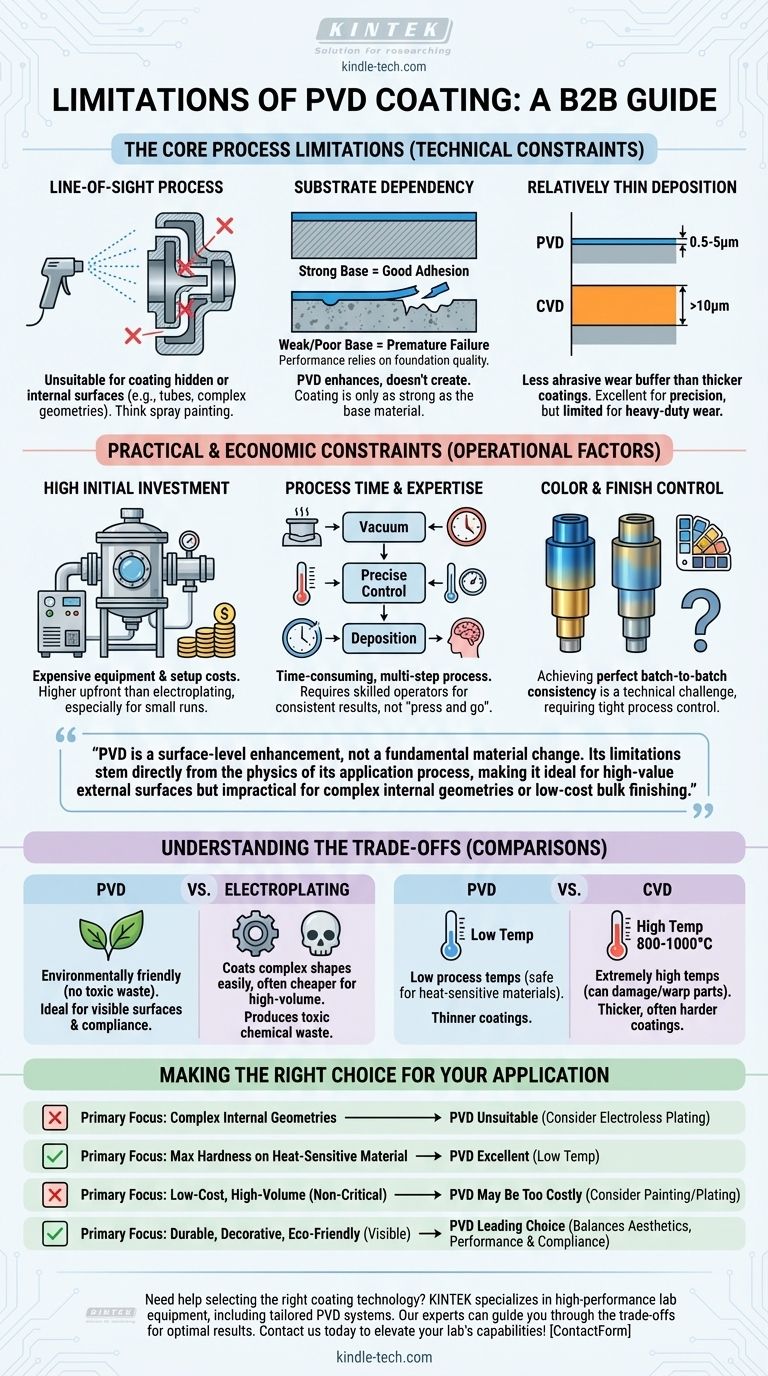
While incredibly effective, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not a universal solution. Its primary limitations are that it is a 'line-of-sight' process, making it unable to coat hidden or internal surfaces, and it requires a significant investment in specialized equipment and expertise. The process can also be time-consuming and its success is highly dependent on the quality of the underlying material.
PVD is a surface-level enhancement, not a fundamental material change. Its limitations stem directly from the physics of its application process, making it ideal for high-value external surfaces but impractical for complex internal geometries or low-cost bulk finishing.

The Core Process Limitations
To understand if PVD is right for your application, you must first grasp its inherent technical constraints. These are not flaws but fundamental characteristics of the technology.
It's a 'Line-of-Sight' Process
The most significant limitation of PVD is that the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the workpiece inside the vacuum chamber.
