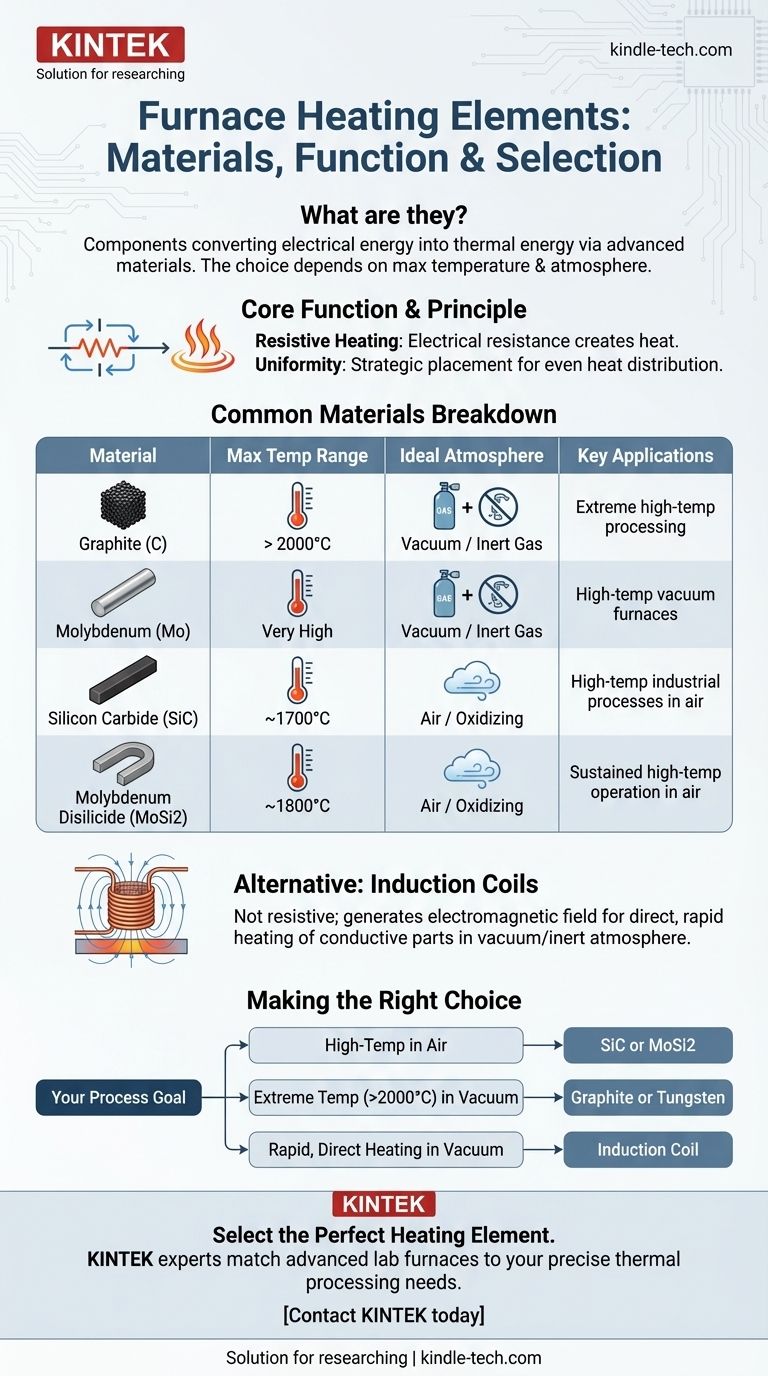
In a furnace, the heating element is the component responsible for converting electrical energy into thermal energy. These elements are typically made from a select group of advanced materials chosen for their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and specific atmospheric conditions. Common materials include graphite, molybdenum, silicon carbide, and molybdenum disilicide, as well as metallic wires and induction coils.
The specific material used for a furnace's heating element is a critical engineering decision. It is dictated not by preference, but by the required maximum operating temperature and the chemical environment inside the furnace chamber.

The Core Function of a Heating Element
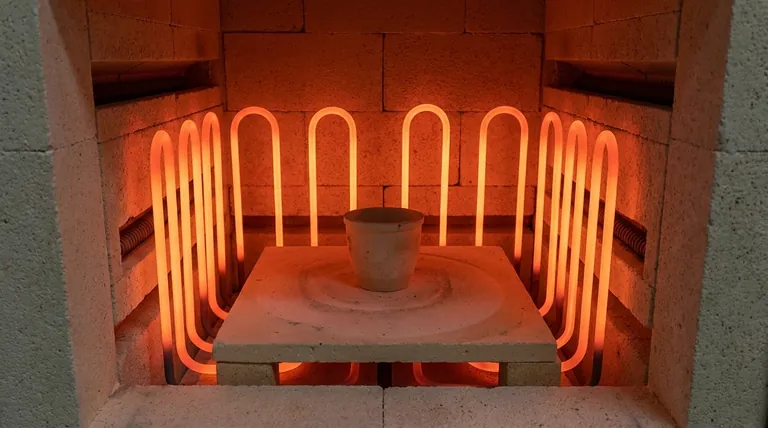
A heating element's job is to get hot when electricity passes through it and then transfer that heat to the furnace chamber and the workload inside. The effectiveness of this process depends on the element's material and its physical design.
The Principle of Resistive Heating
Most furnace heating elements work on the principle of electrical resistance. When an electric current is forced through a material with high resistance, the electrical energy is converted into heat.
Materials like molybdenum, graphite, and silicon carbide are excellent for this purpose because they can maintain their structural integrity and high resistance at incredibly high temperatures.
The Goal: Uniform Heat Distribution
The placement of heating elements is just as important as their material. In high-performance furnaces, elements are often located on multiple sides of the heating chamber.
This strategic placement ensures that heat radiates evenly, creating excellent thermal uniformity and preventing hot or cold spots that could compromise the process.
A Breakdown of Common Heating Element Materials
The choice of element is primarily driven by the process requirements, particularly temperature and atmosphere. Elements can be grouped into several key categories.
Metallic Elements (Molybdenum & Tungsten)
Elements made from pure metals like molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W) are used for very high-temperature applications, often in the form of wires, rods, or strips.
Their key limitation is that they oxidize rapidly in the presence of air at high temperatures. Therefore, they are almost exclusively used in vacuum furnaces or furnaces with a controlled, inert gas atmosphere.
Ceramic & Composite Elements (SiC & MoSi2)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are advanced ceramic-based materials that excel at high-temperature operation.
Unlike pure metals, their primary advantage is the ability to operate at sustained high temperatures (up to 1700°C or higher) in an air atmosphere. This makes them ideal for many industrial processes that do not require a vacuum.
Graphite Elements
For the highest possible temperatures, often exceeding 2200°C, graphite is the material of choice. It is lightweight, has excellent thermal properties, and is relatively cost-effective for its performance.
Like molybdenum, graphite must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent it from burning away (oxidizing) at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves balancing performance, lifespan, and operating conditions. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific application.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the most critical factor. The maximum process temperature you need to achieve will immediately eliminate certain materials from consideration. Graphite and tungsten are for the highest end, while MoSi2 and SiC cover the high-temperature air-atmosphere range.
Furnace Atmosphere
The second critical factor is the atmosphere inside the furnace. If your process runs in open air, you must use an element resistant to oxidation, like Silicon Carbide or Molybdenum Disilicide. If you are running in a vacuum or with inert gas, your options expand to include Molybdenum and Graphite.
An Alternative: Induction Coils
It is important to distinguish induction coils from resistive heating elements. An induction coil does not get hot itself.
Instead, it generates a powerful electromagnetic field. When a conductive workpiece is placed within this field, the field induces an electric current inside the workpiece itself, causing it to heat up directly and rapidly. This is a fundamentally different heating method, not a resistive element material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process requirements will point directly to the ideal heating element technology.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in an air atmosphere: Your best options are Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 2000°C) in a vacuum: You will need to use Graphite or, in some cases, Tungsten elements.
- If your primary focus is rapid, direct heating of a conductive part in a vacuum or controlled atmosphere: An induction coil system is the most appropriate technology.
Understanding these core material properties and their constraints is the key to selecting or specifying the right furnace for your technical goals.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp Range | Ideal Atmosphere | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | > 2000°C | Vacuum / Inert Gas | Extreme high-temperature processing |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Very High | Vacuum / Inert Gas | High-temp vacuum furnaces |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to ~1700°C | Air / Oxidizing | High-temp industrial processes in air |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to ~1800°C | Air / Oxidizing | Sustained high-temp operation in air |
Select the Perfect Heating Element for Your Application
Choosing the right heating element is critical to your process success, impacting temperature uniformity, efficiency, and equipment lifespan. The experts at KINTEK specialize in matching advanced lab equipment, including high-performance furnaces, to your specific technical requirements—whether you need to operate in air, a vacuum, or an inert atmosphere.
We provide solutions for laboratories requiring precise thermal processing. Let us help you optimize your results.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation on your furnace needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the melting point of tungsten in a vacuum? The Real Limit is Sublimation, Not Melting
- Why are separate thermocouples required for magnesium vacuum sublimation? Ensure Precision & Protect Your Equipment
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Is tungsten used in heating elements? Unlocking Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- What is the operating principle of a resistance wire heater? Insights into Joule Heating and Precise Thermal Control
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- Which is better quartz or ceramic heating element? Choose the Right Heat for Your Application
- What is the difference between induction and resistance heating? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source



















