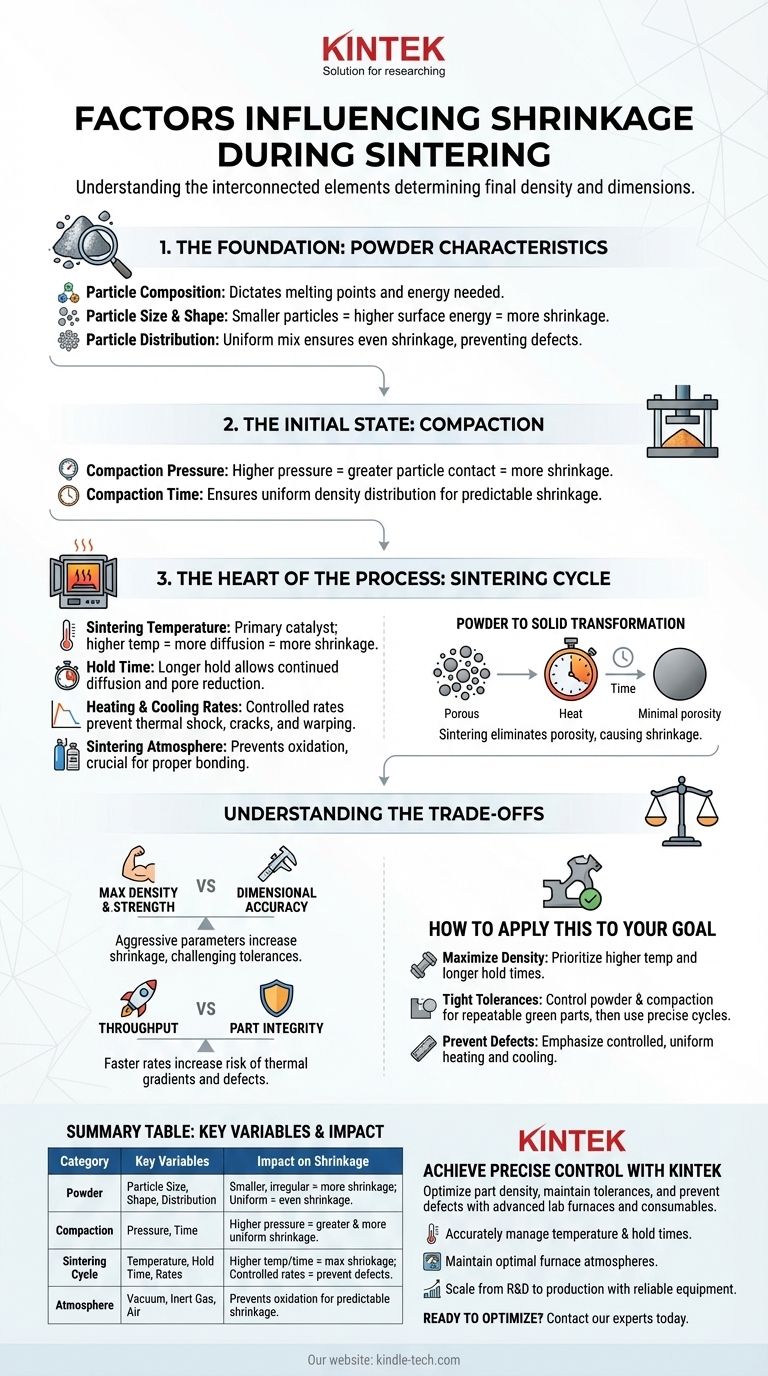
Several critical factors drive shrinkage during sintering. The process is fundamentally influenced by the characteristics of the raw powder, the initial compaction of the part, and the precise conditions of the thermal cycle, including temperature, time, and atmosphere. Each of these elements plays a distinct and interconnected role in determining the final density and dimensions of the component.
Sintering is not a simple heating process; it is a controlled atomic-level transformation. Understanding that shrinkage is a direct consequence of eliminating porosity allows you to manipulate the input variables—from particle size to heating rate—to achieve a predictable and desired outcome.
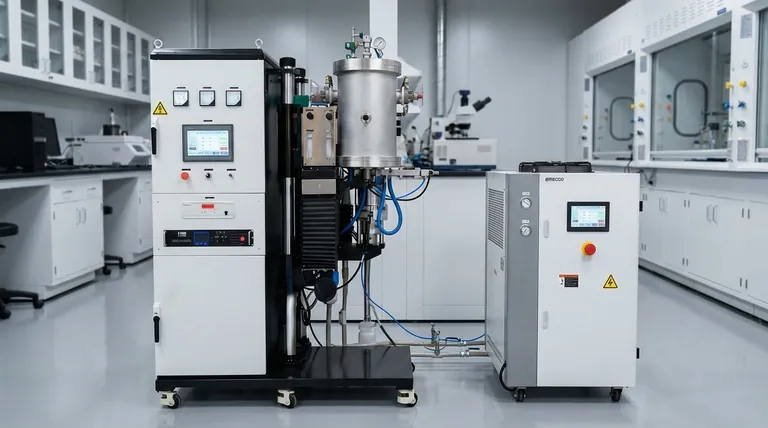

The Foundation: Powder Characteristics
The journey to a finished part begins with the raw material. The inherent properties of the powder establish the baseline for how the material will behave during sintering.
Particle Composition
The chemical makeup of the powder is the most fundamental factor. Different metals, alloys, or ceramics have unique melting points, diffusion rates, and thermal properties, all of which dictate the energy required to initiate and complete the sintering process.
Particle Size and Shape
Smaller particles possess a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. This high surface energy is a primary driving force for sintering, generally leading to faster and more significant shrinkage as the system seeks a lower energy state. Irregularly shaped particles can also increase inter-particle contact, further influencing densification.
Particle Distribution
A uniform distribution of particle sizes is critical for predictable results. A homogenous mix ensures that shrinkage occurs evenly throughout the part, preventing warping, internal stresses, or areas of inconsistent density.
The Initial State: The Role of Compaction
Compaction, or molding, creates the "green" part—the unsintered precursor. The density and integrity of this initial state directly impact the subsequent sintering stage.
Compaction Pressure
Higher compaction pressure forces particles closer together, increasing the initial density of the green part. This enhanced particle-to-particle contact facilitates the atomic diffusion that drives densification, directly influencing the rate and extent of shrinkage.
Compaction Time
While secondary to pressure, the duration of compaction helps ensure that density is distributed evenly throughout the part. This uniformity is essential for predictable shrinkage during the heating phase.
The Heart of the Process: The Sintering Cycle
The thermal cycle is where the transformation from a compacted powder to a solid object occurs. Every variable in this stage must be precisely controlled.
Sintering Temperature
Temperature is the primary catalyst for sintering. Higher temperatures provide the thermal energy required for atoms to diffuse across particle boundaries, filling the voids (pores) between them and causing the part to shrink and densify.
Hold Time
The duration the part is held at the peak sintering temperature is critical. A longer hold time allows the diffusion process to continue for longer, resulting in greater pore reduction and, consequently, more shrinkage. For example, increasing hold time from 30 to 60 minutes can reduce pore size by as much as 25%.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The speed at which the part is heated (ramp-up) and cooled affects the uniformity of the process. A controlled, steady rate prevents thermal shock and ensures the entire part shrinks consistently, minimizing the risk of cracks or warping.
Sintering Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace—whether vacuum, inert gas like argon, or air—is crucial. It prevents undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation, which can inhibit the bonding between particles and negatively affect the final properties of the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing the sintering process always involves balancing competing objectives. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for effective process control.
Strength vs. Dimensional Accuracy
Achieving maximum density and mechanical strength often requires aggressive sintering parameters (high temperature, long hold times). However, this also causes the most significant shrinkage, which can make holding tight dimensional tolerances a challenge.
Throughput vs. Part Integrity
Faster heating and cooling rates can increase production throughput. This speed, however, increases the risk of thermal gradients within the part, which can lead to non-uniform shrinkage, internal stresses, and potential defects.
Eliminating Porosity
Shrinkage is the physical manifestation of reducing or eliminating porosity. The variables that increase shrinkage, such as higher temperatures and longer hold times, are the same ones used to create a fully dense part. Conversely, if some level of porosity is desired, these parameters must be carefully limited.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your specific objective determines which factors you should prioritize.
- If your primary focus is maximizing part density and strength: Prioritize higher sintering temperatures and longer hold times to drive the diffusion process as close to completion as possible.
- If your primary focus is achieving tight dimensional tolerances: Meticulously control powder characteristics and compaction pressure to create a highly repeatable "green" part, then use a precisely controlled thermal cycle.
- If your primary focus is preventing defects like warping or cracking: Emphasize controlled, uniform heating and cooling rates to minimize internal stresses throughout the component.
Mastering these interconnected variables is the key to transforming raw powder into a high-performance, precision-engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Variables | Impact on Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Characteristics | Particle Size, Shape, Distribution | Smaller, irregular particles increase shrinkage; uniform distribution ensures even shrinkage. |
| Compaction (Green Part) | Compaction Pressure, Time | Higher pressure increases particle contact, facilitating greater and more uniform shrinkage. |
| Sintering Cycle | Temperature, Hold Time, Heating/Cooling Rate | Higher temperature and longer hold time maximize shrinkage; controlled rates prevent defects. |
| Atmosphere | Vacuum, Inert Gas, Air | Prevents oxidation, ensuring proper bonding and predictable shrinkage. |
Achieve precise control over sintering shrinkage and optimize your part density with KINTEK.
Understanding the complex interplay of powder properties, compaction, and thermal cycles is essential for producing high-quality, dimensionally accurate sintered components. Whether your goal is maximizing strength, holding tight tolerances, or preventing defects, the right laboratory equipment is critical for repeatable results.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and consumables designed for precise sintering control. Our solutions help you:
- Accurately manage temperature profiles and hold times for consistent shrinkage.
- Maintain optimal furnace atmospheres to ensure proper material bonding.
- Scale from R&D to production with reliable, high-performance equipment.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Do you quench after annealing? Understand the Critical Role of Cooling Rate
- What role do high-temperature furnaces play in ternary alloy phase equilibrium? Precision Tools for Stable Diffusion
- What is the VAR melting process? The Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting
- Is brazing cheaper than welding? Optimize Your Metal Joining Costs for Production
- Can you braze while in a vacuum? Achieve Flawless, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- How do high-precision laboratory furnaces ensure the validity of experiments in nuclear simulation? ±1 K Stability
- Is vacuum casting better than centrifugal? Choose the Right Process for Your Project
- What are the damages of carburization? Prevent Catastrophic Metal Failure in Your Equipment



















