At its core, a pellet mill die is categorized by its fundamental shape and mechanical operation. The two primary types you will encounter are the flat die and the ring die, each suited for different applications and scales of production.
The choice between a pellet mill die is less about which is "better" and more about which system—the flat die's direct pressure or the ring die's high-speed efficiency—is the correct tool for your specific raw material and production volume goals.

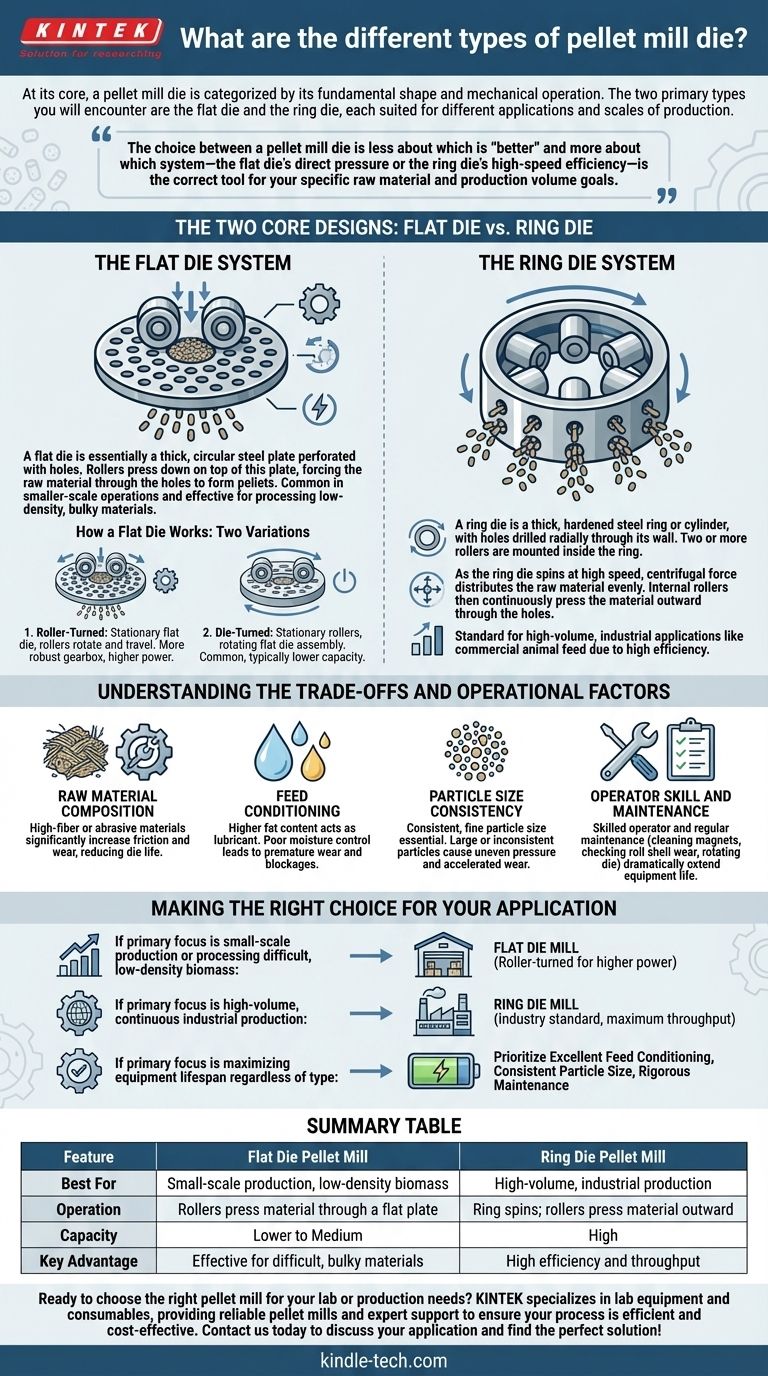
The Two Core Designs: Flat Die vs. Ring Die
The fundamental difference between these designs lies in their geometry and how force is applied to the raw material. This distinction dictates their capacity, cost, and ideal use cases.
