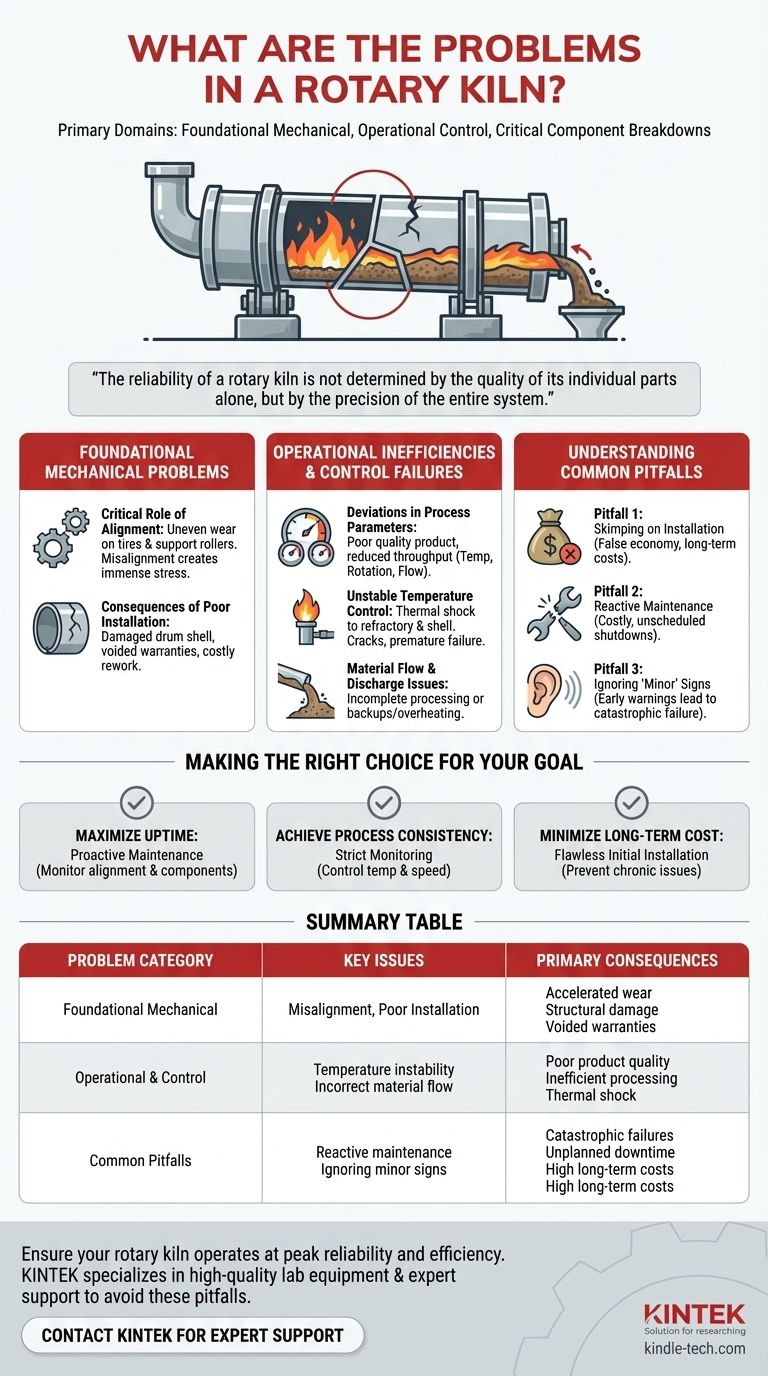
At their core, the problems in a rotary kiln can be categorized into three primary domains: foundational mechanical failures, operational control issues, and critical component breakdowns. The most severe issues often originate from improper installation and alignment, which then cascade into accelerated wear and operational inefficiencies.
The reliability of a rotary kiln is not determined by the quality of its individual parts alone, but by the precision of the entire system. Misalignment during installation and a lack of control over key operational parameters are the root causes of most significant and costly failures.
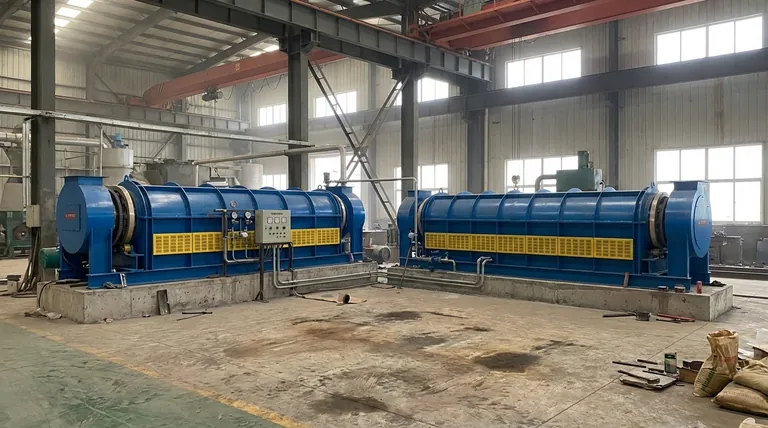

Foundational Mechanical Problems
The structural integrity and alignment of the kiln form the bedrock of its operational health. Errors in this foundation inevitably lead to systemic problems.
The Critical Role of Alignment
Proper alignment of the kiln's drum shell, support rollers, and tires is non-negotiable for smooth operation. Even minor misalignments introduce immense stress on all rotating components.
These stresses concentrate on specific points, leading to uneven wear patterns that accelerate the degradation of expensive parts like the tires and support rollers.
Consequences of Poor Installation
A poorly executed installation can inflict immediate and long-term damage. Improper handling during setup can dent or deform the main drum shell, compromising its structural integrity from day one.
Furthermore, failing to adhere to specified installation procedures or missing critical inspections can lead to costly rework and may even void manufacturer warranties, leaving you financially responsible for premature failures.
Operational Inefficiencies and Control Failures
A rotary kiln is a finely tuned processing environment. Failure to maintain precise control over its operational parameters directly compromises the process and the equipment itself.
Deviations in Process Parameters
The efficiency of processes like calcination or sintering depends on a delicate balance of temperature, rotation speed, and material flow rate.
Any deviation from the designed setpoints can result in an incomplete chemical reaction, a poor-quality final product, or reduced throughput, directly impacting operational profitability.
Unstable Temperature Control
The burner system is the heart of the kiln's thermal process. Unstable flame patterns or failing temperature sensors create temperature fluctuations within the drum.
This instability not only ruins the material being processed but can also cause thermal shock to the refractory lining and the steel shell, leading to cracks and premature failure.
Material Flow and Discharge Issues
The inclination angle and rotation speed are engineered to control how long material stays in the kiln.
If these parameters are incorrect, material may move too quickly, leading to incomplete processing, or too slowly, causing backups, inefficient heat transfer, and potential overheating damage at the discharge end.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Many kiln problems are not sudden events but the result of overlooked details and flawed maintenance philosophies. Recognizing these pitfalls is key to prevention.
Pitfall 1: Skimping on Installation
The most common mistake is attempting to save money on initial installation and alignment. This is a false economy.
The upfront cost of expert installation is minuscule compared to the long-term expenses of unplanned downtime, accelerated component wear, and constant realignment adjustments.
Pitfall 2: Reactive Maintenance
Waiting for a critical component like a burner nozzle or seal to fail before replacing it guarantees costly, unscheduled shutdowns.
A proactive approach, involving regular inspections and scheduled replacement of known wear parts, ensures the kiln remains a reliable asset rather than an unpredictable liability.
Pitfall 3: Ignoring "Minor" Signs
Small indicators like unusual noise, slight vibrations, or minor material spillage from a seal are early warnings of larger problems.
Ignoring these signs allows minor misalignments or component wear to compound, eventually leading to catastrophic failures like a cracked drum shell or major bearing failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance and operational strategy should align directly with your primary business objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Prioritize a rigorous proactive maintenance schedule focused on monitoring alignment and the condition of tires, rollers, and burner components.
- If your primary focus is achieving process consistency: Implement strict monitoring and control systems for all key operational parameters, especially temperature and rotation speed.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term cost: Invest heavily in a flawless initial installation and alignment, as this will prevent the majority of chronic, expensive mechanical issues.
Ultimately, understanding these potential failure points transforms a rotary kiln from a source of operational risk into a consistently reliable and efficient core of your process.
Summary Table:
| Problem Category | Key Issues | Primary Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Foundational Mechanical | Misalignment, Poor Installation | Accelerated wear, Structural damage, Voided warranties |
| Operational & Control | Temperature instability, Incorrect material flow | Poor product quality, Inefficient processing, Thermal shock |
| Common Pitfalls | Reactive maintenance, Ignoring minor signs | Catastrophic failures, Unplanned downtime, High long-term costs |
Ensure your rotary kiln operates at peak reliability and efficiency. The problems of misalignment, operational instability, and component failure can lead to significant downtime and lost revenue. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, consumables, and expert support for laboratory and industrial processes. Our team can help you select the right equipment and implement proactive maintenance strategies to avoid these common pitfalls. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your operational goals and minimize costly kiln failures.
Contact KINTEK for Expert Support
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















