At its core, an electric arc furnace (EAF) can be classified along two primary axes: the type of electrical current it uses and the method by which it transfers heat to the material. The most common types are Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) furnaces, which primarily use a direct arc heating method. A less common indirect arc method is used for more specialized applications.
The choice between furnace types is not about which is universally "better," but which is best suited for a specific operational goal. The decision balances initial capital cost against long-term operating efficiency, energy consumption, and the material being processed.

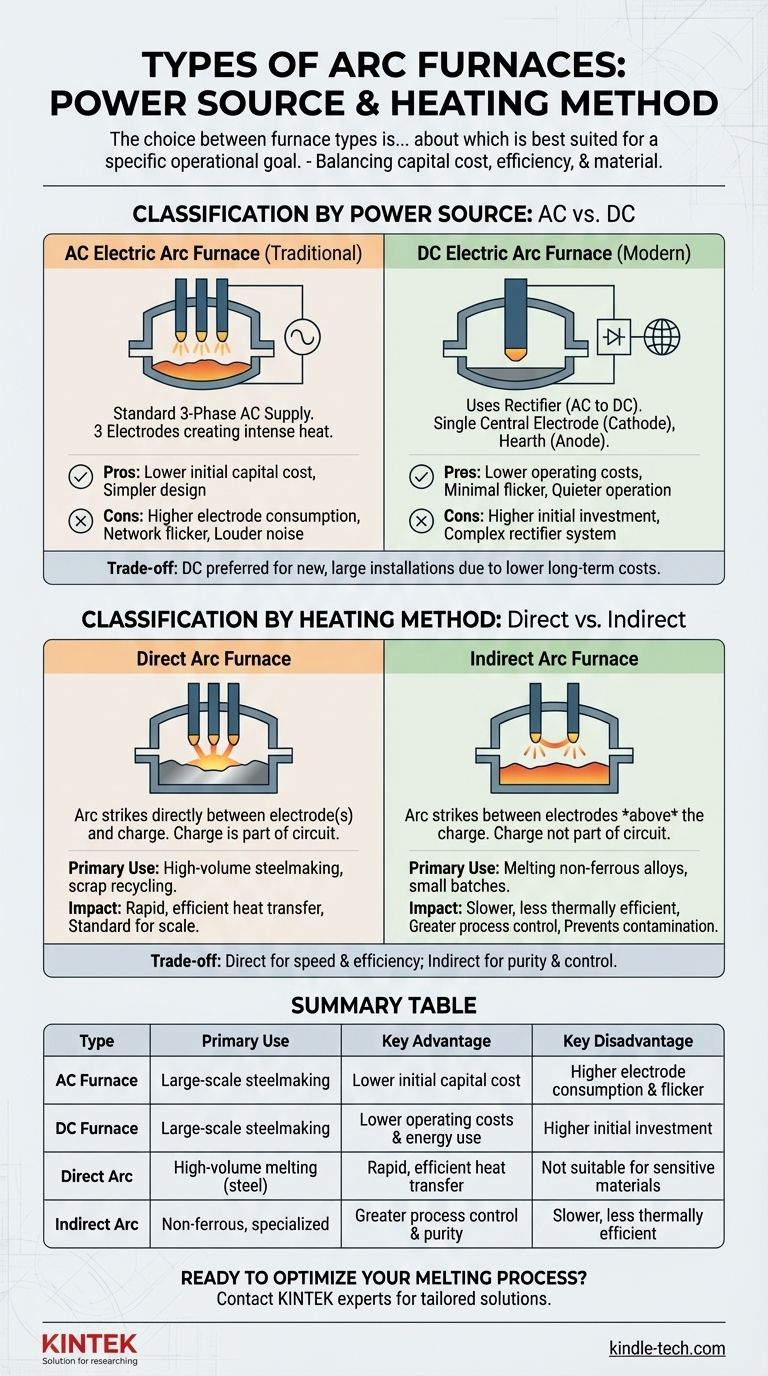
Classification by Power Source: AC vs. DC
The most fundamental distinction in modern arc furnaces is the electrical power system they employ. This choice has significant downstream effects on cost, efficiency, and environmental impact.
The AC Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
The traditional and historically more common design is the AC furnace. It operates using a standard three-phase alternating current power supply.
