While the term "types of quenching" can refer to many specific techniques, the question most often points to the three distinct physical stages of heat transfer that occur during any rapid cooling process. These stages are the vapor phase, the boiling phase, and the convection phase. Understanding these stages is fundamental to controlling the outcome of any heat treatment.
The core principle to grasp is that the "three types" are not different quenching methods, but rather the universal sequence of heat transfer stages—vapor, boiling, and convection. Mastering heat treatment is not about choosing one of the three, but about controlling the timing and intensity of each stage to achieve a desired material property.
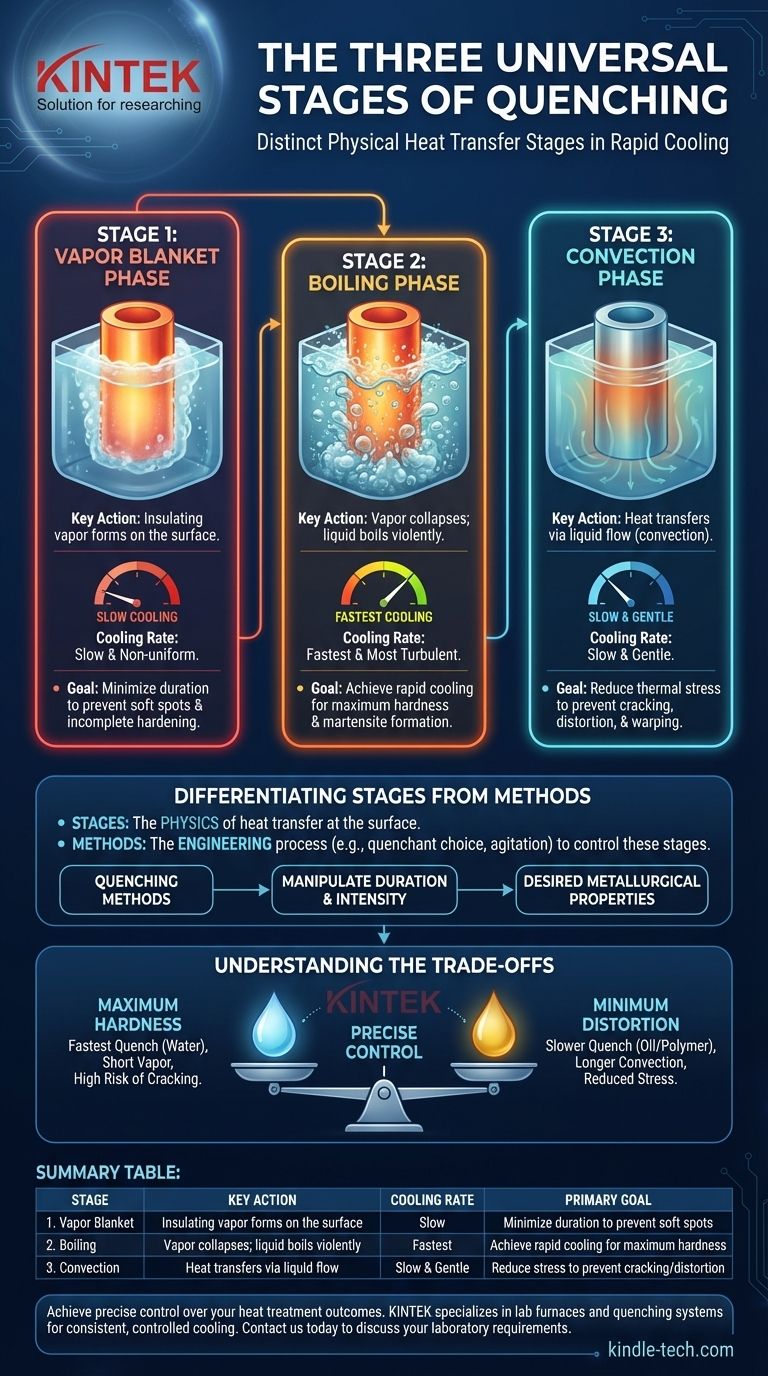
The Universal Stages of Quenching
Every time a hot component is submerged in a liquid quenchant, it passes through the same sequence of heat transfer stages. The duration and intensity of each stage dictate the final hardness, stress, and integrity of the part.
Stage 1: The Vapor Blanket Phase
When the hot metal first enters the cooler liquid, the liquid touching the surface immediately vaporizes. This creates an insulating blanket of vapor that surrounds the part.
