Graphite is a material of extremes, defined by a unique and often paradoxical set of characteristics. It is an excellent conductor of both heat and electricity, yet it can withstand incredibly high temperatures without melting. This combination of properties, along with its increasing strength in high-heat environments, makes it an indispensable material for demanding industrial and technical applications.
While most materials weaken with heat, graphite's defining characteristic is that its mechanical strength actually increases at extreme temperatures. This makes it a critical component for applications like vacuum furnaces and electrodes, where conventional materials would simply fail.
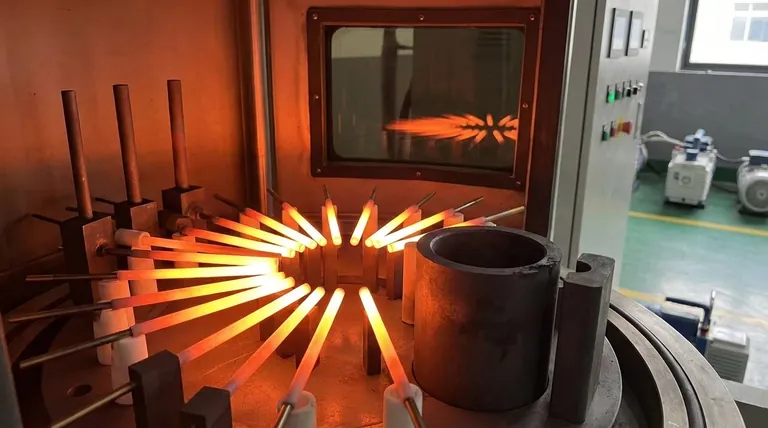
Unrivaled Performance in Extreme Heat
Graphite's behavior under thermal stress is its most remarkable quality. Unlike metals or ceramics that melt or fracture, graphite thrives.
High Temperature Resistance
Graphite has an extremely high melting point and low vapor pressure. This means it remains solid and stable at temperatures that would vaporize many other materials, making it ideal for crucibles and furnace linings.
Increasing Strength with Temperature
This is graphite's most counter-intuitive property. Its mechanical strength improves as temperatures rise, peaking around 1700°C and remaining strong up to 2500°C. This ensures structural components like hearths maintain their shape under intense heat.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite can withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking. This is due to its combination of low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity, which prevents internal stresses from building up.
Excellent Conductivity Properties
Beyond its heat resistance, graphite is also highly effective at transferring energy, both thermal and electrical.
High Thermal Conductivity
Graphite's ability to conduct heat efficiently helps to distribute temperature evenly and minimize hot spots. While its mass can lead to slower initial heating, its conductivity quickly compensates, ensuring uniform thermal performance.
High Electrical Conductivity
With low electrical resistance, graphite is an excellent electrical conductor. This property makes it a primary material for heating elements in furnaces and for electrodes in electrical discharge machining (EDM).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is without its drawbacks. Acknowledging graphite's limitations is key to using it effectively and safely.
Brittleness and Chipping
Despite its high-temperature strength, graphite is a relatively brittle material at room temperature. Components like furnace rails can be prone to chipping or cracking if subjected to sharp physical impacts during loading or handling.
Volatilization and Electrical Discharge
At very high temperatures, graphite can volatilize (turn into a gas), especially in a vacuum. Furthermore, when used as a heating element, it requires careful voltage control (often below 100V) to prevent vacuum discharge, or arcing, which can damage the furnace and the product.
Chemical Reactivity with Oxygen
While chemically resistant in many environments, graphite will oxidize and degrade rapidly when exposed to oxygen at high temperatures. This is why its most advanced applications are often in vacuum or inert gas atmospheres.
Material Purity and Machinability
Modern manufacturing techniques allow for the creation of highly specialized forms of graphite with exceptional purity and precision.
High Purity and Chemical Resistance
Isostatic graphite, a high-density variant, can be produced with extremely low impurity levels (less than 5 parts per million). This high purity, combined with graphite's natural corrosion resistance, makes it perfect for the semiconductor and nuclear industries where contamination is a critical concern.
Ease of Machining
Graphite is relatively easy to machine into complex and precise shapes. This allows for the customization of components like rods, plates, and intricate heating elements to fit exact engineering specifications.
Applying Graphite to Your Application
Choosing and using graphite effectively depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural stability: Leverage graphite's increasing strength with temperature for components like furnace hearths, knowing it will maintain its shape.
- If your primary focus is efficient heat transfer: Utilize its high thermal conductivity for applications requiring uniform heating, such as molds or heat exchangers.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: Employ it for heating elements or electrodes, but engineer the system to manage its voltage limits and prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is purity and chemical inertness: Specify high-purity isostatic graphite for semiconductor or laboratory equipment to avoid contamination.
Understanding this balance of unique strengths and specific limitations is the key to leveraging graphite as a foundational material in advanced engineering.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Strength | Mechanical strength increases up to 2500°C. | Unmatched structural stability in extreme heat. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficiently transfers and distributes heat. | Uniform heating and excellent thermal shock resistance. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low electrical resistance. | Ideal for heating elements and electrodes (e.g., EDM). |
| Machinability & Purity | Easy to machine; high-purity forms available. | Customizable components for sensitive applications (e.g., semiconductors). |
| Key Limitation | Brittle at room temperature; oxidizes in air at high heat. | Requires careful handling and inert/vacuum atmospheres. |
Ready to leverage graphite's unique properties in your lab or process?
Graphite's combination of high-temperature strength, superior conductivity, and machinability makes it a cornerstone material for demanding applications. Whether you need custom furnace components, high-purity crucibles, or efficient heating elements, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the right graphite solution for your specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite products can enhance your project's performance and reliability.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory magnetic stirrer contribute to pre-mixing? Master Your Photocatalytic Reaction Baselines
- What are some disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Size, Strength, and Complexity Limitations
- What is the difference between filtration and centrifugation? A Guide to Size vs. Density Separation
- What is the use of quartz in the glass industry? Essential for High-Performance Fused Quartz Glass
- What are rapid sintering techniques? Unlock Faster, Stronger Material Production
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of filter press? Unlock Superior Solid-Liquid Separation
- Why is programmed temperature control critical for Ce-TiOx/npAu catalysts? Achieve Precision in Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of ultrasonic cleaning equipment in the surface modification of biomedical materials? Boost Adhesion



















