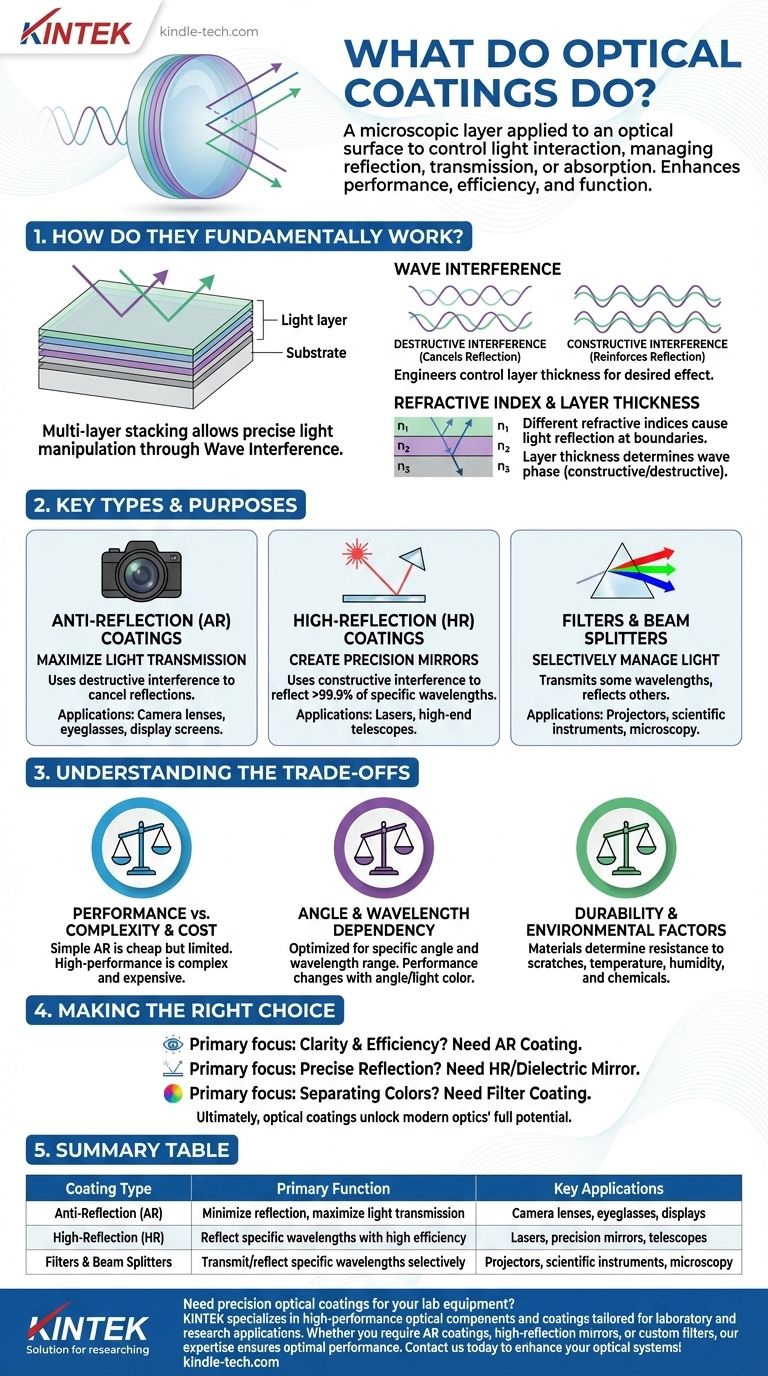
At its core, an optical coating is a microscopic layer of material applied to an optical surface, like a lens or mirror, to precisely control how it interacts with light. By managing the reflection, transmission, or absorption of specific light wavelengths, these coatings dramatically enhance the performance, efficiency, and function of any optical system they are a part of.
The true purpose of an optical coating is not just to cover a surface, but to use the physics of light wave interference to solve a specific problem—whether that's eliminating glare from a camera lens, creating a perfect mirror for a laser, or filtering specific colors for a scientific instrument.

How Do Optical Coatings Fundamentally Work?
The sophisticated performance of modern optical coatings comes from stacking multiple, incredibly thin layers of different materials. This multi-layer design allows for precise manipulation of light.
The Principle of Wave Interference
Light behaves as a wave. When a light wave hits the surface of a coating, some of it reflects. When it hits the next layer, some of it reflects again.
By carefully controlling the thickness of these layers, engineers can ensure that the reflected waves either cancel each other out (destructive interference) or reinforce each other (constructive interference).
The Role of Refractive Index
Each layer of material has a different refractive index, which is a measure of how much it slows down light passing through it.
The boundary between two layers with different refractive indices is what causes light to reflect. Alternating between high and low-index materials is the key to creating the interference effects needed for high performance.
The Importance of Layer Thickness
The thickness of each layer is meticulously controlled, often to a precision of a quarter or half of a specific wavelength of light.
This precise thickness dictates the path length the light travels, determining whether the reflected waves will be in-phase (constructive) or out-of-phase (destructive) when they recombine.
Key Types of Optical Coatings and Their Purpose
While the underlying principle is the same, optical coatings are designed to achieve very different goals.
Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings: Maximizing Light Transmission
The most common type of coating, AR coatings, are designed to create destructive interference for reflected light.
This cancels out reflections and glare, allowing more light to pass through the optic. This is critical for camera lenses, eyeglasses, and display screens, where maximum clarity and brightness are essential.
High-Reflection (HR) Coatings: Creating Precision Mirrors
Conversely, HR coatings (or dielectric mirrors) are engineered for constructive interference.
They stack layers in a way that causes reflected light waves to reinforce each other, creating a mirror that can reflect over 99.9% of light at specific wavelengths. These are vital for lasers and high-end telescopes.
Filters and Beam Splitters: Selectively Managing Light
These advanced coatings are designed to transmit certain wavelengths while reflecting others.
A dichroic filter, for example, can reflect blue light while letting red and green light pass through. This capability is foundational for projectors, fluorescence microscopy, and other instruments that need to separate colors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or designing an optical coating involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" coating for all situations.
Performance vs. Complexity and Cost
A simple, single-layer AR coating is inexpensive but offers limited performance over a narrow range of colors.
A high-performance, multi-layer broadband AR coating is far more effective across the visible spectrum but requires dozens of precisely deposited layers, making it significantly more complex and expensive.
Angle and Wavelength Dependency
The performance of a coating is optimized for a specific range of wavelengths and a specific angle of incidence (the angle at which light strikes the surface).
A coating designed to be anti-reflective for visible light hitting head-on may become highly reflective for the same light coming in at a 45-degree angle or for infrared light.
Durability and Environmental Factors
The materials used for the coating layers determine the optic's resistance to scratching, temperature shifts, humidity, and chemical exposure. A durable coating for a military application will have different materials and trade-offs than one used in a protected lab environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal coating is dictated entirely by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is clarity and efficiency (e.g., camera lenses, display screens): You need an Anti-Reflection (AR) coating to minimize glare and maximize light throughput.
- If your primary focus is precise reflection (e.g., lasers, specialized telescopes): You need a High-Reflection (HR) or dielectric mirror coating to reflect specific wavelengths with minimal loss.
- If your primary focus is separating colors or wavelengths (e.g., scientific instruments, projectors): You need a filter coating, like a dichroic or bandpass filter, to transmit some light while reflecting others.
Ultimately, optical coatings are the invisible technology that unlocks the full potential of modern optics.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection (AR) | Minimize reflection, maximize light transmission | Camera lenses, eyeglasses, displays |
| High-Reflection (HR) | Reflect specific wavelengths with high efficiency | Lasers, precision mirrors, telescopes |
| Filters & Beam Splitters | Transmit/reflect specific wavelengths selectively | Projectors, scientific instruments, microscopy |
Need precision optical coatings for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance optical components and coatings tailored for laboratory and research applications. Whether you require anti-reflection coatings for clarity, high-reflection mirrors for laser systems, or custom filters for spectral analysis, our expertise ensures optimal performance for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your optical systems with the right coating solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer












