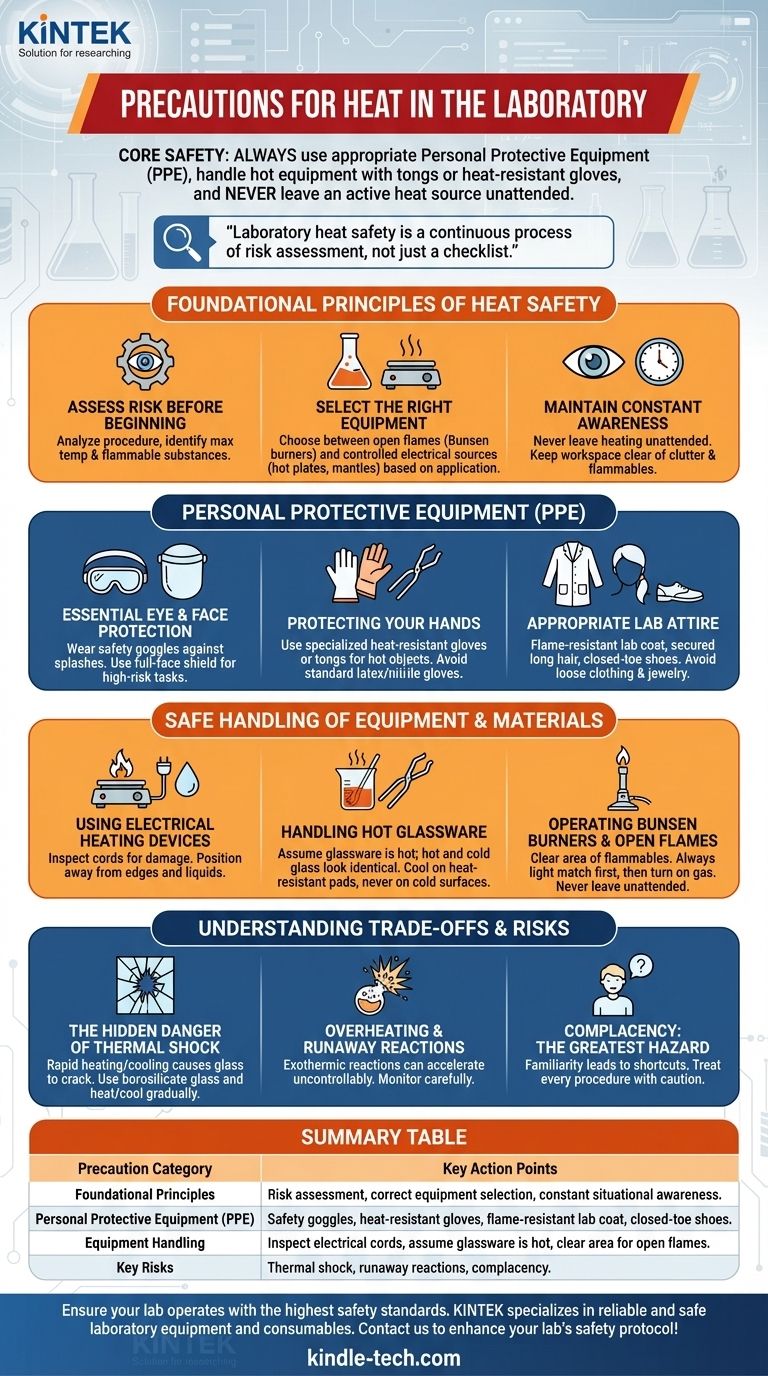
The most critical precautions for heat in the laboratory are to always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), handle hot equipment with tongs or heat-resistant gloves, and never leave an active heat source unattended. You must also ensure your workspace is clear of flammable materials and be fully aware of the location and operation of safety equipment like fire extinguishers and safety showers before you begin.
Laboratory heat safety is not merely a checklist of rules, but a continuous process of risk assessment. It requires understanding your equipment, anticipating potential hazards, and maintaining constant situational awareness to prevent burns and fires.

Foundational Principles of Heat Safety
True laboratory safety goes beyond rote memorization. It involves a mindset built on three core principles that should be applied before and during any procedure involving heat.
Assess the Risk Before You Begin
Before turning on any device, analyze the procedure. Identify the maximum temperature required and note any flammable or volatile substances being used. This initial assessment dictates your choice of equipment and the specific precautions you must take.
Select the Right Equipment for the Job
Not all heat sources are interchangeable. Open flames, like Bunsen burners, are direct ignition sources and must never be used near flammable solvents. Electrical sources, such as hot plates, heating mantles, and ovens, offer more controlled and contained heat, making them safer for many applications.
Maintain Constant Situational Awareness
An unattended experiment is an uncontrolled one. Never leave a heating process unsupervised. Keep your work area organized and free of unnecessary clutter, especially flammable materials like paper towels or solvent bottles.
