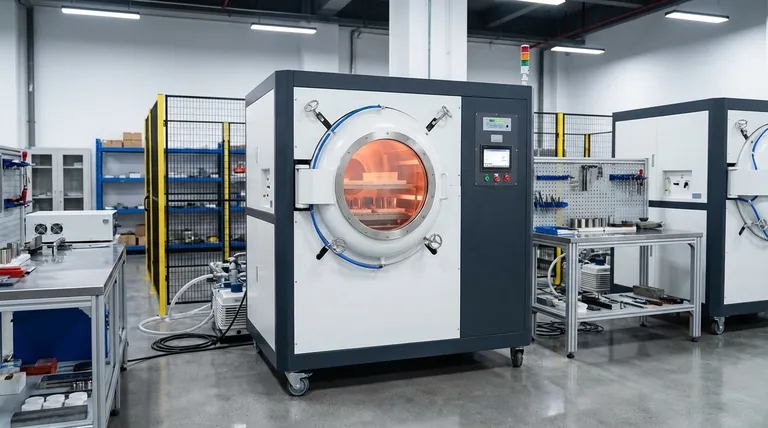
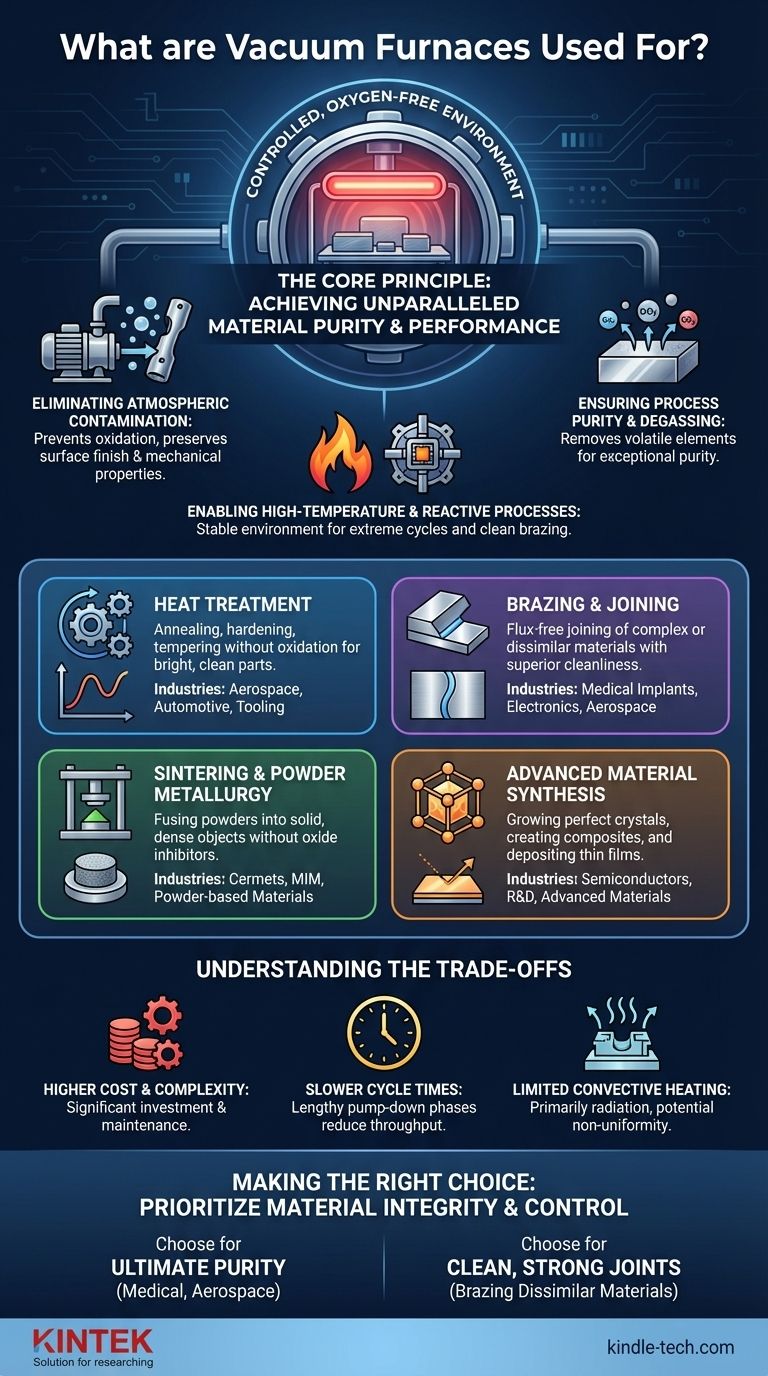
In essence, a vacuum furnace is a specialized high-temperature chamber used for processing materials in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. Its applications span dozens of industries, from aerospace and medical to electronics and energy. The most common processes include the heat treatment of metals, brazing complex assemblies, and sintering powdered materials into solid parts.
The true value of a vacuum furnace isn't just the heat it provides, but the atmosphere it removes. By eliminating air and other contaminants, it prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, enabling a level of material purity and performance that is impossible to achieve in a standard atmospheric furnace.

The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for ultimate control over the material's environment during heating. The vacuum itself is not the tool; it is the perfectly clean slate that allows the thermal process to work without interference.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
When metals are heated in the presence of air, they react with oxygen and nitrogen. This reaction, known as oxidation, creates a brittle, discolored scale on the surface that can compromise the part's integrity and dimensions.
A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases before heating begins. This protects the material's surface finish and ensures its chemical and mechanical properties remain unchanged.
Ensuring Process Purity and Degassing
Many advanced materials, especially for medical or electronic applications, can be contaminated by trace gases or vapors. The vacuum actively pulls these volatile elements out of the material itself in a process called degassing.
This ensures the final product is exceptionally pure and free from internal contaminants that could cause failure later in its life.
Enabling High-Temperature and Reactive Processes
Some advanced materials and alloys require processing temperatures so high that they would be instantly destroyed by air. A vacuum provides a stable, non-reactive environment for these extreme thermal cycles.
It also enables processes like vacuum brazing, where filler metal is drawn into a joint with exceptional cleanliness, creating a bond that is often stronger than the parent materials.
Key Industrial Applications
While the principles are universal, the applications are highly specific and tailored to industry needs. A vacuum furnace is chosen when the outcome must be precise, clean, and repeatable.
Heat Treatment
This is one of the most common uses. Processes like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering (toughening) are performed in a vacuum to prevent surface scaling and decarburization. The result is a bright, clean part that often requires no post-process cleaning.
Brazing and Joining
Vacuum brazing is used to join complex or dissimilar materials, such as metals to ceramics. Because the vacuum environment is so clean, no corrosive chemical fluxes are needed. This is critical for manufacturing medical implants, aerospace components, and electronic devices like X-ray tubes.
Sintering and Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is the process of fusing fine powders into a solid, dense object using heat. Performing this in a vacuum prevents the formation of oxides on individual powder grains, which would inhibit a strong, fully dense bond. This is fundamental to creating cermets, metal injection molded (MIM) parts, and other powder-based materials.
Advanced Material Synthesis
Vacuum furnaces are essential tools in research and development and for manufacturing next-generation materials. This includes growing perfect single crystals for the semiconductor industry, creating carbon-carbon composites for high-performance brakes, and depositing thin films onto surfaces (Chemical Vapor Deposition).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to atmospheric furnaces. They require a system of pumps, seals, and advanced controls, which also increases maintenance complexity and cost.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time. The "pump-down" phase before the heating cycle can be lengthy, which may reduce overall throughput in a high-volume production environment.
Limited Convective Heating
In a vacuum, heat is primarily transferred through radiation, not convection (movement of hot gas). This can lead to slower heating rates and potential non-uniformity with complex part geometries, requiring careful furnace design and part placement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be based entirely on the required properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and performance (e.g., medical implants, aerospace turbines): A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and ensure reliability.
- If your primary focus is creating clean, strong joints between complex or dissimilar materials: Vacuum brazing provides superior results compared to any atmospheric process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume heat treatment where a clean finish is not critical: An atmospheric furnace may be a more cost-effective and faster solution, provided you can accommodate post-process cleaning.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize material integrity and process control above all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Prevents oxidation, eliminates scaling | Aerospace, Automotive, Tooling |
| Brazing | Flux-free joining of dissimilar materials | Medical Implants, Electronics, Aerospace |
| Sintering | Creates fully dense, high-strength parts | Powder Metallurgy, Cermets, MIM |
| Material Synthesis | Enables growth of ultra-pure crystals and composites | Semiconductors, R&D, Advanced Materials |
Ready to achieve unparalleled material purity and performance in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance vacuum furnaces tailored for demanding laboratory applications. Whether you're developing next-generation medical implants, sintering advanced ceramics, or conducting critical R&D, our equipment ensures the contamination-free environment your work requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can solve your specific material processing challenges and elevate your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance



















