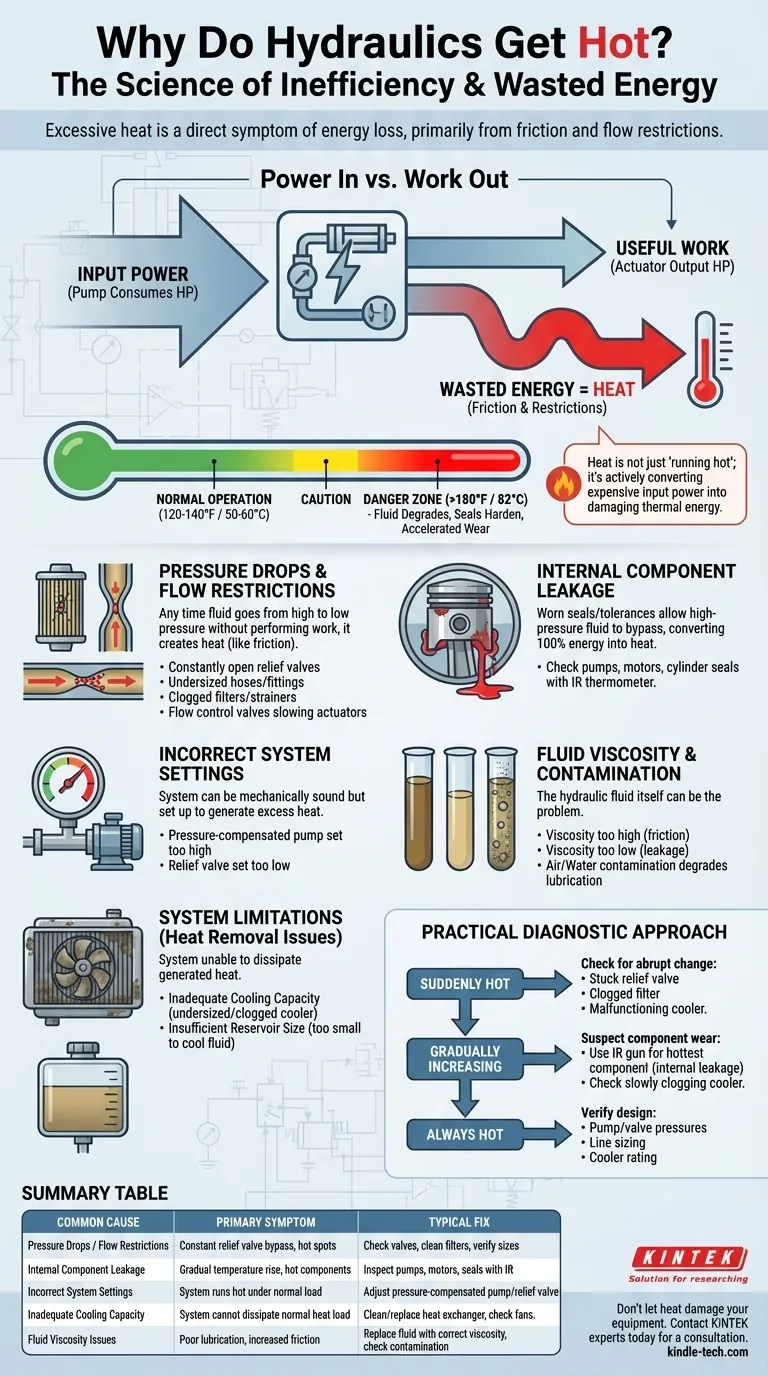
At its core, excessive heat in a hydraulic system is a direct symptom of wasted energy. Every hydraulic system is designed to transmit power, but inefficiencies cause some of that power to be converted into heat instead of useful work. This heat is primarily generated by friction and flow restrictions that force the system's pump to work harder than necessary.
A hydraulic system generating excessive heat is not just running hot; it is actively converting expensive input power into damaging thermal energy. Understanding that heat is a measurement of inefficiency is the first step to diagnosing the root cause and protecting the system.

The Fundamental Principle: Energy and Inefficiency
A hydraulic system's purpose is to move energy from a prime mover (like an electric motor or diesel engine) to an actuator to perform work. Heat is the unavoidable byproduct of this energy transfer.
Power In vs. Work Out
No mechanical system is 100% efficient. The difference between the input horsepower consumed by the pump and the output horsepower delivered by the actuator is lost, primarily as heat. A well-designed system typically operates at 80-90% efficiency.
A significant drop in efficiency means a significant increase in heat generation.
Defining "Excessive" Heat
Most hydraulic systems are designed to operate in a range of 120-140°F (50-60°C).
Operation above 180°F (82°C) is a critical danger zone. At this temperature, hydraulic fluid begins to degrade rapidly, seals harden, and the viscosity drops, which accelerates component wear and internal leakage, creating even more heat in a vicious cycle.
Locating the Sources of Heat Generation
The key to solving an overheating problem is to find where the energy loss is occurring. The heat is a symptom; the energy loss is the disease.
Pressure Drops and Flow Restrictions
This is the most common cause of heat. Any time fluid is forced from an area of high pressure to low pressure without performing useful work, the pressure drop is converted directly into thermal energy.
Think of it like rubbing your hands together vigorously—the friction and resistance create heat. The same happens with fluid molecules under pressure.
Common culprits include:
- Relief valves that are constantly open.
- Flow control valves used to slow actuators.
- Undersized hoses, tubes, or fittings that restrict flow.
- Clogged filters or strainers.
Internal Component Leakage
As components wear, internal seals and tolerances degrade. This allows high-pressure fluid to leak past its intended path directly back to the reservoir or to the low-pressure side of the component.
This internal bypass does no work and converts 100% of its energy into heat. Key components to check for wear are pumps, motors, and cylinder piston seals. An infrared thermometer can often detect a worn component, as it will be significantly hotter than other parts of the system.
Incorrect System Settings
A system can be mechanically sound but still generate excess heat due to improper settings.
The most common error is a pressure-compensated pump set to a much higher pressure than the system requires. The pump will work to maintain this high pressure, and any unused energy is wasted as heat. Similarly, a relief valve set too low will cause fluid to bypass constantly, generating heat.
Fluid Viscosity and Contamination
The hydraulic fluid itself can be the problem. If the oil's viscosity is too high (too thick), it creates excess friction as it moves through the system.
If the viscosity is too low (too thin), it increases internal leakage across component clearances. Both scenarios generate unnecessary heat. Likewise, air or water contamination degrades the fluid's lubricating properties and ability to transfer heat efficiently.
Understanding the System's Limitations
Sometimes, the heat isn't from a fault but from a design or maintenance issue related to heat removal. The system is simply unable to dissipate the heat it generates, even under normal conditions.
Inadequate Cooling Capacity
The heat exchanger, or "cooler," may be the bottleneck. An undersized cooler cannot reject the thermal load produced by the system during normal operation.
More commonly, an existing cooler becomes inefficient. For an air-over-oil cooler, the cooling fins can become clogged with dirt and debris, preventing airflow. For a water-based cooler, internal passages can become blocked by scale or sludge.
Insufficient Reservoir Size
The reservoir's primary job is to store fluid, but it is also the system's primary passive heat dissipator. A reservoir that is too small for the system's thermal load will not provide enough surface area or dwell time for the fluid to cool naturally.
A Practical Diagnostic Approach
To fix an overheating issue, you must move from symptom to cause. Use this framework to guide your investigation.
- If your system suddenly started overheating: Check for an abrupt change. The most likely causes are a stuck-open relief valve, a clogged filter, or a malfunctioning cooler (e.g., a dead fan or clogged fins).
- If your system's temperature has been gradually increasing: Suspect component wear. Use an infrared temperature gun to find the hottest component, which is likely the source of internal leakage. Also, check for a slowly clogging cooler.
- If your system has always run hot since it was built or modified: The problem is likely in the fundamental design. Verify that the pump and relief valve pressures are set correctly, check that lines and valves are sized properly for the required flow, and confirm the cooler is rated for the system's thermal load.
By treating heat as a sign of inefficiency, you can diagnose and solve the underlying problem, restoring the system's performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Common Cause of Overheating | Primary Symptom | Typical Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Drops / Flow Restrictions | Constant relief valve bypass, hot spots | Check valves, clean filters, verify line sizes |
| Internal Component Leakage | Gradual temperature rise, hot components | Inspect pumps, motors, seals with IR thermometer |
| Incorrect System Settings | System runs hot under normal load | Adjust pressure-compensated pump or relief valve settings |
| Inadequate Cooling Capacity | System cannot dissipate normal heat load | Clean or replace heat exchanger, check fan operation |
| Fluid Viscosity Issues | Poor lubrication, increased friction | Replace fluid with correct viscosity, check for contamination |
Is Your Hydraulic System Running Dangerously Hot?
Overheating is more than an inconvenience—it's a sign of costly inefficiency and impending component failure. KINTEK specializes in precision lab and industrial equipment, including hydraulic system components and diagnostic tools. Our expertise helps you:
- Identify the root cause of overheating with reliable measurement tools.
- Source high-quality replacement parts to restore system efficiency.
- Prevent future issues with proper maintenance and fluid management solutions.
Don't let heat damage your equipment and productivity. Contact our experts today for a consultation tailored to your hydraulic system's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps? Achieve Clean, Low-Maintenance Vacuum
- What factors should be considered when selecting an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump? A Guide to Optimal Performance & Longevity
- How does an oil-free diaphragm vacuum pump work? A Guide to Clean, Contamination-Free Vacuum
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- How does the working of oil-free diaphragm vacuum pumps differ from conventional pumps? A Guide to Clean vs. Deep Vacuum


