Because vapor is a poor conductor of heat, the cooling rate during this phase is relatively slow and often non-uniform. A stable, prolonged vapor phase is generally undesirable as it can lead to soft spots and incomplete hardening.
Stage 2: The Boiling Phase
As the surface begins to cool slightly, the vapor blanket becomes unstable and collapses. This allows the liquid quenchant to make direct contact with the metal's surface, where it boils violently.
This stage produces the fastest rate of heat transfer. The turbulent boiling action rapidly pulls heat from the component, which is critical for achieving the high cooling rate needed to form martensite and harden the steel. This is the most important phase for determining final hardness.
Stage 3: The Convection Phase
Once the surface temperature of the component drops below the boiling point of the quenchant, boiling stops. Heat is now removed through liquid convection and conduction.
Cooling during this final stage is much slower and more gentle. This slow cooling helps to relieve thermal stress built up during the rapid boiling phase, reducing the risk of distortion or cracking in the finished part.
Differentiating Stages from Methods
The three stages describe the physics of what is happening at the surface. A quenching method is the engineering process used to control these stages.
What is a Quenching Method?
A quenching method is the specific technique and quenchant (e.g., water, oil, polymer, air) chosen to manipulate the three stages of cooling.
The goal is to manage the duration of each phase—for example, by minimizing the vapor phase and controlling the speed of the convection phase—to achieve precise metallurgical properties.
Common Quenching Methods
Methods like Interrupted Quenching involve pulling the part out of the quenchant before it fully cools to manipulate the convection stage and reduce stress.
Selective Quenching, such as spray or induction quenching, involves applying the quenchant to only specific areas of a part, initiating the three stages only where hardness is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The goal of quenching is to cool metal fast enough to achieve hardness but not so fast that it causes catastrophic failure. This is a balancing act.
The Risk of an Unstable Vapor Phase
A long, stable vapor phase (Stage 1) is the enemy of uniform hardness. Agitating the part or the quenchant helps collapse this vapor blanket faster, promoting a quicker transition to the critical boiling phase.
The Danger of Extreme Cooling
While rapid cooling is necessary, a cooling rate that is too severe through the final convection phase can introduce immense internal stress. This stress can cause the part to distort, warp, or even crack.
Quenchant Selection is Critical
The choice of quenchant is the primary tool for controlling the stages. Water produces a very fast quench with a short vapor phase but a high risk of cracking. Oils are less severe, offering a slower cooling rate that is more forgiving and reduces the risk of distortion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines how you should seek to control the three quenching stages.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: Your goal is to minimize the vapor phase and maximize the duration and intensity of the boiling phase, often using water or an agitated brine.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion and cracking: Your goal is to use a less severe quenchant like oil or to employ a method like interrupted quenching to slow the cooling rate during the final convection phase.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific properties in a localized area: Your goal is to use a selective method like spray quenching to apply the three-stage process only where it is needed.
By understanding the fundamental stages of heat transfer, you gain direct control over the final properties and integrity of your material.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Cooling Rate | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Vapor Blanket | Insulating vapor forms on the surface | Slow | Minimize duration to prevent soft spots |
| 2. Boiling | Vapor collapses; liquid boils violently | Fastest | Achieve rapid cooling for maximum hardness |
| 3. Convection | Heat transfers via liquid flow | Slow & Gentle | Reduce stress to prevent cracking/distortion |
Achieve precise control over your heat treatment outcomes. Understanding the three quenching stages is the first step; having the right equipment is the next. KINTEK specializes in lab furnaces, quenching systems, and consumables that provide the consistent, controlled cooling your laboratory needs. Whether your goal is maximum hardness or minimal distortion, our solutions are designed for reliability and precision. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory requirements and enhance your heat treatment processes. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature of muffle furnace? A Guide from 1100°C to 1800°C
- Why is a high-temperature drying oven required for cellulose residues? Ensure Precise Mass Balance and Dry Weight.
- What are the key functions of muffle or tube furnaces in soil remediation? Stabilize and Recover Heavy Metals Effectively
- Why is a High-Temperature Muffle Furnace used for 600°C TiO2 Calcination? Optimize Catalyst Purity and Phase Stability
- What is the function of a high-temperature air annealing furnace? Restore Stoichiometry in Eu:Y2O3 Ceramics
- Why is a high-quality high-temperature furnace required for YSZ electrolytes? Achieve Dense, High-Conductivity Ceramics
- What is the primary function of high-temperature muffle or tube furnaces for ceramic coatings? Ensure Peak Durability
- What are the features of a laboratory electric furnace? Precision, Speed, and Safety for Your Lab



