Three separate graphite electrodes are lowered into the furnace, one for each phase of the electrical supply. The powerful arc forms between the tips of these electrodes and the metallic charge (scrap metal) below, creating intense heat.
The DC Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
The DC furnace is a more modern evolution of the technology. It uses a rectifier to convert AC power from the grid into DC power.
This design typically uses a single, large graphite electrode at the center of the furnace as the cathode. An electrical connection in the bottom of the furnace hearth acts as the anode, and the arc forms between the central electrode and the charge.
Classification by Heating Method: Direct vs. Indirect
The second classification describes how the arc's energy is physically delivered to the charge. This distinction defines the furnace's primary application.
The Direct Arc Furnace
In a direct arc furnace, the arc is struck directly between the electrode(s) and the metallic charge. The material itself becomes part of the electrical circuit.
This direct contact provides extremely rapid and efficient heat transfer, making it the standard method for high-volume steelmaking and scrap recycling. Both AC and DC furnaces used for steel production are almost exclusively direct arc designs.
The Indirect Arc Furnace
In an indirect arc furnace, the arc is struck between two electrodes positioned above the charge. The charge is not part of the electrical circuit.
Heat is transferred to the material primarily through radiation from the arc and the furnace's refractory lining. This method is slower and less thermally efficient but offers greater control and prevents the charge from being contaminated by the arc. It is used for melting non-ferrous alloys and in smaller, laboratory-scale applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each design presents a unique set of operational advantages and disadvantages. The industry has trended toward DC technology for new, large-scale installations due to its lower operating costs.
AC Furnace: Pros and Cons
The primary advantage of an AC furnace is its lower initial capital cost and simpler design, as it does not require an expensive rectifier system.
However, its operation results in higher electrode consumption, more disruptive electrical network flicker, and significantly louder noise levels compared to a DC furnace.
DC Furnace: Pros and Cons
A DC furnace's main benefits are its operational efficiencies. It boasts lower electrode and energy consumption, creates minimal network flicker, and operates much more quietly.
The main disadvantage is the higher initial investment required for the high-power rectifier and more complex overall system.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating Impact
The choice here is dictated almost entirely by the application. Direct heating is unmatched in speed and energy efficiency for melting steel at scale. Indirect heating is chosen when process purity is critical and direct contact with the powerful arc would be detrimental to the final product's chemistry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of arc furnace technology is a strategic decision that should align directly with your production priorities and financial model.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production with maximum efficiency: A modern DC Direct Arc Furnace is the superior choice due to its lower long-term operating costs and reduced impact on the power grid.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital investment for steelmaking: A traditional AC Direct Arc Furnace remains a viable and proven option, though you must account for higher consumption of electrodes and energy.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals or small, specialized batches: An Indirect Arc Furnace provides the necessary process control and purity, protecting the material from direct arc contact.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental classifications empowers you to select the technology that best serves your specific operational and financial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Type | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Furnace | Large-scale steelmaking | Lower initial capital cost | Higher electrode consumption & network flicker |
| DC Furnace | Large-scale steelmaking | Lower operating costs & energy use | Higher initial investment |
| Direct Arc | High-volume melting (steel, scrap) | Rapid, efficient heat transfer | Not suitable for sensitive materials |
| Indirect Arc | Non-ferrous metals, specialized batches | Greater process control & purity | Slower, less thermally efficient |
Ready to optimize your melting process? The right arc furnace technology is critical for achieving your production goals in efficiency, cost, and material quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your application, whether it's for large-scale steelmaking or specialized metal melting. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treat furnace work? Achieve Pristine, Oxide-Free Metal Parts
- What kind of material is full annealing applied to? Optimize Steel for Maximum Machinability
- What is the significance of using high-vacuum heat treatment furnaces and rapid quenching for zirconium alloys?
- How does annealing change the properties of a metal? Restore Workability and Improve Performance
- Why is a vacuum high-temperature furnace essential for XTO silicification? Ensure Pure Coating for Refractory Metals
- What are the 4 heating techniques used for brazing? Find Your Ideal Method for Stronger Joints
- What is the temperature of a kiln? It Depends on Your Process and Kiln Type
- What is the annealing temperature of molybdenum? Optimize Your Thermal Processing for Pure Mo & Alloys



















