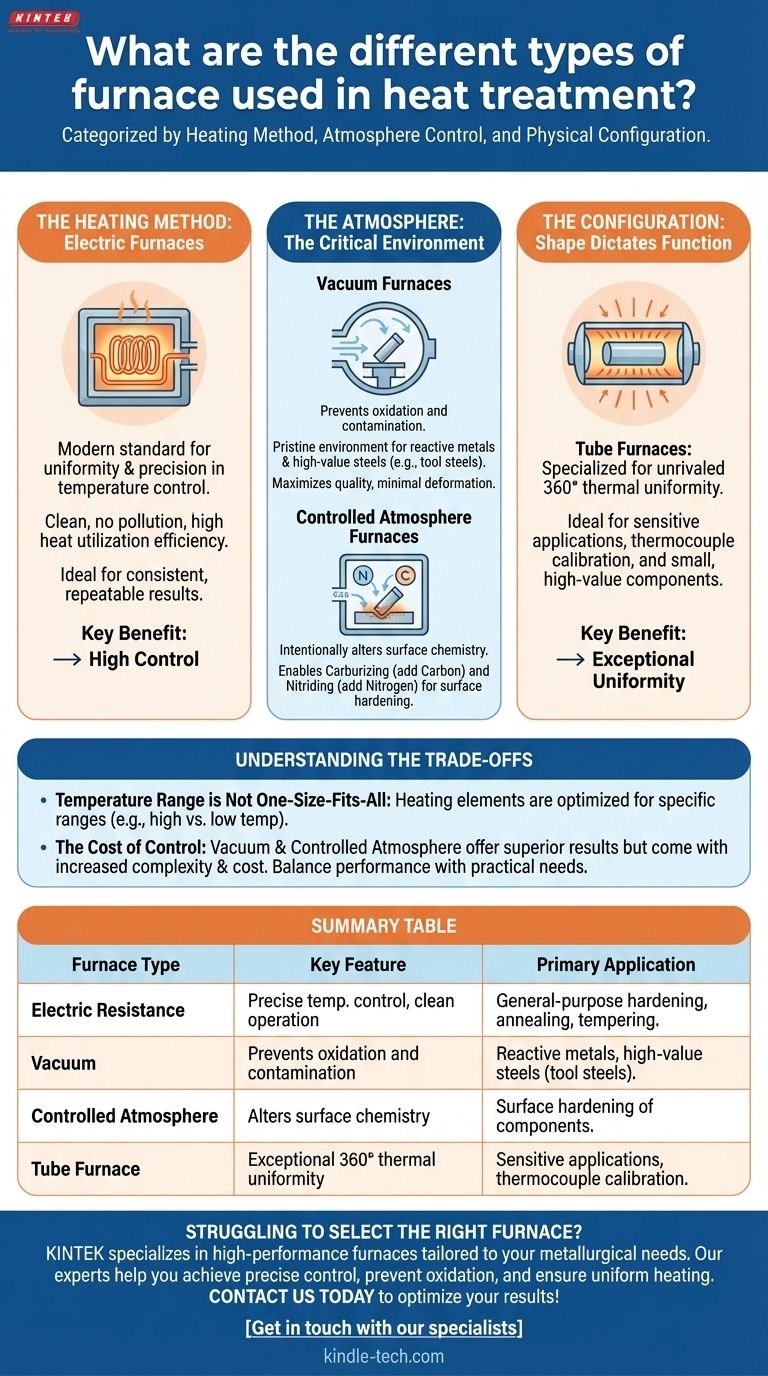
In heat treatment, furnaces are primarily categorized by their heating method, atmosphere control, and physical configuration. The most common types include versatile electric resistance furnaces, highly controlled vacuum furnaces for preventing oxidation, and specialized designs like tube furnaces that offer exceptional thermal uniformity for sensitive applications.
The selection of a heat treatment furnace is not about finding a single "best type," but about matching the furnace's capabilities—specifically its temperature precision and atmospheric environment—to the exact metallurgical requirements of the material and the desired outcome of the process.

The Core Elements of Furnace Design
Understanding the fundamental components that differentiate furnaces is key to selecting the right tool. The design is driven by the specific treatment required for a given material stock and temperature.
The Heating Method: Electric Furnaces
Most modern heat treatment furnaces are electrically powered due to their significant advantages over fuel-fired alternatives.
Electric furnaces provide outstanding uniformity and precision in temperature control. This high degree of control ensures consistent, repeatable results across the entire workpiece.
They also offer high heat utilization efficiency, a clean working environment with no pollution, and the ability to reach very high temperatures using specialized heating elements.
The Atmosphere: The Critical Environment
The atmosphere inside the furnace has a profound impact on the material's surface. The choice between an inert or active atmosphere depends on the material and the process goals.
Vacuum Furnaces A vacuum furnace is used when the primary goal is to prevent any surface reaction, such as oxidation or contamination.
By removing the atmosphere, these furnaces create a pristine environment ideal for treating reactive metals and high-value steels, including tool steels and martensitic stainless steels. This maximizes quality with minimal deformation.
Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces In other cases, the goal is to use the atmosphere to intentionally alter the material's surface. An active, or controlled, atmosphere is used for this purpose.
These atmospheres can prevent undesirable reactions like decarburization (carbon loss) or introduce new elements. Common applications include carburizing (adding carbon) and nitriding (adding nitrogen) to harden the surface of a part.
The Configuration: Shape Dictates Function
The physical design of the furnace is tailored to the type of part being treated and the specific thermal process.
Tube Furnaces A tube furnace is a prime example of a specialized configuration. Its cylindrical design provides unrivaled thermal uniformity around the entire 360° axis of a part.
This makes it ideal for sensitive applications requiring precise and even heating, such as the calibration of thermocouples or the processing of small, high-value components.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Selection
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance requirements with practical limitations. A furnace optimized for one task may be inefficient or unsuitable for another.
Temperature Range is Not One-Size-Fits-All
A furnace designed for very high temperatures (e.g., 1300°C) may not provide the necessary control or efficiency for a low-temperature process (e.g., 300°C).
The heating elements—such as resistance wires, silicon carbide rods, or molybdenum bands—are optimized for specific temperature ranges. Using a furnace far outside its ideal operating window can lead to poor results and inefficiency.
The Cost of Control
While vacuum and controlled atmosphere furnaces offer superior metallurgical results for sensitive materials, they come with increased complexity and cost.
For processes where minor surface oxidation is acceptable or can be removed later, a simpler electric furnace operating in ambient air may be a more cost-effective solution. The cost must be justified by the service demands of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by the primary objective of your heat treatment cycle.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on reactive or high-carbon steels: A vacuum furnace is the essential choice to ensure a clean, uncompromised surface.
- If your primary focus is hardening a part's surface by altering its chemistry: A controlled atmosphere furnace capable of carburizing or nitriding is required.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible thermal uniformity for sensitive or cylindrical parts: A tube furnace configuration offers the most consistent heating.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose hardening, annealing, or tempering with precise temperature control: A standard electric resistance furnace provides the best combination of performance and versatility.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles of heating, atmosphere, and configuration empowers you to select the ideal furnace for your specific metallurgical task.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Resistance | Precise temperature control, clean operation | General-purpose hardening, annealing, tempering |
| Vacuum | Prevents oxidation and contamination | Reactive metals, high-value steels (tool steels) |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Alters surface chemistry (e.g., carburizing, nitriding) | Surface hardening of components |
| Tube Furnace | Exceptional 360° thermal uniformity | Sensitive applications, thermocouple calibration |
Struggling to select the right furnace for your heat treatment process? KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment and consumables, including a wide range of high-performance furnaces tailored to your specific metallurgical needs. Our experts can help you achieve precise temperature control, prevent oxidation, and ensure uniform heating for your most critical applications. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let us help you optimize your heat treatment results! Get in touch with our specialists
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic principle of arc furnace? Harnessing Electricity for Efficient Metal Melting
- What role does a high-temperature annealing furnace play in the heat treatment of 316LN? Master Precision Restoration
- What is the process of consumable electrode arc melting? A Guide to High-Purity Alloy Refining
- What is the contamination in heat treatment? Control Surface Reactions for Superior Component Performance
- Why must a vacuum drying oven be used after preparing composite electrolytes? Ensure Battery Stability and Purity
- Why is a vacuum high-temperature furnace essential for XTO silicification? Ensure Pure Coating for Refractory Metals
- What are the two purposes of case hardening? Achieve Superior Wear and Impact Resistance
- Why is a high vacuum brazing furnace essential for carbon-carbon to metal joints? Secure High-Purity Material Bonding



















