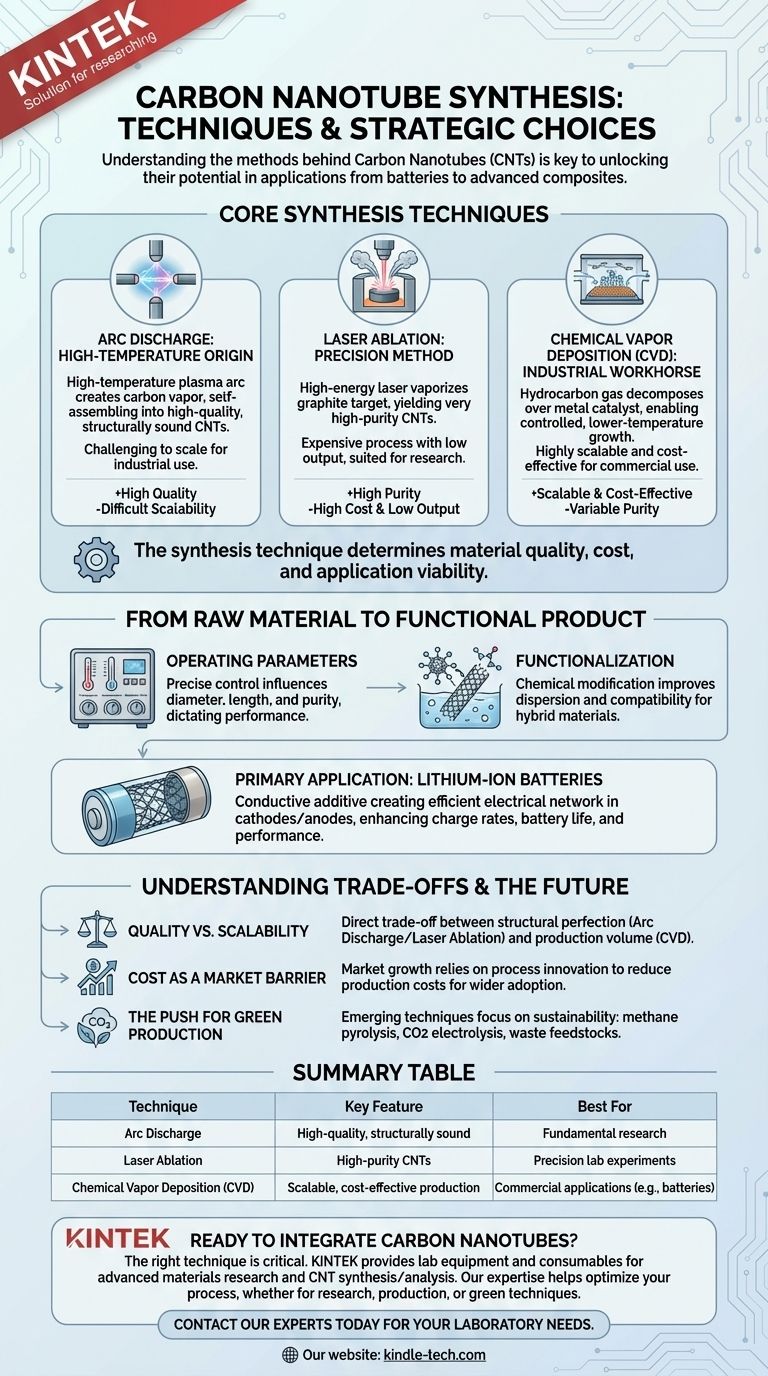
At its core, the "techniques" of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) refer to the methods used for their synthesis. The three primary techniques are arc discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While the first two are traditional methods known for producing high-quality material, CVD has become the dominant commercial process due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness.
The specific synthesis technique used to create carbon nanotubes is not merely a manufacturing choice—it is the single most important factor determining the material's quality, cost, and ultimately, its viability for any given application, from batteries to advanced composites.
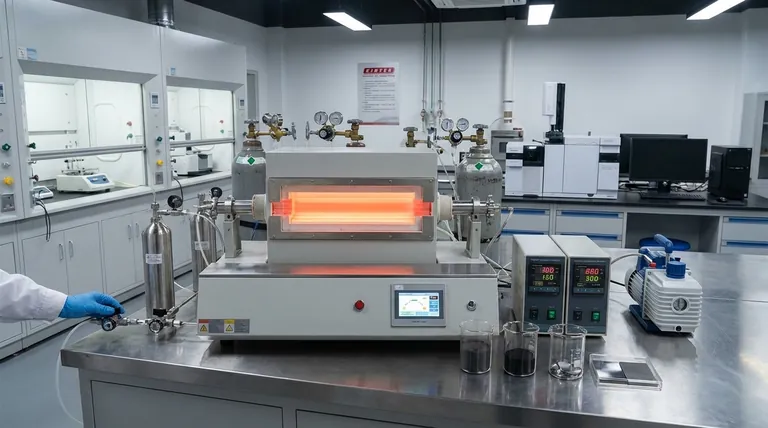

Core Synthesis Techniques Explained
Understanding how carbon nanotubes are made is the first step to understanding their potential. Each method offers a different balance of quality, quantity, and cost.
