Relying solely on a substance's melting point for identification is a fundamentally flawed approach. While it is an essential characteristic, it is not a unique fingerprint. The primary limitations are that many different compounds can share the same melting point, and the presence of even minor impurities can significantly alter the measurement, leading to incorrect conclusions.
A substance's melting point is a necessary but not sufficient piece of evidence for its identification. Think of it as a powerful tool for confirming a hypothesis or assessing purity, but a weak tool for discovering an unknown identity from scratch.

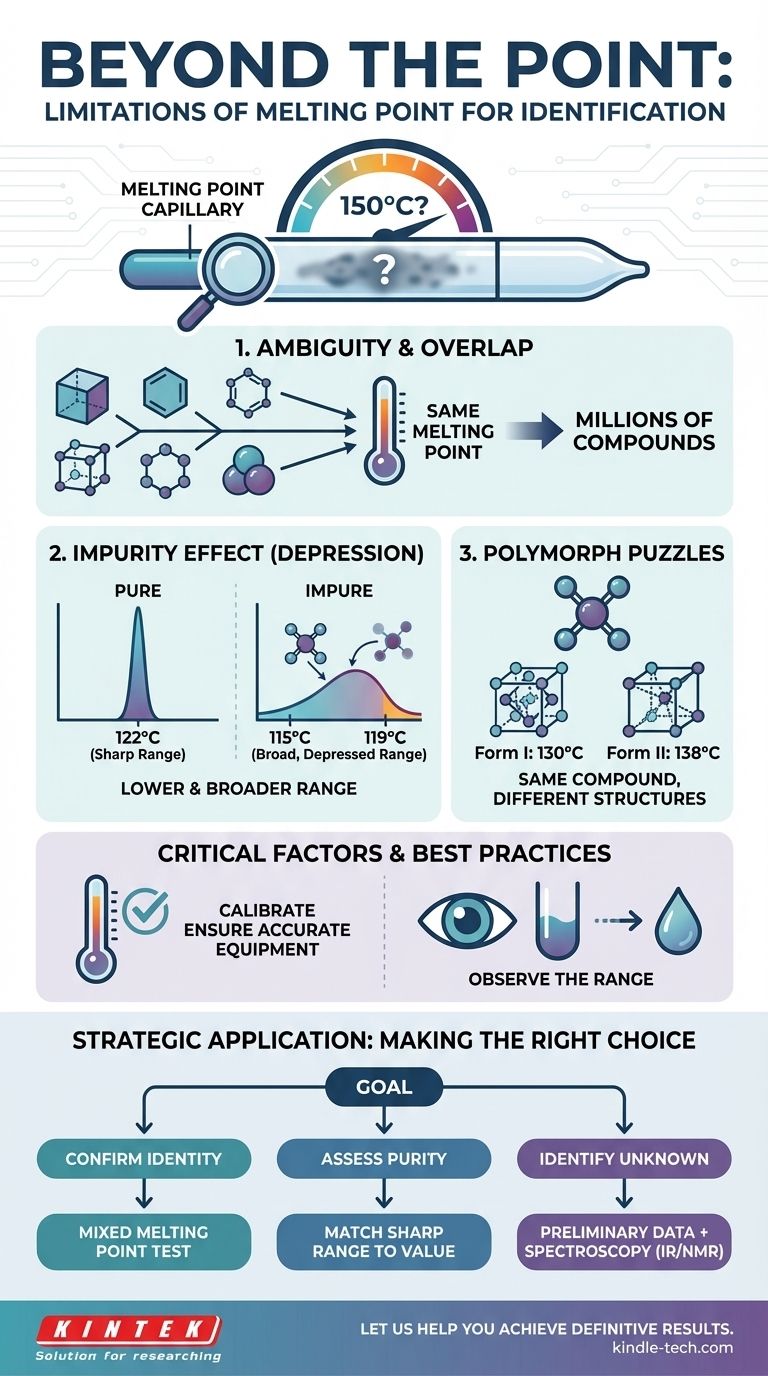
Why a Single Temperature Isn't Enough
The idea that a single number can definitively identify a sample is tempting, but the physical reality is more complex. Several factors can either mislead you or obscure the true identity of your compound.
The Problem of Overlapping Melting Points
The most significant limitation is ambiguity. There are millions of known chemical compounds, but they all melt within a relatively narrow temperature range.
Consequently, it is extremely common for two completely different substances to have identical, or nearly identical, melting points. For example, you might have an unknown white powder that melts sharply at 150°C, but dozens of compounds could fit that description.
