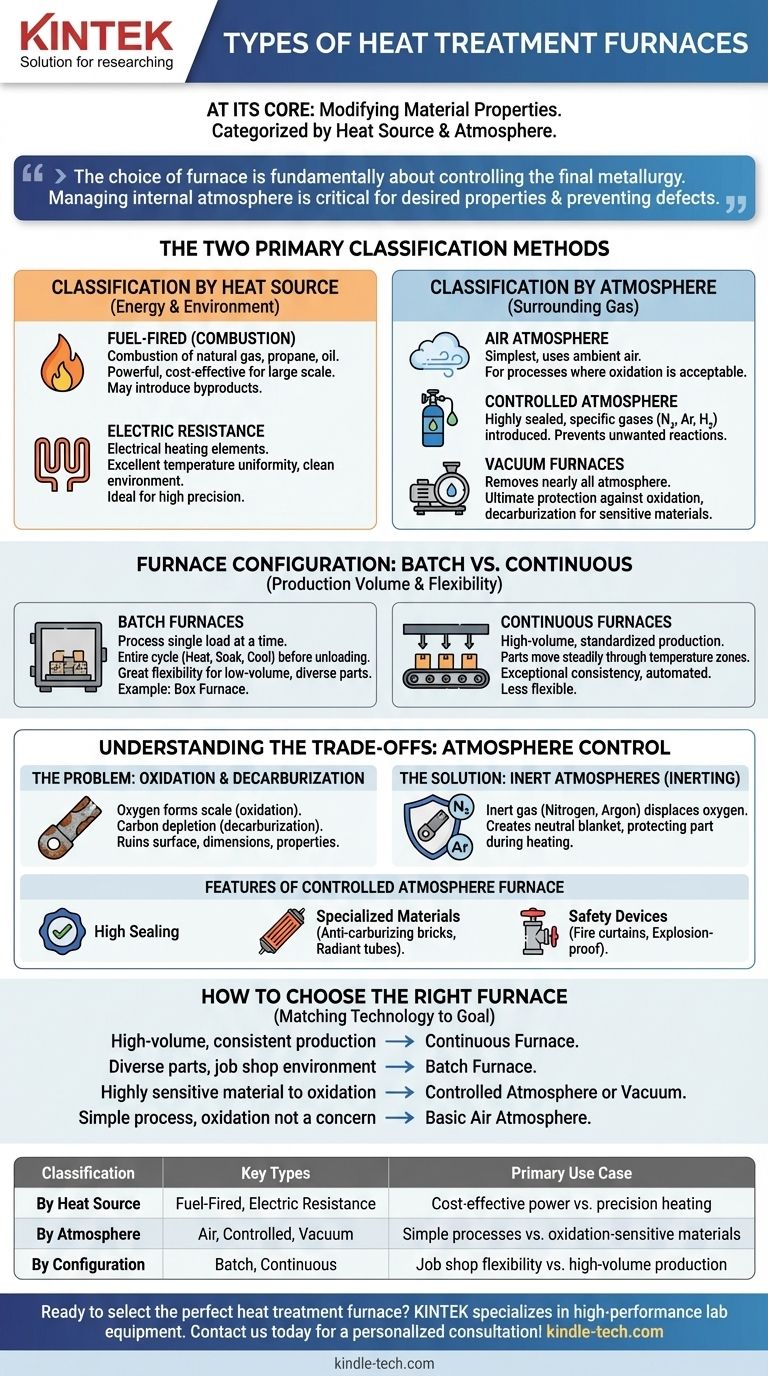
At its core, a heat treatment furnace is a tool for modifying a material's properties, and they are primarily categorized by their heat source and the type of atmosphere they use. The main types are fuel-fired or electric furnaces, which can operate with a simple air atmosphere, a precisely controlled atmosphere using gases like nitrogen, or a vacuum to prevent any surface reactions.
The choice of a heat treatment furnace is fundamentally a decision about controlling the final metallurgy of a part. While factors like heat source and configuration matter, the furnace's ability to manage its internal atmosphere is the most critical element in achieving desired properties and preventing defects like oxidation.

The Two Primary Classification Methods
To select the right furnace, you must first understand the two fundamental ways they are differentiated: how they generate heat and what environment they create around the part.
Classification by Heat Source
The energy source directly impacts temperature uniformity, operational cost, and the furnace environment.
- Fuel-Fired (Combustion) Furnaces: These use the combustion of natural gas, propane, or oil to generate heat. They can be very powerful and cost-effective for large-scale operations but can introduce combustion byproducts into the furnace atmosphere if not designed as an "indirect-fired" system.
- Electric Resistance Furnaces: These use electrical heating elements to generate radiant heat. They offer excellent temperature uniformity and a clean heating environment, making them ideal for processes requiring high precision.
