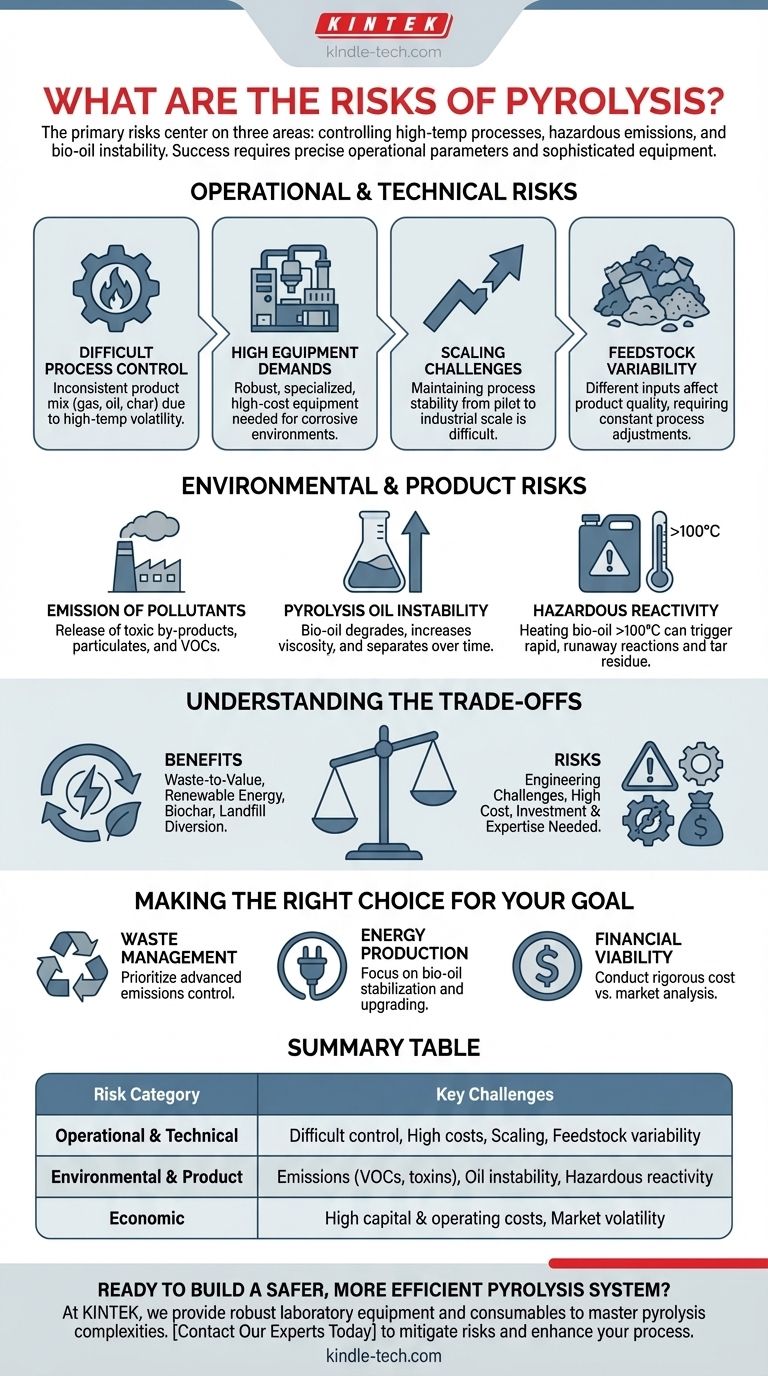
The primary risks of pyrolysis center on three key areas: the difficulty in controlling the high-temperature process, the potential for hazardous environmental emissions, and the chemical instability of its liquid product, known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil. These challenges require sophisticated equipment and precise operational parameters to manage effectively.
While pyrolysis holds significant promise for converting waste into valuable resources, its core risks are not accidental but are inherent to its complex chemical nature. Success depends on mastering the process to mitigate environmental hazards and ensure the quality of the final products.

