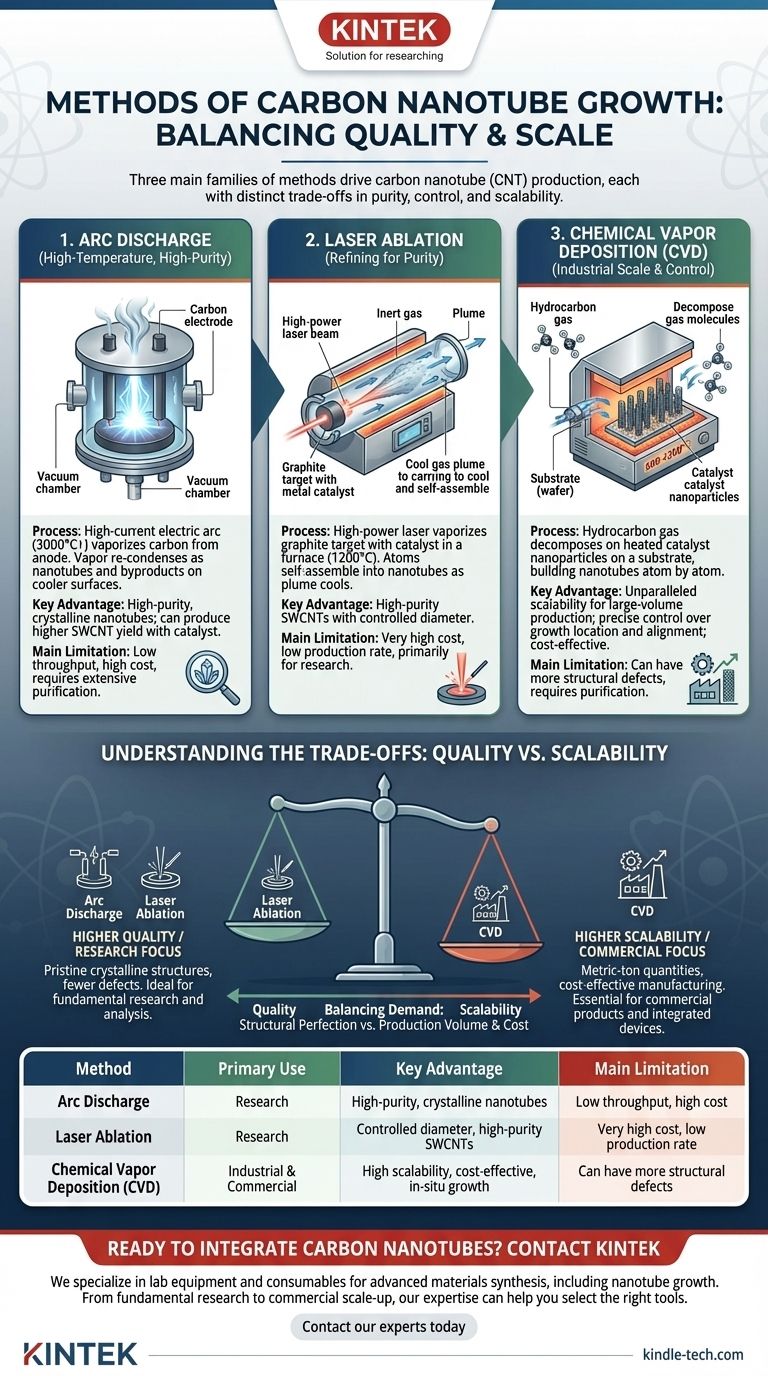
In essence, carbon nanotubes are primarily grown using three distinct families of methods: Arc Discharge, Laser Ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While the first two are high-temperature evaporation techniques excellent for producing high-quality material for research, CVD is the dominant industrial method due to its unparalleled scalability and control over the growth process.
The choice of a nanotube growth method is a critical engineering decision, balancing the competing demands of structural perfection, production volume, and cost. While older methods produce pristine nanotubes, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the workhorse that makes most modern nanotube applications possible.

The High-Temperature, High-Purity Methods
The earliest methods for creating carbon nanotubes (CNTs) involved vaporizing solid carbon at extremely high temperatures. These techniques are still used in research settings where material purity is paramount.
Arc Discharge: The Original Discovery Method
This technique involves creating a high-current electric arc between two carbon electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere. The intense heat, reaching over 3000°C, vaporizes carbon from the positive electrode (anode).
The vaporized carbon then re-condenses on the cooler surfaces of the reactor, forming a mixture of nanotubes and other carbon byproducts like amorphous carbon and fullerenes.
By including a metal catalyst (like nickel or cobalt) in the anode, the process can be tuned to produce a higher yield of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs). Without it, multi-walled nanotubes (MWCNTs) are the primary product.