Think of it like spray painting: any surface that is not directly exposed to the spray nozzle will not get coated. This makes PVD unsuitable for coating the insides of long tubes, complex internal channels, or the hidden faces of assembled parts.
Substrate Dependency
A PVD coating does not create a high-performance part; it enhances one. The final properties, from hardness to corrosion resistance, are a combination of the coating and the base material it is applied to.
If the underlying substrate is soft, improperly prepared, or has poor adhesion characteristics, the coating will fail prematurely. The coating is only as strong as the foundation it rests upon.
Relatively Thin Deposition
PVD coatings are extremely thin, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns.
This is an advantage for precision components where dimensional tolerances are critical. However, for applications requiring heavy-duty wear resistance, this thin layer may provide less of a lifespan buffer than thicker coatings like hard chrome or those applied via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Practical and Economic Constraints
Beyond the physics of the process, PVD carries operational and financial considerations that can make it a non-starter for certain projects.
High Initial Investment
PVD requires sophisticated and expensive equipment, including a large vacuum chamber, powerful pumping systems, and advanced power supplies.
This high capital cost means the process is often more expensive upfront than traditional methods like electroplating, especially for smaller production runs.
Process Time and Expertise
Creating the necessary vacuum and meticulously controlling the deposition parameters is a time-consuming, multi-step process.
It demands a high level of operator expertise to manage variables like temperature, pressure, and gas composition to achieve consistent results. This is not a simple "press and go" operation.
Color and Finish Control
While PVD can produce a stunning array of colors, achieving perfect, batch-to-batch consistency is a technical challenge.
Slight variations in the process can lead to subtle shifts in color. This requires extremely tight process control, which adds to the complexity and cost, particularly for demanding aesthetic applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No coating technology is perfect. The limitations of PVD are best understood when compared to other common industrial processes.
PVD vs. Electroplating
Electroplating (like chrome plating) can coat complex shapes more easily and is often cheaper for high-volume production.
However, PVD is a vastly more environmentally friendly process, as it does not produce the toxic chemical waste associated with plating. This is a critical consideration in modern manufacturing.
PVD vs. CVD
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) can produce thicker, and often harder, coatings.
The key trade-off is temperature. CVD requires extremely high temperatures (800-1000°C), which can damage or warp many metal substrates. PVD operates at much lower temperatures, making it safe for a wider variety of heat-sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct coating requires aligning the technology's capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries: PVD is unsuitable; consider electroless plating or other chemical processes that do not rely on line-of-sight.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness on a heat-sensitive material: PVD is an excellent candidate because its low process temperatures prevent damage to the substrate.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost, high-volume finish for non-critical parts: The high capital and operational costs of PVD may make traditional painting or electroplating more economical.
- If your primary focus is a durable, decorative, and environmentally friendly finish for visible surfaces: PVD is a leading choice, perfectly balancing aesthetics, performance, and regulatory compliance.
Understanding these limitations allows you to leverage PVD's powerful advantages for the right applications, ensuring a successful and cost-effective outcome.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Line-of-Sight Process | Coating material travels in straight lines; cannot coat hidden or internal surfaces. | Unsuitable for complex internal geometries, tubes, or assembled parts. |
| Substrate Dependency | Coating performance relies on the quality, preparation, and adhesion of the base material. | Poor substrate leads to premature coating failure; requires high-quality foundations. |
| High Initial Investment | Requires expensive vacuum chambers, pumping systems, and advanced power supplies. | Higher upfront costs compared to electroplating, especially for small batches. |
| Process Time and Expertise | Multi-step, time-consuming process demanding precise control of temperature, pressure, and gas composition. | Not ideal for quick-turn projects; requires skilled operators for consistency. |
| Thin Deposition | Coatings are typically 0.5–5 microns thick, limiting heavy-duty wear resistance. | Less buffer for extreme abrasion vs. thicker coatings like CVD or hard chrome. |
Need help selecting the right coating technology for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including PVD systems tailored to your specific needs. Our experts can guide you through the trade-offs between PVD, CVD, and electroplating to ensure optimal results for your applications—whether you're enhancing durability, achieving precise finishes, or meeting environmental standards. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can elevate your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















