charging (The Batch Process)
Top-charging is the most common method, especially for furnaces processing scrap steel. The entire furnace roof swings away, and a large "bucket" drops a full charge of scrap into the vessel.
This method defines the EAF as a batch process. A batch of scrap is charged, melted down, refined, and then tapped before the cycle begins again.
While highly flexible for handling various types and sizes of scrap, this method loses significant thermal energy each time the roof is opened for charging.
Continuous Charging (The Efficiency Process)
Continuous charging methods are designed to improve energy efficiency by using the furnace's hot off-gas to preheat the incoming raw materials.
Furnaces using systems like Consteel or a Shaft Furnace continuously feed material, such as Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) or scrap, into a preheating zone before it enters the main furnace vessel.
This approach transforms the EAF into a more continuous, stable operation. It dramatically reduces energy consumption and is ideal for operations with a consistent, uniform feedstock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an EAF type is not about selecting the "best" technology in a vacuum, but about balancing investment costs, operational expenses, and strategic goals.
AC EAF: Lower CAPEX, Higher OPEX
The primary advantage of an AC furnace is its lower initial capital expenditure (CAPEX). The electrical systems are simpler and less expensive than their DC counterparts.
However, they typically have higher long-term operating expenses (OPEX) due to greater electrode consumption and the potential need for expensive flicker-compensation equipment.
DC EAF: Higher CAPEX, Lower OPEX
DC furnaces require a more complex and expensive power system, including large rectifiers to convert AC to DC, leading to a higher initial investment.
These costs are often justified by a lower total cost of ownership. The significant savings on electrodes, energy, and refractory lining wear can provide a strong return on the initial investment over the furnace's life.
Batch vs. Continuous: Flexibility vs. Efficiency
Top-charging offers maximum flexibility to process a wide variety of scrap materials, which is crucial in a volatile scrap market. This comes at the cost of thermal efficiency.
Continuous charging systems are far more energy-efficient but are less flexible. They perform best with a consistent, known feedstock and represent a higher initial investment due to their complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The ideal EAF configuration depends entirely on your operational priorities, from available capital to long-term efficiency goals.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment for a scrap-based operation: An AC top-charging EAF remains a viable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational efficiency and grid stability: A DC EAF is the modern standard, offering substantial savings on electrodes and energy for large-scale production.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency with a consistent feedstock (like DRI): A continuously charged EAF, often in a DC configuration, provides the lowest energy consumption and highest productivity.
Understanding these core classifications allows you to align the furnace technology with the operational and economic model that best suits your strategic goals.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Source | AC EAF | Lower CAPEX, higher electrode consumption, grid flicker | Minimizing initial investment, scrap-based operations |
| DC EAF | Higher CAPEX, lower OPEX (up to 50% less electrode use), stable arc | Long-term efficiency, large-scale production, grid stability | |
| Charging Method | Top-Charging (Batch) | High flexibility for various scrap, significant thermal loss | Operations requiring feedstock flexibility |
| Continuous Charging | High energy efficiency, preheats material, requires consistent feedstock | Maximizing efficiency with consistent materials like DRI |
Ready to Optimize Your Steel Production?
Choosing the right Electric Arc Furnace is critical to your operational efficiency and bottom line. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to support the research, development, and quality control processes for the steel industry.
We help you:
- Analyze and select the ideal furnace technology for your specific needs.
- Improve process efficiency with precise measurement and control tools.
- Ensure product quality with reliable consumables and analytical instruments.
Let KINTEK's expertise in laboratory solutions empower your decision-making and enhance your production capabilities.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















