While highly efficient for specific applications, the primary disadvantages of the extrusion process are its high initial setup costs, its limitation to parts with a uniform cross-section, and the potential for dimensional variations in the final product. These factors make it a specialized process that is not suitable for all manufacturing needs.
Extrusion is an exceptional manufacturing method for high-volume production of continuous linear parts, but its core limitations are economic and geometric. The process is defined by its uniform profile, and its cost-effectiveness is only realized at scale.
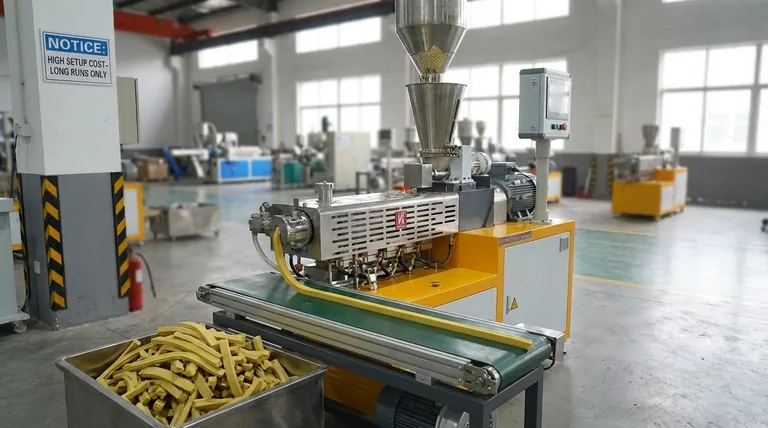

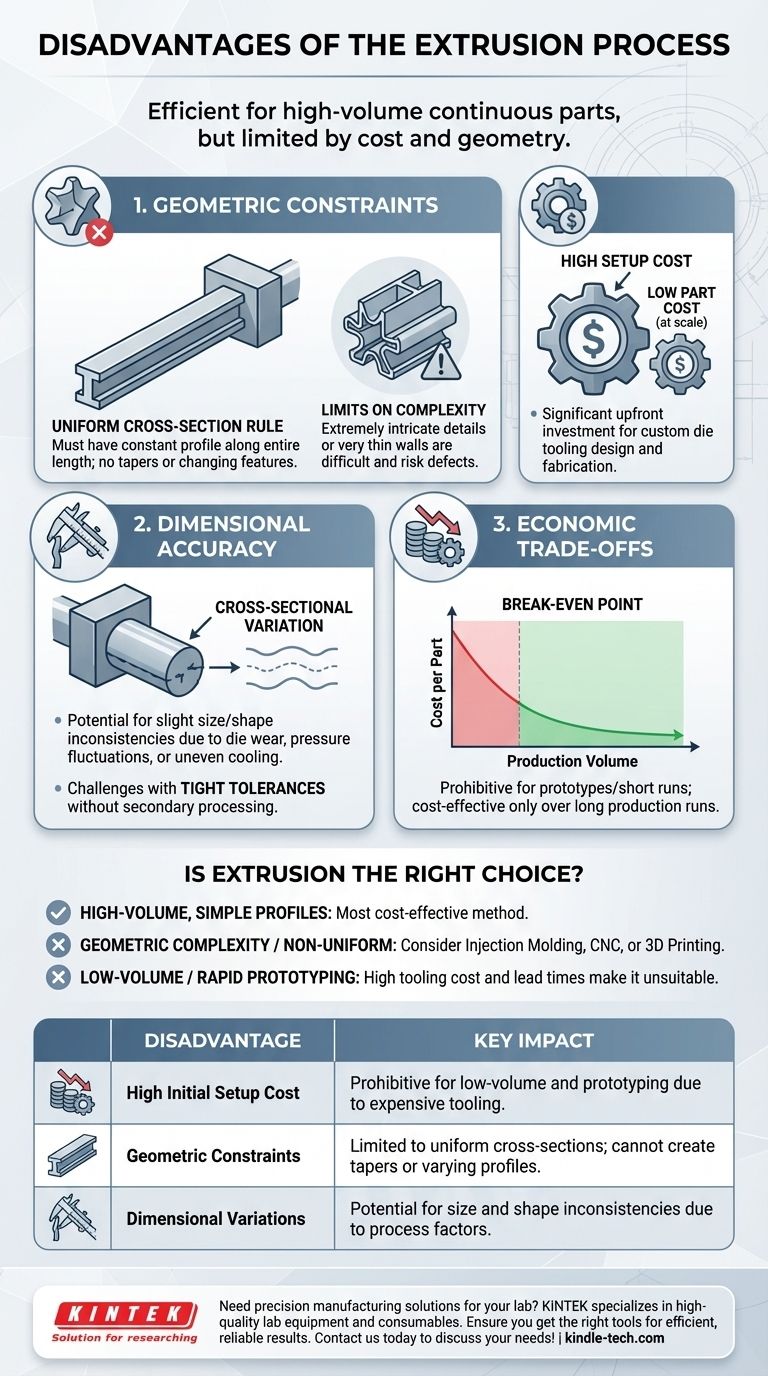
The Challenge of Geometric Constraints
The fundamental nature of extrusion—pushing material through a shaped die—creates inherent limitations on the geometry of the parts you can produce.
The Uniform Cross-Section Rule
The most significant limitation is that the cross-section of the extruded part must be the same along its entire length.
This means you cannot create parts with varying profiles, tapers, or features that change along the axis of the extrusion.
Limits on Product Complexity
While the cross-section itself can be complex, there are practical limits. Extremely intricate details or features with very thin walls can be difficult to extrude reliably and may lead to defects.
The Issue of Dimensional Accuracy
Achieving perfect dimensional stability can be a challenge in the extrusion process, requiring careful control of process variables.
Understanding Cross-Sectional Variation
Slight variations in the final product's size and shape can occur. This can be caused by die wear over long production runs, pressure fluctuations, or uneven cooling as the material exits the die.
These factors mean that extrusion may not be the ideal choice for components that demand exceptionally tight tolerances without secondary processing.
Understanding the Economic Trade-offs
The financial model for extrusion is heavily weighted toward high-volume production, making it unsuitable for small-scale projects.
High Initial Setup Cost
The primary economic drawback is the high initial cost for tooling. Creating a custom steel die is a specialized process that requires significant upfront investment in both design and fabrication.
