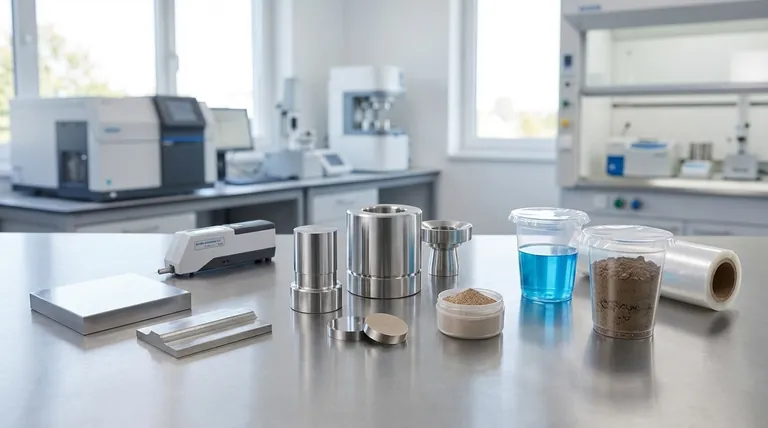
In short, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) can analyze an extremely wide variety of materials, including solids, liquids, and powders. Suitable samples range from natural geological materials like rocks and soils to industrial products like cement, metals, alloys, ceramics, and even biological matter or precipitates from solutions.
The specific material you can analyze is less important than how you prepare it. The fundamental goal of any XRF sample preparation is to present a perfectly flat, clean, and homogeneous surface to the instrument to ensure the data is accurate and repeatable.

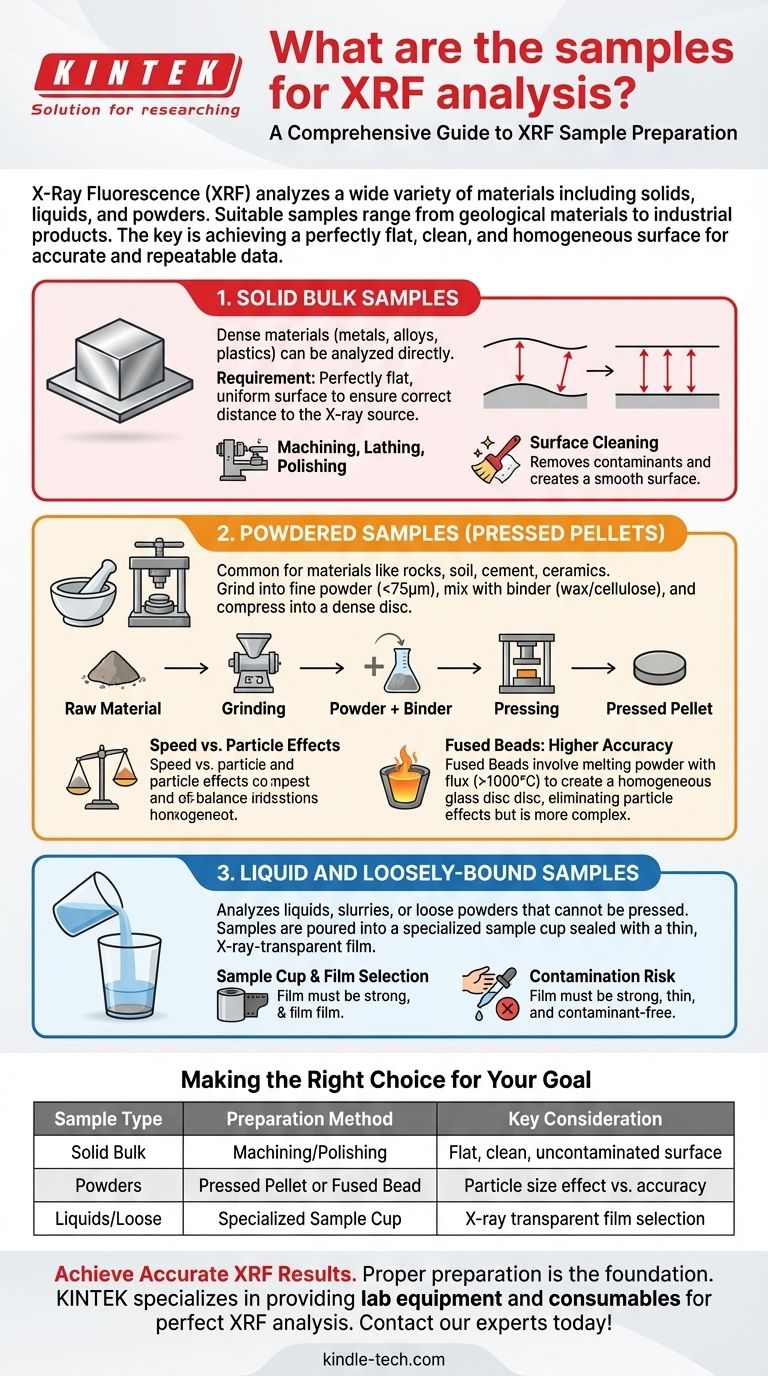
The Three Primary Forms of XRF Samples
To get reliable results, a sample must be prepared into one of three primary forms. The method you choose depends on the original state of your material and the analytical accuracy you require.
Solid Bulk Samples
Solid, dense materials like metals, alloys, or certain plastics can often be analyzed directly. The defining requirement is that the surface being measured must be perfectly flat and uniform.
An irregular surface changes the distance between the sample and the instrument's X-ray source and detector. Since XRF systems are calibrated for a fixed distance, any variation will skew the intensity of the elemental signals, leading to inaccurate results.
Preparation typically involves machining, lathing, or polishing the sample to create a smooth surface. It is also critical to clean the surface to remove any contaminants.
Powdered Samples (Pressed Pellets)
This is one of the most common methods for XRF. Materials like rocks, minerals, soil, cement, and ceramics are first ground into a very fine powder, typically smaller than 75 micrometers.
This fine powder is then often mixed with a binding agent, such as a wax or cellulose. The binder helps the particles stick together and improves flow during pressing.
Finally, the powder-binder mixture is compressed under high pressure in a die to form a dense, solid disc known as a pressed pellet.
Liquid and Loosely-Bound Samples
XRF can also analyze liquids, slurries, or loose powders that cannot be pressed.
These samples are prepared by simply pouring them into a specialized sample cup. The bottom of the cup is then sealed with a thin, X-ray-transparent film.
The choice of film is critical. It must be strong enough to hold the sample without leaking but thin enough not to absorb the X-rays from the elements of interest. It must also be free of any elemental contaminants that could interfere with the analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each preparation method comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right one is a balance between accuracy, speed, and cost.
Pressed Pellets: Speed vs. Particle Effects
Pressed pellets are popular because the method is fast, relatively low-cost, and suitable for a huge range of materials.
However, its main drawback is the "particle size effect." If the sample is not ground finely or uniformly enough, larger particles of certain elements can disproportionately affect the results, reducing accuracy. The binding agent also slightly dilutes the sample.
Fused Beads: Accuracy vs. Complexity
For the highest level of accuracy with powdered samples, an alternative method is creating a fused bead. The sample powder is mixed with a flux (like a lithium borate salt) and heated in a crucible to over 1000°C until it melts.
The molten mixture is then cooled into a perfectly homogeneous glass disc. This process completely eliminates the particle size effect, yielding superior results. The trade-offs are that it is more time-consuming, requires specialized high-temperature equipment, and the flux significantly dilutes the sample, which can make it difficult to measure trace-level elements.
Solid Samples: Contamination Risk
When preparing solid bulk metals or alloys, the primary risk is surface contamination. Using polishing media or cleaning tools that contain interfering elements can ruin a measurement.
To avoid this, it is standard practice to use dedicated preparation tools (e.g., separate files or grinding papers) for different types of alloys to prevent cross-contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your analytical objective determines the correct preparation path.
- If your primary focus is routine process control or rapid screening: Pressed pellets offer the best balance of speed, cost, and acceptable accuracy.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible accuracy for certification or research: Fused beads are the gold standard for powdered materials, as they eliminate physical effects.
- If your primary focus is analyzing solid metals or alloys: Your effort should be concentrated on proper machining and polishing to create a perfectly flat and uncontaminated surface.
Ultimately, proper sample preparation is the foundation of all reliable XRF analysis.
Summary Table:
| Sample Type | Preparation Method | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Bulk (Metals, Alloys) | Machining/Polishing | Flat, clean, uncontaminated surface |
| Powders (Soil, Cement, Rocks) | Pressed Pellet or Fused Bead | Particle size effect vs. accuracy |
| Liquids & Loose Materials | Specialized Sample Cup | X-ray transparent film selection |
Achieve accurate and reliable XRF results with the right sample preparation. The quality of your data starts with how you prepare your samples. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need for perfect XRF analysis—from durable pellet presses and dies for creating consistent pressed pellets to high-quality films for liquid sample cups.
Whether you're in mining, metallurgy, ceramics, or environmental testing, our expertise ensures your laboratory operates at peak efficiency. Let us help you optimize your XRF workflow. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in electrode sheets? Optimize Connectivity & Stability
- What is the primary purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press at 500 MPa? Optimize Solid-State Battery Density
- What are the components of a forging press? Understand the Core Systems for Shaping Metal
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized in the preparation of samples during the solvent precipitation recovery of polyamides? Achieve Precise Densification
- What are the advantages of pressed pellet technique? Enhance Precision & Accuracy in Sample Analysis
- What are the advantages of using KBr in IR spectroscopy sample preparation? Achieve Clean, Accurate Spectra
- What is the basic concept of XRF? A Non-Destructive Guide to Elemental Analysis
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in the fabrication of Na3FePO4CO3 experimental electrode sheets?



















