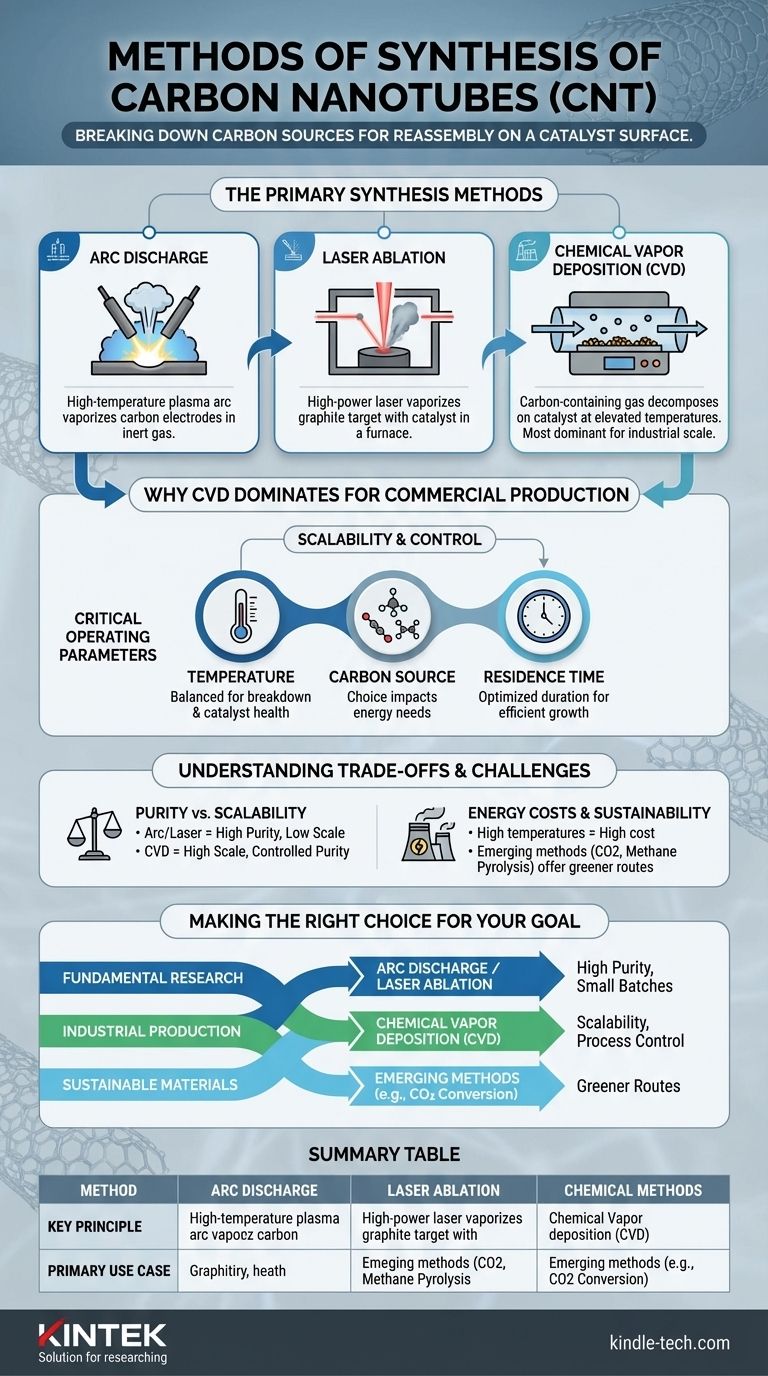
At its core, the synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) involves providing a carbon source with enough energy to break down and reassemble on a catalyst surface. The primary methods are arc discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), with CVD being the overwhelmingly dominant process for commercial-scale production today due to its scalability and control.
The central challenge in CNT synthesis is not simply creating nanotubes, but controlling their structure and purity at a viable cost. While older methods produce high-quality material, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) offers the most practical path for industrial applications by carefully managing temperature, feedstock, and reaction time.

The Primary Synthesis Methods
To understand the landscape of CNT production, we must look at the three foundational techniques. Each operates on a different principle to supply the necessary energy and carbon atoms for nanotube growth.
Arc Discharge
This was one of the earliest methods developed. It involves creating a high-temperature plasma arc between two carbon electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere. The intense heat vaporizes the carbon, which then condenses to form CNTs.
Laser Ablation
In this method, a high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target mixed with a metal catalyst. The laser vaporizes the target material, creating a plume of carbon and catalyst atoms inside a high-temperature furnace, where they self-assemble into nanotubes.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the most widely used industrial method. It involves flowing a carbon-containing gas (a hydrocarbon feedstock) over a substrate coated with catalyst particles at elevated temperatures. The gas decomposes on the catalyst, and the carbon atoms assemble into nanotubes.
Why Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Dominates
CVD has become the standard for a clear reason: it offers superior control over the final product and is far more scalable than the other methods. Success with CVD hinges on precisely managing a few critical operating parameters.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is a crucial factor. It must be high enough to break down the carbon feedstock gas and facilitate the catalytic reaction, but not so high that it damages the catalyst or creates unwanted by-products.
The Impact of the Carbon Source
The choice of carbon feedstock directly impacts the energy required for synthesis. Gases like acetylene can be direct precursors, while methane and ethylene require more energy for thermal conversion before they can contribute to CNT growth. Methane is the most energy-intensive of the three.
The Importance of Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the carbon gas spends in the reaction zone. This parameter requires careful optimization. If the time is too short, the carbon source is wasted; if it is too long, by-products can accumulate and hinder further growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While CVD is the dominant method, it is not without its complexities. The pursuit of high-quality, cost-effective CNTs involves navigating several key trade-offs.
Purity vs. Scalability
Arc discharge and laser ablation can produce very high-purity CNTs but are difficult and expensive to scale up. CVD offers excellent scalability for mass production, but controlling the purity and structure of the resulting nanotubes remains a significant engineering challenge.
Energy Costs and Feedstock
The high temperatures required for all methods represent a major operational cost. Furthermore, the energy needed to convert stable feedstocks like methane into reactive carbon atoms adds to the overall expense and environmental footprint of the process.
The Rise of Sustainable Methods
To address these challenges, innovation is pushing towards more sustainable approaches. Emerging methods include using captured carbon dioxide via electrolysis in molten salts or the direct pyrolysis of waste methane, turning potential pollutants into valuable materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a synthesis method depends entirely on the intended application and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or producing small batches of very high-purity CNTs: Arc discharge or laser ablation are often suitable choices despite their higher cost and lower yield.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production for composites, electronics, or coatings: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only commercially viable method due to its scalability and process control.
- If your primary focus is sustainable materials and next-generation technology: Investigating emerging methods like methane pyrolysis or CO2 conversion is crucial for developing greener and more cost-effective production routes.
Ultimately, understanding the principles behind each synthesis method is the key to unlocking the transformative potential of carbon nanotubes for any application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Principle | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | Vaporizes carbon electrodes with a plasma arc. | High-purity CNTs for research. |
| Laser Ablation | Uses a laser to vaporize a graphite target. | High-purity CNTs for research. |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Decomposes carbon gas on a catalyst at high temperatures. | Industrial-scale production for composites, electronics, and coatings. |
Ready to integrate Carbon Nanotubes into your research or production line? The right synthesis method is critical for achieving your goals in purity, scalability, and cost. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for CNT research and development, including systems for CVD processes. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your laboratory's specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovative work with CNTs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty


