Arc Discharge: The High-Temperature Origin
This was one of the first methods used to produce CNTs. It involves creating a high-temperature plasma arc between two carbon electrodes.
As the carbon vaporizes in the arc, it cools and self-assembles into nanotubes. This technique can produce high-quality, structurally sound CNTs but is difficult to scale for industrial production.
Laser Ablation: The Precision Method
Similar to arc discharge, laser ablation uses a high-energy laser to vaporize a graphite target in a high-temperature furnace.
The resulting carbon vapor condenses to form nanotubes. While it yields very high-purity CNTs, the process is expensive and has low output, making it suitable for research but not for large-scale commercial use.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Industrial Workhorse
CVD is the most prevalent technique for commercial CNT production. It involves flowing a hydrocarbon gas (like methane) over a substrate coated with metal catalyst particles at elevated temperatures.
The catalyst breaks down the gas, and the carbon atoms reassemble into nanotubes. CVD is favored because it operates at lower temperatures and allows for much greater control over the growth process, making it highly scalable and more cost-effective.
From Raw Material to Functional Product
Simply producing raw nanotubes is not enough. The true technical challenge lies in refining and integrating them into useful materials and devices.
The Importance of Operating Parameters
The final properties of the CNTs are highly sensitive to the synthesis conditions. Factors like temperature, the concentration of the carbon source, and residence time must be precisely controlled.
These parameters directly influence the diameter, length, and purity of the nanotubes, which in turn dictates their performance in an application.
Functionalization: Unlocking Potential
As-produced CNTs are often inert and difficult to disperse in other materials like polymers or liquids. Functionalization is a secondary chemical process that attaches other molecules to the surface of the nanotubes.
This crucial step modifies their properties, making them more compatible for creating hybrid materials and conductive composites.
Primary Application: Lithium-Ion Batteries
The most significant commercial use of CNTs today is as a conductive additive in lithium-ion batteries.
Their high aspect ratio and excellent conductivity create an efficient electrical network within the battery's cathode and anode. This improves charge rates, extends battery life, and enhances overall performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CNT "technique" is a matter of navigating fundamental engineering and economic trade-offs. No single method is perfect for every goal.
Quality vs. Scalability
There is a direct trade-off between the structural perfection of the nanotubes and the volume of production.
Arc discharge and laser ablation produce higher-quality material but at a high cost and low volume. CVD offers industrial-scale volume, which is essential for applications like batteries, but may result in a wider variety of CNT types and purities.
Cost as a Market Barrier
While prices have fallen dramatically, the cost of high-performance CNTs can still be a significant barrier for their use in bulk materials like concrete or asphalt.
Market growth depends on continued process innovation to drive down production costs and enable wider adoption.
The Push for Green Production
Emerging techniques are focused on sustainability and cost reduction. These include using waste feedstocks or alternative carbon sources.
Methods like methane pyrolysis (splitting methane into hydrogen and solid carbon) or capturing CO2 via electrolysis represent the next frontier, aiming to create value from emissions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best approach depends entirely on your objective, balancing the need for purity, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Arc discharge or laser ablation will provide the high-purity material needed for controlled lab experiments.
- If your primary focus is commercial product development: Partnering with a large-scale CVD manufacturer is the only viable path to secure the volume and cost structure required for markets like batteries or conductive polymers.
- If your primary focus is next-generation sustainable technology: Investigating emerging "green" synthesis routes will be critical for developing products with a lower environmental footprint and potentially lower cost.
Ultimately, the future of carbon nanotubes hinges on successfully bridging the gap between innovative synthesis and practical, large-scale application.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Discharge | High-quality, structurally sound CNTs | Fundamental research |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity CNTs | Precision lab experiments |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Scalable, cost-effective production | Commercial applications (e.g., batteries, polymers) |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or product development?
The right synthesis technique is critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for advanced materials research, including CNT synthesis and analysis.
Our expertise can help you select the right tools to optimize your process, whether you are focused on high-purity research, scalable production, or exploring next-generation green techniques.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques



