Laser Ablation: Refining for Purity
Laser ablation is a refinement of the same basic principle. Instead of an electric arc, a high-power laser beam is aimed at a graphite target that contains a small amount of metal catalyst.
The process takes place in a tube furnace at high temperatures (around 1200°C). The laser pulse vaporizes the target, creating a plume of carbon and catalyst atoms that are then carried by an inert gas flow.
As the plume cools, the atoms self-assemble into nanotubes. This method is known for producing a high yield of high-purity SWCNTs with a controlled diameter, but its high cost and low production rate limit it almost exclusively to research.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Path to Industrial Scale
CVD is fundamentally different from the vaporization methods. It is a "bottom-up" technique that builds nanotubes atom by atom on a surface, making it the most versatile and scalable method by far.
The Core Principle: Catalytic Decomposition
In a CVD process, a substrate coated with a thin layer of catalyst nanoparticles (typically iron, cobalt, or nickel) is heated in a furnace.
A carbon-containing gas, known as a hydrocarbon feedstock (like methane, ethylene, or acetylene), is then introduced into the reactor.
At temperatures between 600-1200°C, the catalyst nanoparticles "crack" the hydrocarbon molecules, and the carbon atoms precipitate out to form the cylindrical lattice of the nanotube.
Why CVD Dominates Commercial Production
The primary advantage of CVD is scalability. The process can be scaled up to large industrial reactors for producing nanotubes in metric-ton quantities.
Furthermore, CVD offers unparalleled control. By patterning the catalyst on a substrate, engineers can grow nanotubes in specific locations. This allows for the creation of vertically aligned "CNT forests," which are crucial for applications in thermal interfaces, electronics, and sensors.
Key CVD Variations
The flexibility of CVD has led to several specialized versions. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), for example, uses an electric field to create a plasma, which helps decompose the hydrocarbon gas at lower temperatures and promotes the growth of vertically aligned nanotubes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Scalability
No single method is universally superior; the best choice depends entirely on the intended application. The decision is a trade-off between the structural quality of the nanotubes and the cost and volume of production.
Purity and Structural Defects
Arc discharge and laser ablation generally produce nanotubes with higher crystalline quality and fewer structural defects. However, the resulting material is a raw "soot" that requires extensive and costly purification to remove catalyst and amorphous carbon.
CVD-grown nanotubes can have more defects and often contain encapsulated catalyst particles. While purification is still necessary for many applications, the process is generally more straightforward for large batches.
Cost and Throughput
This is the clearest distinction. Arc discharge and laser ablation are high-energy, low-throughput processes. They are expensive and not suitable for producing the quantities needed for commercial products like composites or battery electrodes.
CVD is the undisputed leader in cost-effective, high-volume manufacturing. It is the only method that can produce nanotubes at a price point and scale that makes commercial applications economically viable.
Control and In-Situ Growth
CVD's ability to grow nanotubes directly on a substrate is a unique and powerful advantage. This in-situ growth is essential for fabricating integrated devices in the semiconductor industry or creating advanced composite materials where the nanotubes are grown directly on the reinforcing fibers. The other methods only produce a powder that must be mixed in later.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a synthesis method requires a clear understanding of your end goal. The properties required for a university research experiment are vastly different from those needed for a commercial product.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine nanotube properties: Arc discharge or laser ablation will provide the highest-quality, most crystalline samples for analysis.
- If your primary focus is developing a commercial product or scalable application: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only industrially viable method for cost-effective, large-scale production.
- If your primary focus is integrating CNTs directly into electronic devices or advanced composites: A substrate-based CVD process is the necessary approach for controlled placement and aligned growth.
Understanding these core trade-offs between quality, scale, and control is the first step toward effectively harnessing the remarkable properties of carbon nanotubes for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | Research | High-purity, crystalline nanotubes | Low throughput, high cost |
| Laser Ablation | Research | Controlled diameter, high-purity SWCNTs | Very high cost, low production rate |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Industrial & Commercial | High scalability, cost-effective, in-situ growth | Can have more structural defects |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or product development?
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced materials synthesis, including nanotube growth. Whether you are exploring fundamental research with high-purity samples or scaling up for commercial production with CVD, our expertise can help you select the right tools for your specific application.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's nanotube synthesis goals and accelerate your project from concept to reality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of coating using sputtering technique? Superior Film Quality & Material Versatility
- What is chemical Vapour deposition method for thin film deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Coatings
- What is thermal vapour deposition for thin films? A Simple Guide to High-Purity Coatings
- What is chemical vapor deposition for CNT? The Leading Method for Scalable Carbon Nanotube Synthesis
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What information does a thermocouple at the substrate bottom provide in LCVD? Master Precise Temperature Control
- What are the different tool coating methods? PVD vs. CVD Explained for Optimal Performance
- What are the hazards of chemical vapor deposition? Key Risks and Safer Alternatives



