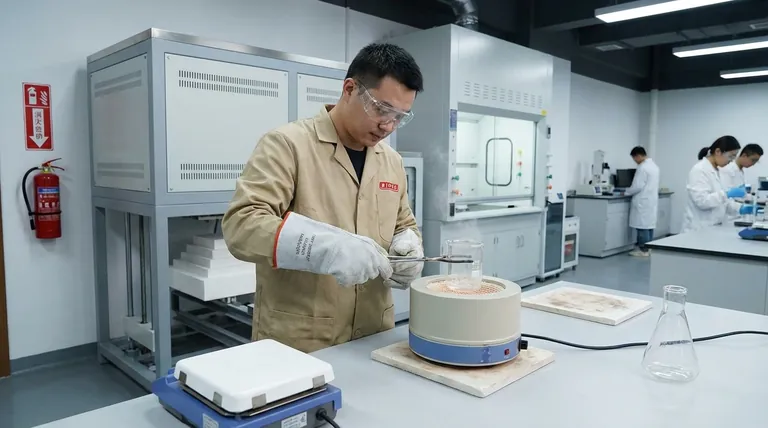
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Your First Defense
Your PPE is the final barrier between you and an accident. Wearing it correctly and consistently is non-negotiable.
Essential Eye and Face Protection
Safety goggles must be worn at all times to protect against splashes of hot liquids. For procedures with a higher risk of splashing or popping, a full-face shield should be worn over your goggles.
Protecting Your Hands
Use tongs, forceps, or heat-resistant gloves specifically designed for high temperatures when handling hot flasks, beakers, or crucibles. Never use standard latex or nitrile gloves to handle hot objects, as they will melt to your skin.
Appropriate Lab Attire
A flame-resistant lab coat should be worn and buttoned. Secure any long hair and avoid loose clothing or jewelry that could catch fire or knock over equipment. Always wear closed-toe shoes to protect your feet from spills.
Safe Handling of Equipment and Materials
Each piece of heating equipment has its own risk profile. Understanding how to operate them correctly is essential for preventing accidents.
Using Electrical Heating Devices
Inspect the power cords of hot plates and heating mantles for any signs of fraying or damage before plugging them in. Position equipment away from the edge of the bench and ensure no water or flammable liquids can spill onto the electrical components.
Handling Hot Glassware
One of the most common lab injuries is burning your hand on glassware that you thought was cool. Hot glass and cold glass look identical. Always assume glassware is hot. Place hot items on a ceramic tile or heat-resistant pad to cool, never directly on a cold benchtop which could cause it to shatter.
Operating Bunsen Burners and Open Flames
Before lighting a Bunsen burner, clear the area of all flammable materials, especially volatile solvents. Always light the match or striker first, then turn on the gas. Adjust the flame to the proper height and color for your task and never, ever leave it unattended.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential for many experiments, heat introduces significant energy and risk into your environment. Ignoring these risks leads to the most severe lab accidents.
The Hidden Danger of Thermal Shock
Rapidly heating or cooling glassware creates thermal stress, which can cause it to crack or shatter violently. Use borosilicate glass (Pyrex or Kimax) rated for heating, and always heat and cool it gradually to avoid thermal shock.
Overheating and Runaway Reactions
Some chemical reactions release heat (exothermic reactions). If not properly controlled, external heating can cause the reaction rate to accelerate uncontrollably, leading to pressure buildup, explosions, or the release of toxic fumes.
Complacency: The Greatest Hazard
The biggest risk is becoming too comfortable. Familiarity can lead to shortcuts, like failing to wear PPE for a "quick" task or leaving a hot plate on while you step away. Every procedure, no matter how routine, must be treated with the same level of caution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your safety strategy should adapt to the specific task at hand. Before applying heat, review your goal and choose the safest, most effective approach.
- If your primary focus is heating flammable liquids: Your only choice is to use a controlled, flameless heat source like a steam bath, water bath, or heating mantle to eliminate any risk of ignition.
- If your primary focus is heating glassware to high temperatures: Assume all glassware is hot until proven otherwise and always use tongs or heat-resistant gloves for handling.
- If your primary focus is setting up any heating experiment: Always perform a final safety check of your workspace, ensuring it's clear of clutter and that emergency equipment is accessible before you begin.
Ultimately, safety is an active process, not a passive state.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Category | Key Action Points |
|---|---|
| Foundational Principles | Risk assessment, correct equipment selection, constant situational awareness. |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Safety goggles, heat-resistant gloves, flame-resistant lab coat, closed-toe shoes. |
| Equipment Handling | Inspect electrical cords, assume glassware is hot, clear area for open flames. |
| Key Risks | Thermal shock, runaway reactions, complacency. |
Ensure your lab operates with the highest safety standards. KINTEK specializes in reliable and safe laboratory equipment and consumables. From heat-resistant gloves to controlled heating mantles, our products are designed to protect your team and your research. Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's safety protocol!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature limit on a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Model
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction
- What are the materials used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Durable Construction & Optimal Performance
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- What are the uses of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Essential for Drug Purity & Safety



















