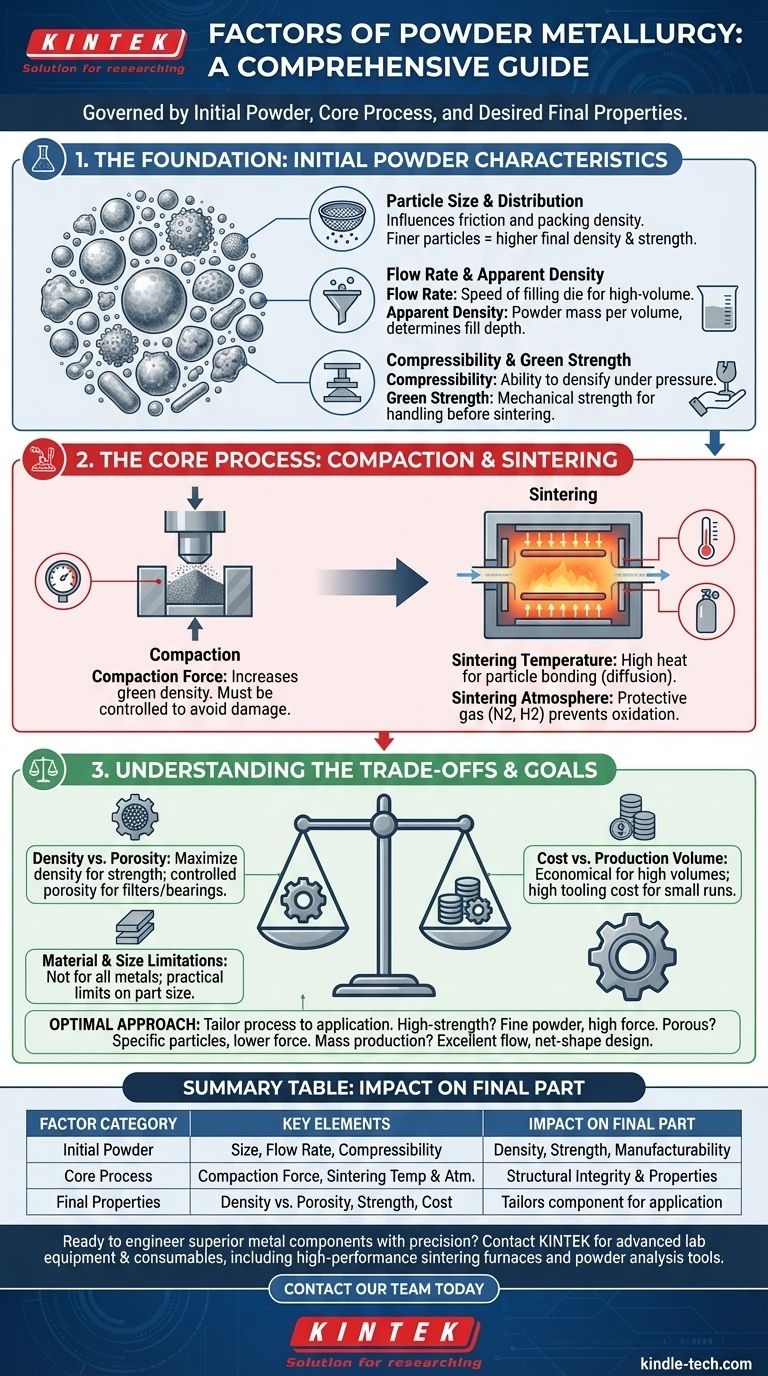
In essence, powder metallurgy is governed by three primary categories of factors: the characteristics of the initial metal powder, the parameters of the core manufacturing process, and the desired properties of the final product. The success of any powder metallurgy application hinges on the precise control and interplay of these elements, from the flow rate of the raw powder to the temperature and atmosphere within the sintering furnace.
The critical takeaway is that powder metallurgy is not a single technique but a system. The properties of the final component are directly determined by the quality of the starting powder and the precise control of the compaction and sintering processes. Mastering this relationship is the key to unlocking its potential.

The Foundation: Initial Powder Characteristics
The entire powder metallurgy (PM) process begins with the powder itself. The physical and chemical properties of these particles are the fundamental building blocks that dictate how the material will behave during manufacturing and its ultimate performance.