The Break-Even Point
Because of the high tooling costs, extrusion only becomes cost-effective over long production runs. The cost per part drops significantly at high volumes, but for prototypes or short runs, the initial investment is prohibitive.
Is Extrusion the Right Choice for Your Project?
Evaluating these disadvantages against your specific goals will determine if extrusion is the correct manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a simple, continuous profile: Extrusion is likely the most cost-effective method available, and the initial setup cost will be easily justified.
- If your primary focus is geometric complexity or requires non-uniform shapes: You should immediately consider alternative processes like injection molding, CNC machining, or 3D printing.
- If your primary focus is low-volume runs or rapid prototyping: The high tooling cost and lead times of extrusion make it an unsuitable choice compared to more agile methods.
Understanding these core limitations is the key to leveraging extrusion's immense power for the right application.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Initial Setup Cost | Prohibitive for low-volume production and prototyping due to expensive custom die tooling. |
| Geometric Constraints | Limited to parts with a uniform cross-section; cannot create tapers or varying profiles. |
| Dimensional Variations | Potential for size and shape inconsistencies due to die wear, pressure changes, or uneven cooling. |
Need precision manufacturing solutions for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Whether your project requires extrusion or an alternative process, our expertise ensures you get the right tools for efficient, reliable results. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is the role of high-speed melt mixing equipment? Key to RPE/CSPE Thermoplastic Elastomer Synthesis
- What is the screw extrusion process? A Guide to Continuous Plastic Profiling
- What is the difference between extrusion and co-extrusion? Engineer Multi-Material Parts
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- How does extrusion work step by step? A Guide to the Continuous Manufacturing Process



















