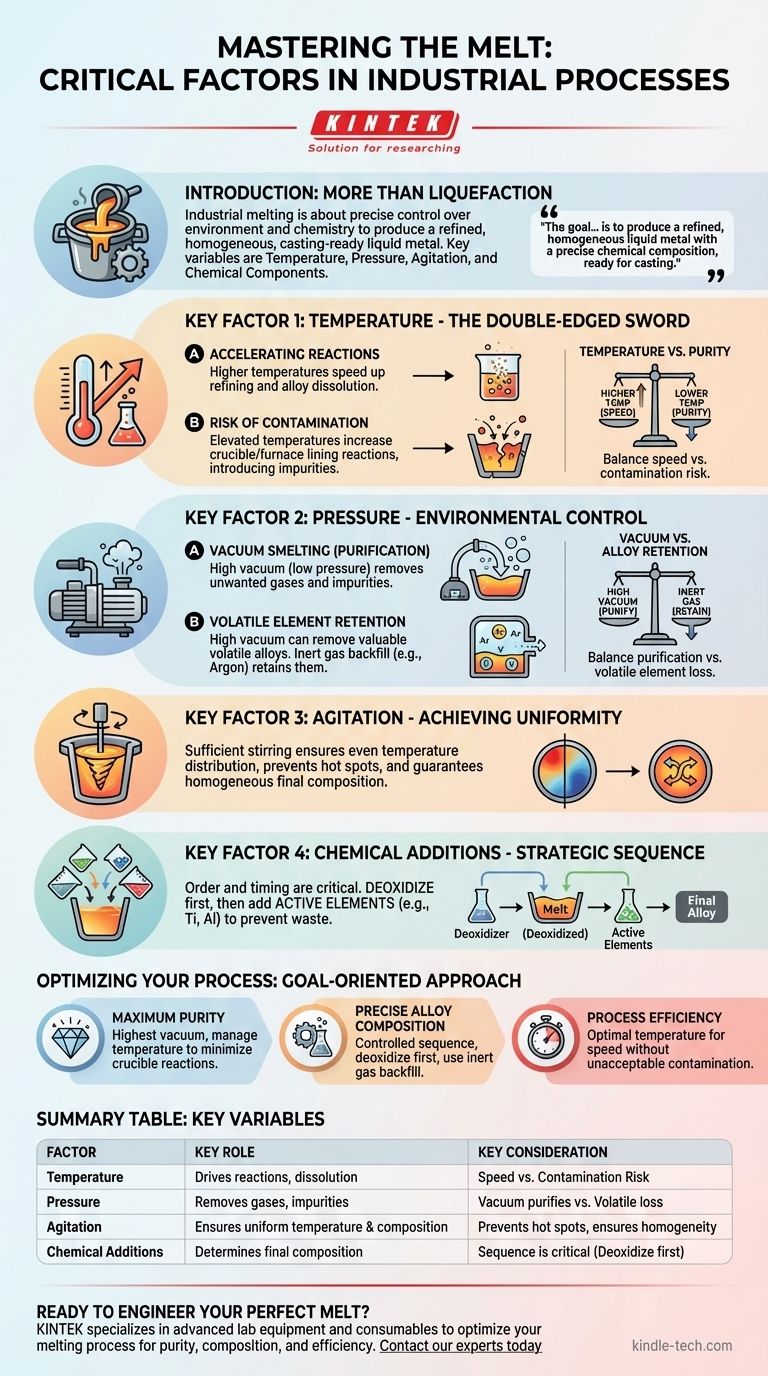
In a controlled melting process, the critical factors are not just about reaching a certain temperature, but about precisely managing the molten material's environment and chemistry. The key variables that affect the outcome are temperature, pressure, physical agitation, and the strategic addition of chemical components. Mastering these allows you to control the purity, homogeneity, and final composition of the melt.
The goal of industrial melting is rarely just to create a liquid. It is to produce a refined, homogenous liquid metal with a precise chemical composition, ready for casting. This requires balancing competing factors like temperature and pressure to facilitate desired reactions while preventing contamination and the loss of valuable elements.

The Role of Temperature in Refining
Temperature is the primary driver of the melting process, but its effects are more complex than simply turning a solid into a liquid. It acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions within the melt.
Accelerating Metallurgical Reactions
Higher temperatures increase the rate of desired reactions. This can speed up the refining process, allowing impurities to be removed more quickly and helping alloying elements dissolve into the molten pool efficiently.
The Risk of Contamination
However, elevated temperatures are a double-edged sword. They also accelerate unwanted reactions, particularly between the molten metal and the crucible or furnace lining. This can introduce contaminants like oxygen, compromising the purity of the final product.
Controlling the Environment with Pressure
The pressure of the atmosphere above the melt is a powerful tool for purification. In many advanced applications, this involves creating a strong vacuum.
The Power of Vacuum Smelting
Operating under a high vacuum (low pressure) helps pull unwanted dissolved gases, like hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the molten metal. It also helps remove impurities that have a higher vapor pressure than the base metal, causing them to essentially boil off and be extracted.
Protecting Volatile Elements
A vacuum is not always the answer. If you are creating an alloy with volatile elements (those that evaporate easily), a high vacuum will pull them out of the melt along with the impurities. To prevent this loss, the process is often backfilled with an inert gas, like argon, to raise the pressure and keep these valuable elements in the solution.
Achieving Homogeneity and Composition
A molten pool can suffer from variations in temperature and chemical makeup. Ensuring the final product is uniform requires managing both physical mixing and the chemical state of the melt.
The Importance of Stirring
Sufficient stirring or agitation of the molten pool is essential. It ensures that temperature is distributed evenly, prevents hot spots, and guarantees that any added alloying elements are mixed thoroughly for a perfectly uniform composition.
The Strategic Sequence of Alloying
The order and timing of additions are critical. For instance, active alloying components that react strongly with oxygen (like titanium or aluminum) should only be added after the melt has been fully deoxidized. Adding them too early would cause them to be consumed in reactions with oxygen, wasting the material and failing to achieve the desired final chemistry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a melting process is an exercise in balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" setting, only the best setting for a specific goal.
Temperature vs. Purity
The central trade-off is speed versus quality. A higher temperature accelerates the process but increases the risk of contamination from the crucible. A lower temperature protects purity but extends the time required for refining.
Vacuum vs. Alloy Retention
A high vacuum is excellent for removing gaseous impurities but can lead to the loss of valuable volatile alloying elements. You must balance the need for purification against the need to maintain the target composition, often using an inert gas backfill as a compromise.
Optimizing Your Melting Process
Your approach should be dictated by the primary goal for your material. Each objective requires a different balance of the core factors.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Emphasize achieving the highest possible vacuum and carefully managing temperature to minimize reactions with the crucible.
- If your primary focus is a precise alloy composition: Stress the importance of a controlled sequence of additions, performing deoxidation first, and using an inert gas atmosphere to retain volatile elements.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Prioritize finding the optimal temperature that accelerates reactions without introducing unacceptable levels of contamination, thereby minimizing furnace time.
By understanding how these variables interact, you can move from simply melting metal to engineering a material with predictable, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Role in Melting | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Drives refining reactions and alloy dissolution. | Higher temps speed up the process but increase contamination risk. |
| Pressure | Removes dissolved gases and volatile impurities. | A vacuum purifies but can also remove valuable volatile alloying elements. |
| Agitation | Ensures uniform temperature and chemical composition. | Prevents hot spots and guarantees a homogenous final product. |
| Chemical Additions | Determines the final alloy composition. | Sequence is critical; deoxidize before adding active elements like titanium. |
Ready to Engineer Your Perfect Melt?
Achieving precise control over temperature, pressure, and chemistry is key to producing high-purity, homogenous metals. The right lab equipment is fundamental to mastering this balance.
KINTEK specializes in the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to optimize your melting process. Whether your goal is maximum purity, precise alloy composition, or improved efficiency, we have the solutions to help you succeed.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the high temperature of a muffle furnace? From 1100°C to 1700°C+ for Your Lab Needs
- What is the structure of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What are the materials used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Durable Construction & Optimal Performance
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model



















