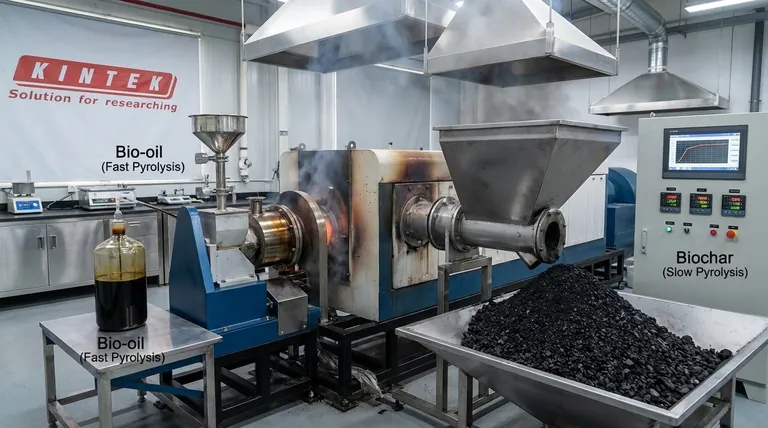
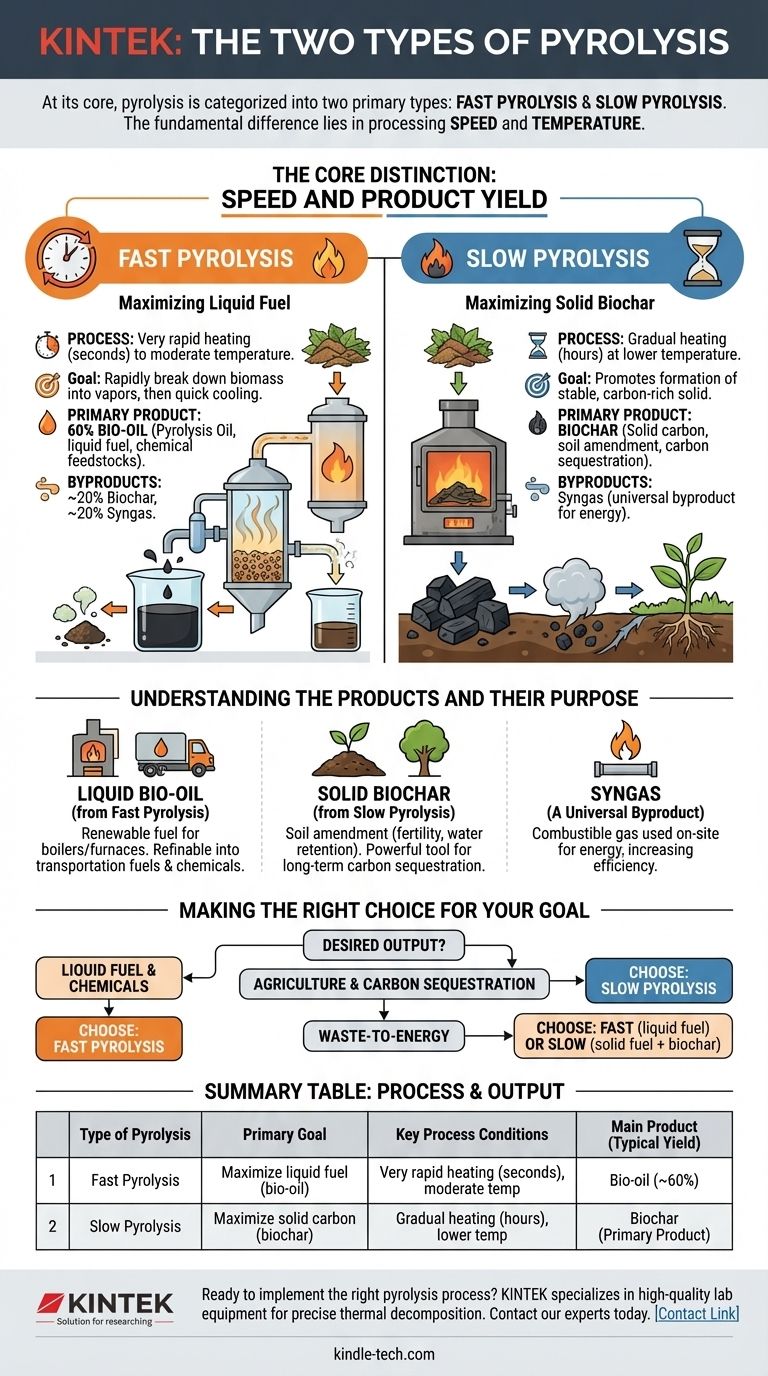
At its core, pyrolysis is categorized into two primary types: fast pyrolysis and slow pyrolysis. The fundamental difference between them lies in the processing speed and temperature, which in turn dictates the primary product you create. Fast pyrolysis is completed in seconds to maximize liquid bio-oil, while slow pyrolysis takes hours to maximize solid biochar.