The Influence of Impurities
The purity of your sample has a dramatic effect on its melting behavior. This phenomenon, known as melting point depression, is a core principle in chemistry.
When an impurity is present, two things happen: the melting point lowers, and the melting range broadens. An impure sample of Compound A, which should melt at 122°C, might begin to melt at 115°C and not become fully liquid until 119°C. This result could easily be mistaken for a pure sample of a completely different Compound B.
The Challenge of Polymorphs
Polymorphs are different crystalline structures of the same exact compound. Because melting involves breaking down a crystal lattice, different lattice arrangements can require different amounts of energy to disrupt.
This means a single compound can exhibit multiple, distinct melting points depending on its crystalline form. This is a common challenge in pharmaceutical and materials science, where the crystal structure is as important as the chemical formula.
The Critical Role of Calibration and Observation
The limitations aren't just theoretical; they are also practical. The quality of your data depends entirely on the accuracy of your equipment and the rigor of your observation.
Is Your Equipment Accurate?
An uncalibrated thermometer or melting point apparatus will produce useless data. As a guiding principle, a measurement system is only as reliable as its verification.
Just as a high-end furnace requires calibration at multiple temperatures to ensure accuracy across its full operating range, a scientific thermometer must be verified against known standards. Relying on a single calibration point can introduce errors at different parts of the temperature scale.
Observing the Melt: Range vs. Point
A critical piece of data is not just the final temperature, but the melting range. This is the span from when the first drop of liquid appears to when the last crystal melts.
A pure substance typically melts over a very sharp, narrow range (often less than 2°C). In contrast, an impure substance melts gradually over a broad range. This observation of how it melts is often more informative than the number itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Melting point analysis is not a useless technique; its power lies in its proper application. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses is key to using it effectively.
Strength: Confirming a Suspected Identity
If you have a strong reason to believe your unknown is Compound X, melting point is an excellent confirmation tool. If your sample melts sharply at the literature value for Compound X, it provides strong evidence that your suspicion is correct.
Strength: Assessing Purity
This is where the technique truly shines. A sharp melting range that matches the established value for a pure compound is a reliable indicator of high purity. Conversely, a depressed and broad melting range is a clear sign that impurities are present and purification is needed.
Weakness: Initial Discovery
Melting point is a poor tool for identifying a complete unknown from a vast pool of possibilities. The high probability of overlapping melting points makes it a guessing game at best. It should be used to narrow down possibilities, not to pinpoint an answer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To move from a guess to a definitive conclusion, you must combine melting point analysis with other techniques. Your strategy should change based on your objective.
- If your primary focus is confirming a suspected identity: Perform a mixed melting point test. Grinding your unknown with a pure sample of the suspected compound should result in no change to the melting point if they are identical.
- If your primary focus is assessing purity: A sharp melting range matching the literature value confirms high purity. A broad, depressed range indicates impurities are present.
- If your primary focus is identifying a complete unknown: Use melting point as a preliminary data point, then employ more definitive spectroscopic methods (like IR or NMR) to determine the compound's actual structure.
Ultimately, confident chemical analysis comes not from a single measurement, but from the convergence of multiple, independent lines of evidence.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Overlapping Melting Points | Many different compounds share the same melting temperature, leading to ambiguity. |
| Impurity Influence (Depression) | Lowers the melting point and broadens the range, obscuring the true compound identity. |
| Polymorphs | The same compound can have different melting points based on its crystal structure. |
| Equipment Calibration | Inaccurate thermometers or uncalibrated apparatus produce unreliable data. |
Ensure Accurate and Reliable Sample Analysis
While melting point is a valuable tool for confirming identity and assessing purity, it is not a definitive identification method on its own. Confident analysis requires a combination of techniques and reliable equipment.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the precise melting point apparatus, calibration standards, and support you need to integrate this technique effectively into your workflow.
Let us help you achieve definitive results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is heat treatment in simple terms? A Guide to Transforming Material Properties
- How does heat treatment affect microstructure? Mastering the Balance Between Hardness and Toughness
- What is the process of physical vapor deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Coating
- Why are vacuum pumps and pressure control systems necessary in an USP setup? Achieve High-Purity Powder Synthesis
- How hot can metal get? From Melting Points to Plasma Temperatures
- What is the mechanism of spark plasma sintering? Unlock Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- Why is the use of a high-temperature drying oven necessary for aluminum sludge recycling? Ensure Data Precision
- Which is better upflow or downflow furnace? The right choice depends on your home's layout.



















