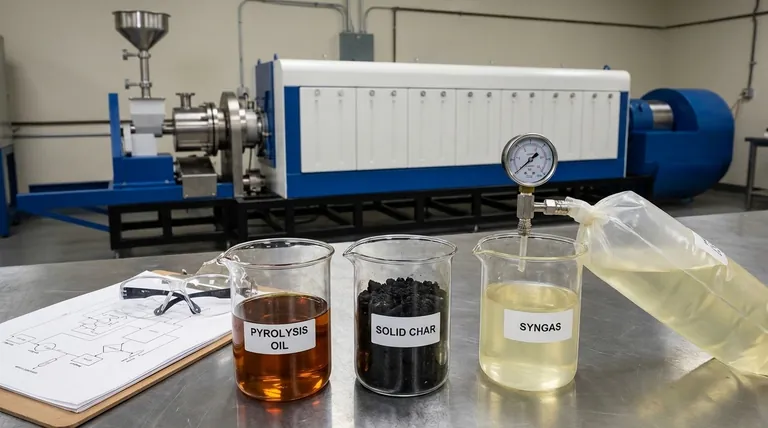
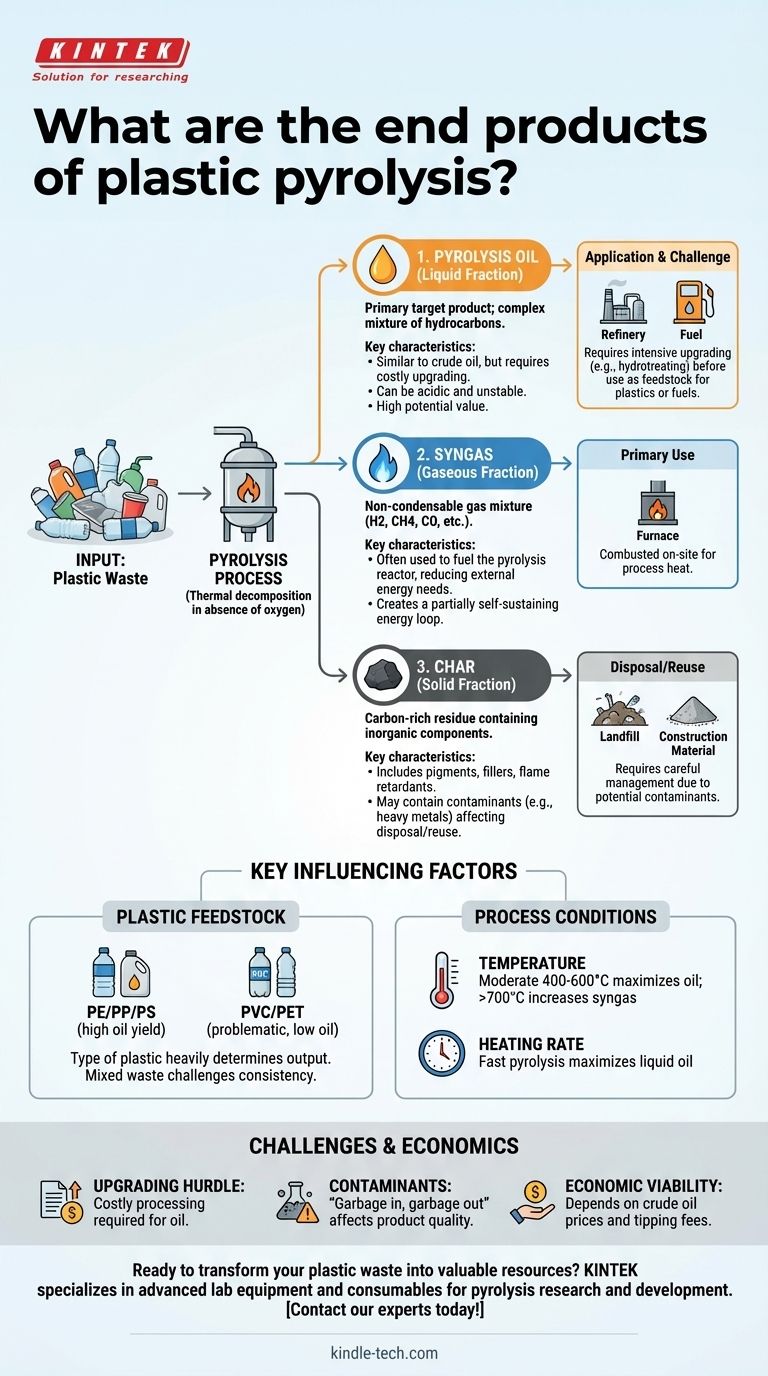
In short, plastic pyrolysis breaks down waste plastics into three primary products: a liquid pyrolysis oil (often called TPO, or tire-derived pyrolysis oil, when from tires), a non-condensable synthetic gas (syngas), and a solid carbon residue (char). The specific proportion and quality of these outputs are not fixed; they depend heavily on the type of plastic being processed and the specific conditions of the pyrolysis reaction.
While pyrolysis successfully converts plastic waste into marketable products, the central challenge is not in the conversion itself, but in the quality, consistency, and economic viability of the resulting outputs. The liquid oil, the most valuable product, is not a direct substitute for crude oil and requires significant, costly upgrading to be useful in traditional refineries.

A Detailed Look at the Pyrolysis Outputs
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. It breaks down long polymer chains in plastics into smaller, simpler molecules. Each of the three resulting fractions has distinct characteristics and potential uses.
The Liquid Fraction: Pyrolysis Oil
This is typically the primary target product, representing the highest potential value. It is a complex mixture of various hydrocarbon compounds.
Its composition is somewhat similar to conventional crude oil, but with critical differences. Raw pyrolysis oil is often acidic, contains oxygen, water, and contaminants like chlorine and nitrogen derived from the plastic feedstock. It can also be unstable, thickening over time.
The Gaseous Fraction: Synthetic Gas (Syngas)
This non-condensable gas is a mixture of hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and other light hydrocarbons.
The primary use for this syngas is to be combusted on-site to provide the energy needed to heat the pyrolysis reactor. This creates a partially self-sustaining energy loop, reducing the external energy requirements and operational costs of the facility.
The Solid Fraction: Char
The final product is a solid, carbon-rich residue known as char. This material also contains all the inorganic components from the original plastic waste.
These components include pigments, fillers, flame retardants, and other additives. As a result, the char can contain heavy metals and other contaminants, which dictates its potential for reuse or the requirements for its disposal.
Key Factors That Determine the End Products
The output of a pyrolysis unit is highly sensitive to both its inputs and its operational parameters. Understanding these variables is crucial to evaluating the technology's effectiveness.
The Critical Role of Plastic Feedstock
The type of plastic processed is the single most important factor. Common plastics like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS) yield a high percentage of liquid oil.
Conversely, other plastics are highly problematic. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) releases highly corrosive hydrochloric acid gas when heated, which can severely damage equipment. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), used in water bottles, yields very little oil and produces more char and gas.
This makes processing mixed municipal plastic waste a significant technical challenge, as the output quality becomes unpredictable and contaminants are always present.
The Influence of Process Conditions
Engineers can manipulate the process to favor certain outputs.
Temperature is a key lever. Moderate temperatures (400-600°C) tend to maximize the yield of liquid oil. Very high temperatures (>700°C) "crack" the molecules further, producing more syngas.
Heating rate also plays a role. "Fast pyrolysis," where the plastic is heated very quickly, is the standard method for maximizing liquid oil production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, pyrolysis is not a simple solution. The reality involves significant technical and economic hurdles that must be considered.
The "Upgrading" Hurdle for Pyrolysis Oil
The single greatest challenge is the quality of the pyrolysis oil. It cannot be pumped directly into a conventional oil refinery.
Before it can be used as a feedstock for new plastics or fuels, it must undergo an intensive and costly upgrading process, such as hydrotreating. This process uses hydrogen to remove contaminants (like chlorine, sulfur, and nitrogen) and stabilize the oil. This step adds significant expense and complexity to the overall system.
Contaminants and Consistency
The principle of "garbage in, garbage out" applies directly to pyrolysis. Any non-plastic contamination in the feedstock, such as food residue, paper, or dirt, will end up in the final products, primarily the char and oil.
This lack of consistency in the feedstock makes it difficult to produce a consistent, on-spec product, which is a major concern for potential buyers like refineries.
Economic Viability
The business case for plastic pyrolysis often hinges on the price of crude oil and the cost of waste disposal (tipping fees).
When oil prices are high and tipping fees are substantial, pyrolysis can be economically attractive. However, if the cost of upgrading the oil outweighs its market value, the entire process can quickly become unprofitable without subsidies.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your assessment of pyrolysis should depend entirely on your intended application for its outputs.
- If your primary focus is circularity (plastic-to-plastic): Recognize that the oil requires extensive upgrading and purification to become a suitable feedstock for creating new, virgin-equivalent plastics.
- If your primary focus is energy recovery (plastic-to-fuel): The raw oil and syngas can be used as industrial fuel, but the oil may require pre-treatment to be compatible with standard engines or boilers due to its acidity and contaminants.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is highly effective, but you must have a clear and environmentally sound plan for managing the solid char residue, which may be classified as a hazardous material.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis not as a simple recycling method but as a complex chemical conversion process with specific challenges and outputs is the key to its successful implementation.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil (Liquid) | Primary target product; a mix of hydrocarbons. | Similar to crude oil but requires costly upgrading; can be acidic and unstable. |
| Syngas (Gas) | Non-condensable gas mixture (H2, CH4, CO, etc.). | Often used to fuel the pyrolysis reactor, reducing external energy needs. |
| Char (Solid) | Carbon-rich residue containing inorganic additives. | May contain contaminants (e.g., heavy metals), affecting disposal/reuse options. |
Ready to transform your plastic waste into valuable resources? The pyrolysis process is complex, and the quality of your end products—oil, syngas, and char—depends on precise control and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focused on optimizing oil yield, analyzing syngas composition, or handling char residue, our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Let's build a sustainable solution for your laboratory needs together. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What is the impact of pyrolysis techniques on biochar characteristics application to soil? Tailor Biochar for Your Soil's Needs
- What is the theory of pyrolysis? A Guide to Thermal Decomposition for Waste and Energy Solutions
- What is a rotary kiln electric furnace? Achieve Superior Uniform Heating for Your Materials
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- How is heat supplied in pyrolysis? Choose the Right Heating Method for Your Process
- What are rotary kilns made of? A Guide to Durable Steel Shells and Refractory Linings
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature of regeneration? Optimize Your Desiccant System's Efficiency



