The choice between fast and slow pyrolysis is not arbitrary; it's a strategic decision. Your end goal—whether to produce liquid fuel or a solid carbon product—determines which process is the correct one to use.

The Core Distinction: Speed and Product Yield
The rate at which you heat the organic material (feedstock) is the most critical variable. This heating rate directly influences whether the output is predominantly a liquid, a solid, or a gas.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Fuel
Fast pyrolysis involves heating organic material very quickly (in seconds) to a moderate temperature in an oxygen-free environment. The goal is to rapidly break down the biomass into vapors.
These vapors are then cooled just as quickly to condense them into a dark, viscous liquid known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
A typical yield from fast pyrolysis is approximately 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% syngas, making it the preferred method for creating liquid fuels.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solid Biochar
Slow pyrolysis is a much longer process, often taking several hours at a lower temperature. This gradual heating promotes the formation of a stable, carbon-rich solid.
This solid product is called biochar (or charcoal when derived from wood). It is the primary output of this process.
Because the reactions are slow, more of the carbon remains in a solid structure rather than being vaporized, maximizing the biochar yield.
Understanding the Products and Their Purpose
Each pyrolysis type is optimized for a specific output. Understanding the use case for each product is key to selecting the right process.
Liquid Bio-oil (from Fast Pyrolysis)
Bio-oil is a complex mixture that can be used as a renewable fuel for boilers and furnaces.
It can also be refined further into higher-grade transportation fuels or processed to extract valuable platform chemicals.
Solid Biochar (from Slow Pyrolysis)
Biochar is a highly porous and stable form of carbon. Its primary use is as a soil amendment to improve fertility and water retention in agriculture.
It is also a powerful tool for carbon sequestration, as it locks carbon into a solid form that resists decomposition for hundreds or thousands of years.
Syngas (A Universal Byproduct)
Both fast and slow pyrolysis produce a non-condensable gas called syngas.
This gas is combustible and is almost always used on-site to provide the heat energy required to run the pyrolysis plant itself, making the overall process more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process vs. Equipment
It is easy to get confused by the many technical terms surrounding pyrolysis. The most important distinction to make is between the process type and the equipment used to achieve it.
The Process Defines the Goal (Fast vs. Slow)
The decision to use fast or slow pyrolysis is the highest-level strategic choice. It is entirely based on whether you want to produce primarily liquid bio-oil or solid biochar.
Equipment Enables the Process (Reactors & Furnaces)
Terms like fluidized-bed, rotary kiln, or batch furnace refer to the specific machinery used to implement the process.
For example, a fluidized-bed reactor is excellent for the rapid heat transfer needed in fast pyrolysis. A simpler batch kiln is perfectly suitable for the gradual heating required for slow pyrolysis. This equipment is the means to an end, not a type of pyrolysis itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice must be driven by your desired output. A process optimized for one product is inherently suboptimal for the other.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuel or chemical feedstocks: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary approach to maximize bio-oil yield.
- If your primary focus is creating a stable solid for agriculture or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the optimal method to maximize biochar production.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: Both methods are valid, but fast pyrolysis generates a transportable liquid fuel while slow pyrolysis creates a solid fuel and a valuable co-product (biochar).
Understanding this fundamental choice between speed and output empowers you to select the correct thermal decomposition strategy for your specific material and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Type of Pyrolysis | Primary Goal | Key Process Conditions | Main Product (Typical Yield) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize liquid fuel (bio-oil) | Very rapid heating (seconds), moderate temperature | Bio-oil (~60%) |
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize solid carbon (biochar) | Gradual heating (hours), lower temperature | Biochar (Primary Product) |
Ready to implement the right pyrolysis process for your laboratory or production needs? The choice between fast and slow pyrolysis is critical for achieving your target product yield. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and reactors necessary for precise thermal decomposition research and development. Whether you're optimizing for bio-oil or biochar production, our expertise can help you select the right system. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas














