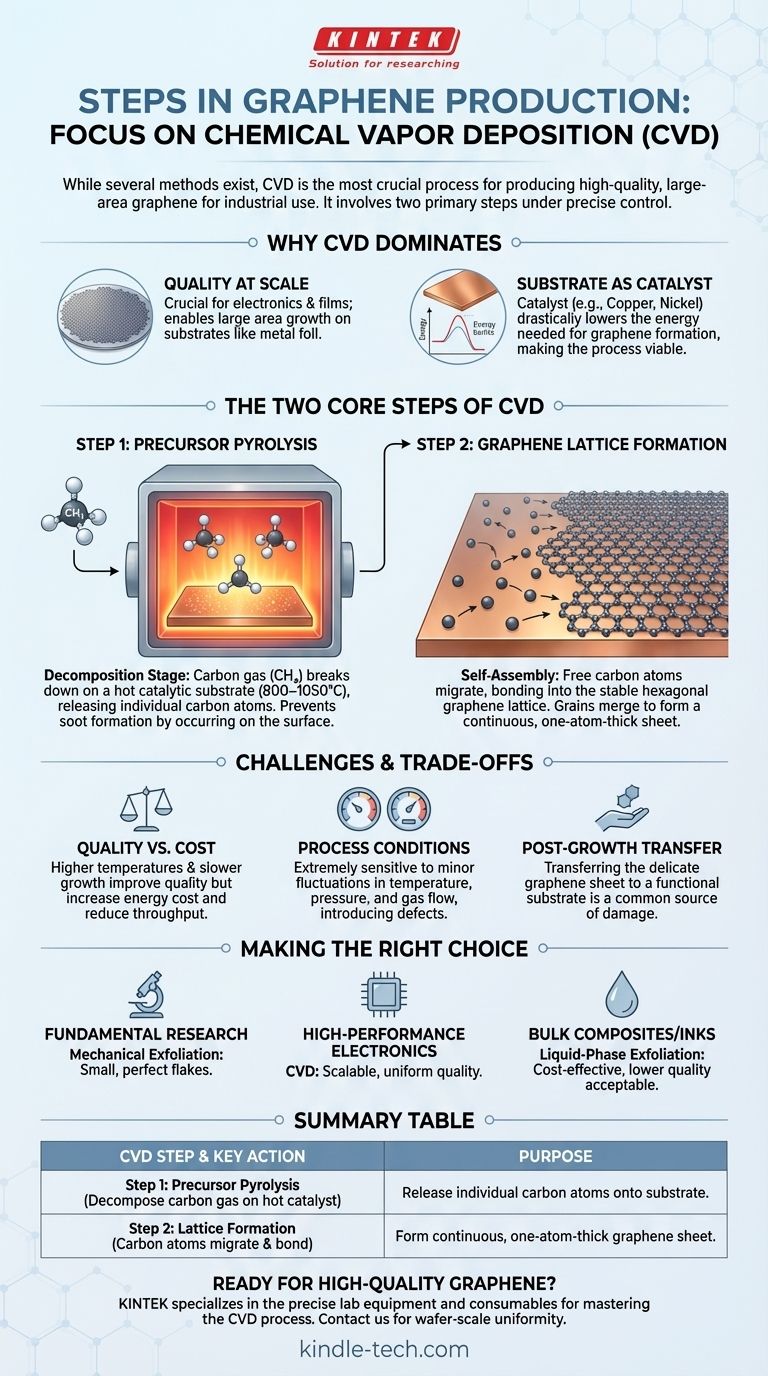
While several methods exist to create graphene, the most crucial process for producing high-quality, large-area material for industrial use is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This technique essentially involves two primary steps: first, breaking down a carbon-source gas into individual atoms on a hot substrate, and second, the self-assembly of those atoms into a one-atom-thick sheet of graphene.
The core challenge in producing graphene is not merely following a set of steps, but mastering a delicate, high-temperature process. Success depends on precisely balancing temperature, pressure, and catalytic activity to achieve high quality and large scale at a reasonable cost.
Why Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Dominates
Other methods, like mechanical exfoliation (the "Scotch tape" method), are excellent for fundamental research but are not scalable. CVD is the only proven technique capable of producing the large, uniform sheets of high-quality graphene required for applications in electronics and advanced materials.
The Need for Quality at Scale
CVD stands apart because it can grow graphene over large areas, such as an entire metal foil. This is a fundamental requirement for manufacturing electronic components or transparent conductive films.
The Substrate as a Catalyst
In the CVD process, the substrate—typically a copper or nickel foil—is not just a passive surface. It acts as a catalyst, dramatically lowering the immense energy (temperatures often over 2500°C) that would otherwise be needed to form the graphene lattice. This catalytic action is what makes the process viable.
Breaking Down the Two Core Steps of CVD
The entire CVD process takes place within a specialized chamber where temperature, pressure, and gas flow are meticulously controlled.
Step 1: Precursor Pyrolysis
This is the decomposition stage. A carbon-containing precursor, most commonly methane gas (CH₄), is introduced into the chamber.
The high temperature of the catalytic substrate (typically 800–1050°C) breaks the chemical bonds of the gas molecules. This pyrolysis releases individual carbon atoms onto the surface.
Crucially, this reaction must happen on the substrate itself. If it occurs in the gas phase away from the surface, the carbon atoms will clump together to form soot, which degrades the quality of the final graphene film.
Step 2: Graphene Lattice Formation
Once free on the catalytic surface, the individual carbon atoms migrate and begin to bond with each other.
Driven by thermodynamics, they arrange themselves into the most stable configuration: the iconic hexagonal lattice structure of graphene. This process starts at various points, forming "islands" or "grains" of graphene that grow and merge to form a continuous sheet.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While the steps are straightforward in theory, executing them to produce high-quality material is a significant engineering challenge. The process is a constant balancing act.
The Battle Between Quality and Cost
Higher temperatures and slower growth rates generally produce graphene with fewer defects and larger crystal grains, which improves its electrical properties. However, this directly increases energy consumption and reduces throughput, driving up the cost.
The Impact of Process Conditions
The final quality of the graphene is extremely sensitive to physical conditions. Minor fluctuations in temperature, chamber pressure, or the flow rate of the carrier gas can introduce defects or impurities into the delicate atomic structure.
The Post-Growth Transfer
After growth, the graphene sheet is on a metal foil and must be transferred to a functional substrate, like silicon or plastic. This transfer process is delicate and a common source of tears, wrinkles, and contamination, which can compromise the material's superior properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the different production methods is key to selecting the right type of graphene for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Mechanical exfoliation can provide small but nearly perfect flakes ideal for scientific study.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: CVD is the only viable path, requiring investment in precise process control to ensure wafer-scale uniformity and quality.
- If your primary focus is in bulk composites or conductive inks: Liquid-phase exfoliation may be a more cost-effective choice, as the lower electrical quality is often acceptable for these applications.
Ultimately, the "best" method for producing graphene is entirely dependent on the final application and its unique performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| CVD Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Precursor Pyrolysis | Decompose carbon gas (e.g., methane) on a hot catalytic substrate. | Release individual carbon atoms onto the substrate surface. |
| Step 2: Lattice Formation | Carbon atoms migrate and bond into a hexagonal lattice on the substrate. | Form a continuous, one-atom-thick sheet of graphene. |
Ready to produce high-quality graphene for your research or industrial application? The precise control required for successful CVD is our specialty. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables essential for mastering the graphene production process, from high-temperature furnaces to gas handling systems. Let our experts help you achieve the wafer-scale uniformity and quality your project demands. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the catalytic CVD process? Unlock Precise Control for Advanced Materials Growth
- How does temperature affect deposition? Master the Science of Gas-to-Solid Transformation
- What is the process of chemical vapor infiltration? A Guide to Creating High-Performance CMCs
- What are the properties of diamond like carbon? Unlock Superior Surface Performance
- What is sputtering method of thin film deposition? A Guide to Precision Coating
- What are the primary advantages of the DC sputtering technique? High-Speed Coating for Industrial Scale
- How does a hollow-type dielectric window compare to a planar quartz window? Boost Plasma CVD Uniformity
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of MOCVD? Scaling High-Quality Semiconductor Production



