Operational and Technical Risks
The fundamental challenge of pyrolysis is managing a complex thermal decomposition process under extreme conditions. This creates several direct operational hurdles.
Difficulty in Process Control
The high-temperature environment makes it difficult to precisely control the chemical reactions. This lack of fine control can lead to an inconsistent mix of decomposition products.
As a result, the quality and composition of the resulting oil, gas, and char can vary significantly from one batch to the next.
High Demands for Equipment
The process requires robust, specialized equipment capable of withstanding high temperatures and corrosive environments.
This translates into high capital and operating costs, which can be a significant barrier to implementation and profitability.
Challenges in Scaling Up
Moving from a laboratory or pilot scale to a full-sized industrial operation presents major technical difficulties.
Maintaining process stability and product consistency at a larger scale is a well-known engineering challenge in this field.
Feedstock Variability
Pyrolysis can technically handle diverse inputs, from biomass to plastics, but this feedstock variability is also a risk.
Different materials break down differently, affecting the chemical makeup and quality of the final bio-oil and biochar, requiring constant adjustments to the process.
Environmental and Product Risks
If the operational side is not perfectly managed, the risks can extend to the environment and the final products themselves, creating safety and usability concerns.
Emission of Pollutants
Improperly controlled pyrolysis can release harmful by-products into the atmosphere.
These include toxic by-products, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which pose risks to both environmental and human health.
Pyrolysis Oil Instability
The liquid output, often called bio-oil, is not a stable, finished product like crude oil. It is a reactive mixture of intermediate chemical compounds.
Over time, this oil can degrade. Its viscosity gradually increases, and it can even separate into different phases due to slow condensation reactions, making storage and transport difficult.
Hazardous Reactivity
Heating this bio-oil above 100°C can trigger rapid, runaway reactions.
This can produce a solid, tar-like residue and release a new wave of volatile organic compounds, creating a significant handling hazard.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is critical to view these risks in the context of the technology's potential benefits. Pyrolysis is not inherently flawed, but it is a demanding process with clear trade-offs.
The Promise of a Circular Economy
The primary benefit of pyrolysis is its ability to convert waste streams into valuable products.
It can produce renewable energy in the form of bio-oil, create biochar for soil amendment and carbon sequestration, and divert waste from landfills, all of which are significant environmental advantages.
Risk as an Engineering Challenge
The risks of pyrolysis are not insurmountable but are engineering and chemical challenges that require investment and expertise.
Advanced process controls, sophisticated off-gas treatment systems, and post-processing technologies for bio-oil stabilization are all key to building a safe and efficient system. The high cost and complexity are the price for its unique waste-to-value capability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To properly assess pyrolysis, you must weigh the risks against your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Prioritize investment in advanced emissions control systems and flexible process parameters to safely handle variable feedstock.
- If your primary focus is energy production: Focus on the post-processing and upgrading steps required to stabilize the bio-oil and make it a reliable, long-term fuel source.
- If your primary focus is financial viability: Conduct a rigorous analysis of the high capital costs versus the fluctuating market value of bio-oil and biochar to ensure a sustainable business model.
A clear understanding of these risks is the first and most critical step toward engineering a safer and more effective pyrolysis system.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Operational & Technical | Difficult process control, high equipment costs, scaling challenges, feedstock variability |
| Environmental & Product | Emission of pollutants (VOCs, toxins), pyrolysis oil instability, hazardous reactivity |
| Economic | High capital and operating costs, market volatility of end products |
Ready to build a safer, more efficient pyrolysis system?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to help you master the complexities of pyrolysis. Whether you're focused on waste management, energy production, or ensuring financial viability, our solutions are designed to mitigate risks and enhance your process control and product quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific pyrolysis goals and help you convert waste into valuable resources safely and effectively.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