The Flat Die System
A flat die is essentially a thick, circular steel plate perforated with holes. Rollers press down on top of this plate, forcing the raw material through the holes to form pellets.
This design is common in smaller-scale operations and is particularly effective for processing low-density, bulky materials that may be difficult to feed into other systems.
How a Flat Die Works: Two Variations
There are two distinct mechanical configurations for a flat die mill, each with its own advantages.
- Roller-Turned: In this setup, the flat die itself remains stationary while the rollers rotate and travel across its surface, pressing the material into the holes. This design often features a more robust gearbox, delivering higher power and capacity.
- Die-Turned: Here, the rollers are stationary while the entire flat die assembly rotates beneath them. This forces the material under the rollers and through the perforations. This is a common and effective design, though typically associated with lower capacity than roller-turned models.
The Ring Die System
A ring die is a thick, hardened steel ring or cylinder, with holes drilled radially through its wall. Two or more rollers are mounted inside the ring.
As the ring die spins at high speed, centrifugal force distributes the raw material evenly along its inner surface. The internal rollers then continuously press the material outward through the holes, forming pellets.
This design is the standard for high-volume, industrial applications like commercial animal feed production due to its high efficiency and throughput.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Factors
Choosing the right type of die is only the first step. The performance and lifespan of any die are heavily influenced by operational factors, regardless of its design.
Raw Material Composition
The nature of your input material is critical. High-fiber or abrasive materials significantly increase friction and wear, which will reduce the operational life of the die.
Feed Conditioning
Proper conditioning is non-negotiable for die longevity. Higher fat content acts as a natural lubricant, reducing friction. Conversely, poor moisture control makes material harder to extrude, leading to premature wear and blockages.
Particle Size Consistency
A consistent, fine particle size in the mash feed is essential. Large or inconsistent particles cause uneven pressure on the die face, leading to inefficient pelleting and accelerated, localized wear.
Operator Skill and Maintenance
A skilled operator is crucial. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning magnets to remove metal debris, checking roll shell wear, and ensuring uniform die wear by rotating it, can dramatically extend the life of your equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the scale of your operation and the nature of the materials you plan to process.
- If your primary focus is small-scale production or processing difficult, low-density biomass: A flat die mill is the superior choice, with roller-turned models providing higher power for demanding materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous industrial production: A ring die mill is the established industry standard, designed for maximum throughput and efficiency with more uniform feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan regardless of type: You must prioritize excellent feed conditioning, consistent particle size, and a rigorous daily maintenance schedule.
Ultimately, understanding these core designs empowers you to select the system that aligns perfectly with your operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Flat Die Pellet Mill | Ring Die Pellet Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Small-scale production, low-density biomass | High-volume, industrial production |
| Operation | Rollers press material through a flat plate | Ring spins; rollers press material outward |
| Capacity | Lower to Medium | High |
| Key Advantage | Effective for difficult, bulky materials | High efficiency and throughput |
Ready to choose the right pellet mill for your lab or production needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable pellet mills and expert support to ensure your process is efficient and cost-effective. Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ring Press Mold for Lab Applications
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
People Also Ask
- Are wood pellets made from sawdust? Unlock the Secret to High-Performance Fuel
- What are the two classifications of press machines? Single Punch vs. Rotary Presses Explained
- What are the different pill presses? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production Scale
- What is the purpose of a pellet mill die chamber? The Heart of High-Density Pellet Production
- What is the advantage of a single punch tablet machine? Ideal for Low-Waste R&D and Formulation Testing
- What are pill presses used for? Transforming Powders into Precise Tablets for Medicine, Supplements, and More
- How fast is the rotary tablet press? Unlock Peak Production Speeds for Your Tablets
- Which type of tablet press is more suitable for large scale production? Rotary Presses for High-Volume Efficiency



















