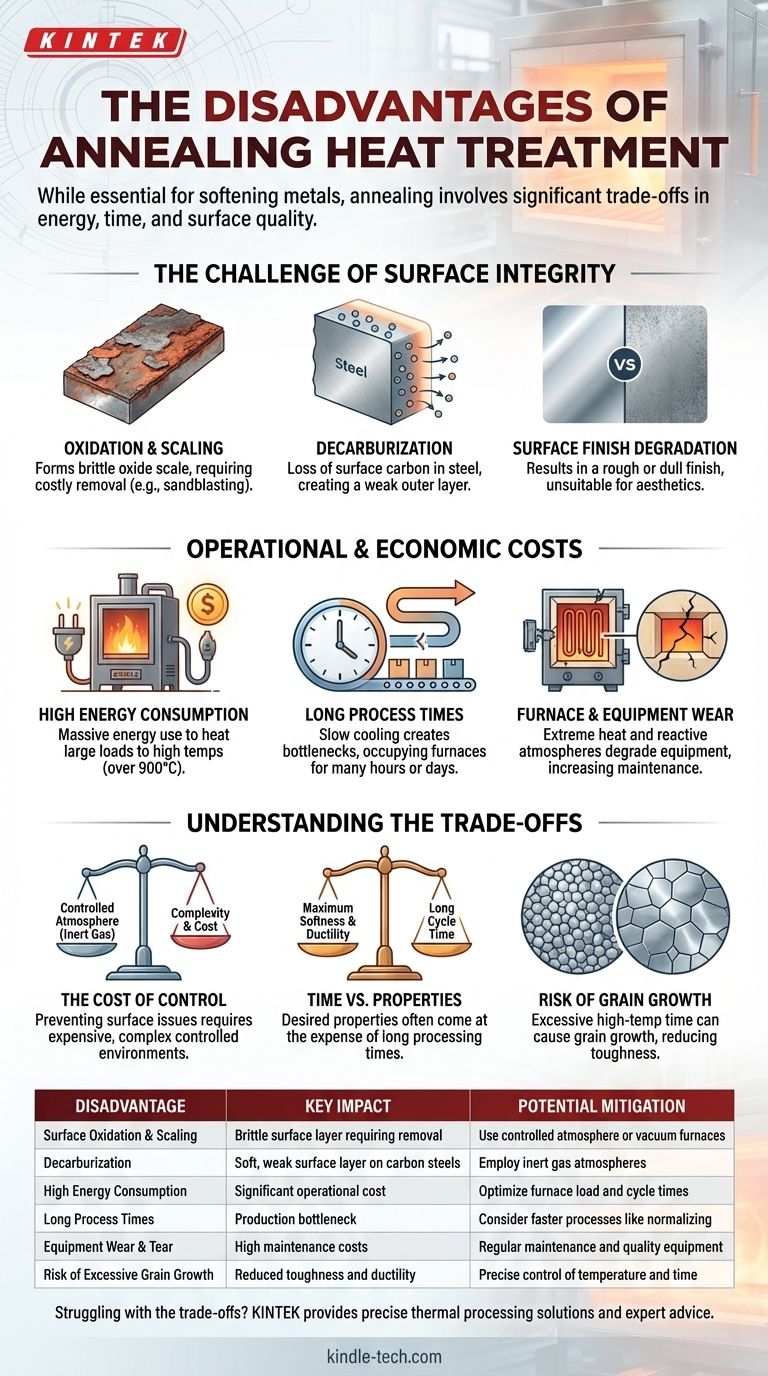
While an essential process for softening metals and relieving internal stresses, annealing is not without significant drawbacks. Its primary disadvantages revolve around high energy and time consumption, the potential for undesirable surface changes like oxidation and decarburization, and the operational costs and complexities of managing the heat treatment environment.
The disadvantages of annealing are not flaws in the process itself, but rather inherent trade-offs. The high cost in time and energy, along with the risk to surface integrity, are the price paid for achieving maximum ductility and softness in a material.

The Challenge of Surface Integrity
The high temperatures required for annealing create a reactive environment where the metal's surface can be easily altered, often for the worse.
Oxidation and Scaling
When heated in the presence of oxygen, most metals will form a layer of oxide scale on their surface. This brittle layer must often be removed through costly secondary processes like sandblasting or acid pickling, adding steps and expense to production.
Decarburization
For carbon steels, the high-temperature environment can cause carbon to diffuse out of the surface. This loss of carbon, known as decarburization, creates a soft, weak outer layer on the component, which can be detrimental to its final performance.
Surface Finish Degradation
Even if heavy scaling is avoided, the process can result in a rough, dull, or non-bright surface finish. This is often unacceptable for applications where aesthetics or a specific surface texture is required without further polishing.
Operational and Economic Costs
Annealing is often one of the most resource-intensive steps in a manufacturing process, impacting both budget and timeline.
High Energy Consumption
Bringing a large furnace and its entire workload up to a high temperature (often over 900°C or 1650°F) and holding it there for an extended period consumes a massive amount of energy, representing a significant operational cost.
Long Process Times
Proper annealing requires very slow, controlled cooling to achieve the desired microstructure. This means furnaces can be occupied for many hours, or even days, for a single batch, creating a bottleneck that slows down overall production throughput.
Furnace and Equipment Wear
The extreme temperatures and potentially reactive furnace atmospheres take a toll on equipment. Electric heating elements can erode, and refractory linings within the furnace will degrade over time, leading to high maintenance costs and downtime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of annealing are best understood as a series of trade-offs between desired properties, cost, and complexity.
The Cost of Control
Preventing the surface issues described above requires a controlled atmosphere. Using inert gases (like argon) or reducing gases to displace oxygen prevents oxidation and decarburization but adds significant complexity and cost related to gas management and furnace sealing.
Time vs. Properties
The long cycle time is a direct trade-off for achieving maximum softness, ductility, and stress relief. Faster heat treatment processes like normalizing or stress relieving exist, but they do not produce the same refined grain structure and level of softness as a full anneal.
The Risk of Grain Growth
Holding a metal at a high temperature for too long can cause its internal crystalline grains to grow excessively large. While the material will be very soft, large grains can significantly reduce its toughness and ductility, making it more brittle under impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process requires balancing the metallurgical goal with the practical realities of production.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and formability: Full annealing is the correct choice, but you must budget for the long cycle times and plan for potential post-process surface finishing.
- If your primary focus is cost and speed: Consider if a faster process like normalizing or a lower-temperature stress relief cycle can meet your minimum property requirements without the full expense of annealing.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a pristine surface: You must invest in a vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace, accepting the higher equipment and operational costs to avoid surface degradation.
By understanding these trade-offs, you can engineer a thermal process that delivers the necessary material properties while effectively managing costs and production time.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact | Potential Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Oxidation & Scaling | Brittle surface layer requiring costly removal | Use controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnaces |
| Decarburization | Soft, weak surface layer on carbon steels | Employ inert gas atmospheres |
| High Energy Consumption | Significant operational cost due to high temperatures | Optimize furnace load and cycle times |
| Long Process Times | Production bottleneck; slow controlled cooling | Consider faster processes like normalizing if suitable |
| Equipment Wear & Tear | High maintenance costs for furnace components | Regular maintenance and quality equipment investment |
| Risk of Excessive Grain Growth | Reduced toughness and ductility | Precise control of temperature and time |
Struggling with the trade-offs of annealing? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for precise thermal processing. Whether you need a reliable furnace for controlled atmosphere annealing or expert advice on selecting the right heat treatment process for your materials, our team is here to help. Contact us today to optimize your laboratory's efficiency and achieve your material property goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.



