Classification by Atmosphere
The atmosphere is the gas (or lack thereof) surrounding the part during the heating cycle. It is the single most important factor for controlling surface chemistry.
- Air Atmosphere Furnaces: These are the simplest type, using the ambient air inside the furnace. They are suitable for processes where surface oxidation is not a concern or is even desired.
- Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces: These are designed to be highly sealed. They allow for the introduction of specific gases—such as nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen—to create a precisely managed environment. This is essential for preventing unwanted reactions.
- Vacuum Furnaces: For the highest level of protection, vacuum furnaces remove nearly all atmosphere. This is the ultimate way to prevent oxidation and decarburization, critical for sensitive materials like titanium alloys and high-purity tool steels.
Furnace Configuration: Batch vs. Continuous
Beyond heat and atmosphere, furnace design is categorized by how material moves through it. This choice is driven entirely by production volume and part variety.
Batch Furnaces
Batch furnaces process a single part or a single load of parts at a time. The entire thermal cycle—heating, soaking, and cooling—occurs before the furnace is opened and the load is removed.
A classic example is the box furnace. They offer great flexibility for processing parts of different sizes and thermal requirements, making them ideal for low-volume production, job shops, or research and development.
Continuous Furnaces
Continuous furnaces are designed for high-volume, standardized production. Parts are loaded onto a conveyor (like a mesh belt or rollers) and move steadily through different temperature zones within the furnace.
This configuration ensures every part sees the exact same thermal cycle, leading to exceptional consistency. They are highly automated and efficient but lack the flexibility of batch furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Need for Atmosphere Control
The decision to use a more complex and expensive controlled atmosphere furnace comes down to protecting the material from harm.
The Problem: Unwanted Surface Reactions
When steel is heated in the presence of oxygen, it forms an oxide layer, or scale. This is known as oxidation.
Furthermore, the carbon within the steel can react with the atmosphere and be depleted from the surface, a process called decarburization. Both of these phenomena can ruin a part's surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties.
The Solution: Inert Atmospheres
To prevent these reactions, an inert atmosphere is used to displace the oxygen. As noted in process documentation, this is typically achieved by purging the furnace with nitrogen or argon.
These gases are non-reactive and create a neutral blanket around the part, protecting it throughout the high-temperature cycle. This process is often referred to as inerting.
Features of a Controlled Atmosphere Furnace
To maintain this protective environment, these furnaces require specific design features:
- High Sealing: The furnace chamber must be exceptionally well-sealed to prevent the expensive controlled atmosphere from leaking out and, more importantly, to stop air from leaking in.
- Specialized Materials: Refractory bricks must be anti-carburizing to avoid reacting with the atmosphere. Heating elements are often contained within radiant tubes to separate them from the process atmosphere.
- Safety Devices: Because process gases can be flammable (like hydrogen) or pose an asphyxiation risk (like nitrogen), these furnaces are equipped with fire curtains at openings and explosion-proof devices to ensure safe operation.
How to Choose the Right Furnace
Your choice should be guided by your material, your production volume, and your final quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: A continuous furnace (like a mesh belt or roller hearth) is the most efficient choice.
- If you process diverse parts with varying requirements: A batch furnace (like a box furnace) offers the necessary flexibility for a job shop environment.
- If your material is highly sensitive to oxidation (e.g., tool steel, titanium): You must use a controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnace to protect its surface integrity.
- If your process is simple and surface oxidation is not a concern: A basic air atmosphere electric or fuel-fired furnace is the most cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the technology to your specific metallurgical goal.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| By Heat Source | Fuel-Fired, Electric Resistance | Cost-effective power vs. precision heating |
| By Atmosphere | Air, Controlled, Vacuum | Simple processes vs. oxidation-sensitive materials |
| By Configuration | Batch, Continuous | Job shop flexibility vs. high-volume production |
Ready to select the perfect heat treatment furnace for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including batch, continuous, and controlled atmosphere furnaces designed to protect your materials and ensure precise results. Our experts can help you choose the right technology to achieve your metallurgical goals. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between thermal evaporation and molecular beam epitaxy? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How do you make THC isolate from distillate? Master the Advanced Lab Purification Process
- What are the two important principles of heat treatment? Achieve Optimal Material Properties for Your Lab
- What features should be considered when choosing an ultra low temperature freezer? Secure Your Samples with Precision
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis plant? Turn Waste into Profit with Advanced Recycling
- What is the most common heat treatment process to increase hardness? Mastering Steel Hardening & Tempering
- How does biochar improve water quality? An Engineered Solution for Contaminant Removal
- What are the driving forces of sintering? Understanding the Thermodynamics for Better Materials



