Particle Size and Distribution
The size and shape of the individual metal particles are paramount. They directly influence friction between particles, which affects how densely the powder can be packed.
Finer particles generally lead to a higher final density and strength, while a specific distribution is often engineered to achieve optimal packing.
Flow Rate and Apparent Density
Flow rate measures how quickly a powder can fill a die cavity. A consistent and rapid flow is critical for high-volume, automated production to ensure each part is uniform.
Apparent density is the mass of the powder per unit volume in its loose state. This factor helps determine the necessary "fill depth" in the die to achieve the target compacted density.
Compressibility and Green Strength
Compressibility is the powder's ability to be densified under pressure. A highly compressible powder allows for the creation of a dense part with lower compaction forces.
After compaction but before sintering, the part is known as a "green compact." Green strength is the mechanical strength of this fragile compact, which must be sufficient to allow for handling and transfer to the sintering furnace without breaking.
The Core Process: Compaction and Sintering
Once the powder is selected, it moves into the manufacturing stages. The control exerted during these steps transforms the loose powder into a solid, functional component.
Compaction Force
This is the pressure applied to the powder within the die to form the green compact. Higher compaction forces reduce the space between particles, increasing the green density of the part.
The force must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired density without damaging the tooling or introducing stress fractures into the compact.
Sintering Temperature
Sintering is a heat treatment where the green compact is heated in a furnace to a temperature below the melting point of the primary metal.
This high temperature provides the energy for the particles to bond together, a process called diffusion, which gives the part its final strength and integrity. Ultra-high-temperature furnaces are often required for this critical step.
Sintering Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the sintering furnace is a crucial process factor. It must be carefully controlled to prevent oxidation of the metal particles at high temperatures.
Protective or reactive gases, such as nitrogen or hydrogen mixtures, are used to remove contaminants and facilitate the bonding between particles, especially for materials like magnetic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Powder metallurgy is a powerful technology, but its application involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for successful part design and production.
Density vs. Porosity
The most fundamental trade-off in PM is between density and porosity. For high-strength structural parts, the goal is to maximize density and eliminate pores.
However, for other applications, controlled porosity is the desired outcome. Products like porous, oil-impregnated bearings and sintered metal filters are designed specifically to have a network of interconnected voids.
Cost vs. Production Volume
Powder metallurgy excels at producing complex, net-shape parts in high volumes with minimal material waste. This makes it extremely cost-effective for mass production.
The initial cost of tooling (the dies and punches) can be significant, however. This makes PM less economical for very small production runs or one-off prototypes.
Material and Size Limitations
While versatile, PM is not suitable for all materials. Certain metals with low compressibility or high reactivity can be challenging to process.
Furthermore, there are practical limits on part size. Extremely large or heavy components are difficult to produce due to the immense compaction forces and furnace sizes required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal approach to powder metallurgy depends entirely on the intended application of the final component.
- If your primary focus is high-strength structural parts: Prioritize fine, highly compressible powders and use high compaction forces with a precisely controlled sintering cycle to maximize final density.
- If your primary focus is creating porous components (like filters or bearings): Carefully select particle size and shape and use lower compaction forces to achieve a specific, controlled level of porosity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex shapes: Optimize for powders with excellent flow rates to enable high-speed manufacturing and design parts that fully leverage PM's net-shape capabilities.
By understanding and controlling these key factors, you can engineer materials and components with unique properties tailored to nearly any application.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Elements | Impact on Final Part |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Powder | Particle Size, Flow Rate, Compressibility | Determines density, strength, and manufacturability |
| Core Process | Compaction Force, Sintering Temperature & Atmosphere | Defines final structural integrity and properties |
| Final Properties | Density vs. Porosity, Strength, Cost | Tailors the component for its specific application |
Ready to engineer superior metal components with precision?
The factors of powder metallurgy are complex, but mastering them is the key to creating high-performance, cost-effective parts. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables—including high-performance sintering furnaces and powder analysis tools—that your laboratory needs to control every variable and achieve exceptional results.
Let our expertise support your innovation. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solutions for your powder metallurgy challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- How does a magnetron sputtering work? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification



















