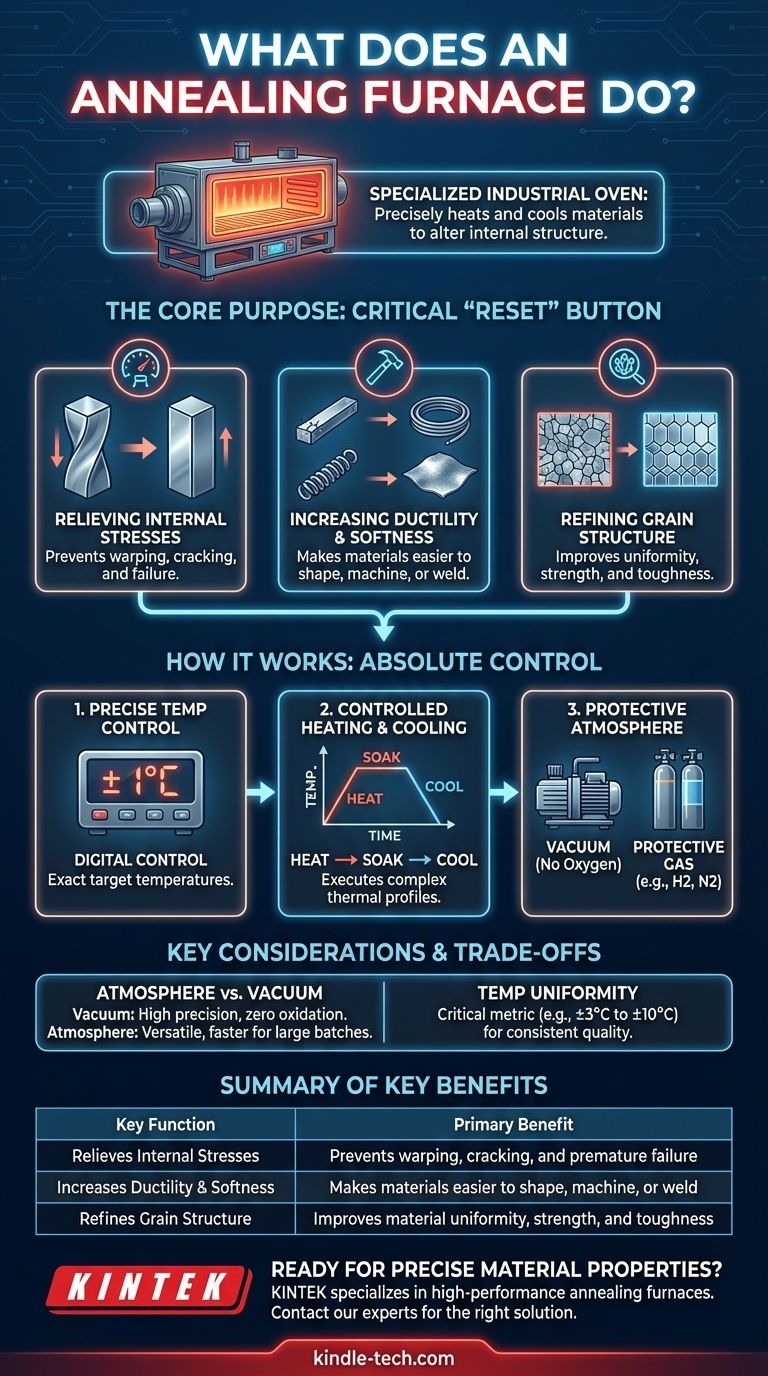
In essence, an annealing furnace is a specialized industrial oven that precisely heats and cools materials—primarily metals—to alter their internal structure. This controlled thermal process is not about melting the material, but rather about changing its physical and sometimes chemical properties to make it more useful for subsequent manufacturing steps or for its final application.
The core purpose of an annealing furnace is to undo the negative effects of prior manufacturing processes. It relieves internal stresses, increases softness and ductility, and refines the material's grain structure, making it less brittle and easier to shape, machine, or weld.

The Core Principle: Why Annealing is Necessary
Materials, especially metals, accumulate stress and hardness during processes like casting, forging, or cold-working (stamping, drawing). Annealing serves as a critical "reset" button to restore desirable properties.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding or heavy machining create immense internal stress within a material's structure. These stresses can lead to warping, cracking, or premature failure later on. Annealing provides the thermal energy needed for the material's atoms to rearrange into a more stable, lower-stress state.
Increasing Ductility and Softness
Hardness is not always a desirable trait. A material that is too hard becomes brittle and is difficult to form or shape without breaking. Annealing softens the material, increasing its ductility (the ability to be stretched or drawn into a wire) and malleability (the ability to be hammered or pressed into shape).
Refining Grain Structure
The microscopic crystalline structure, or "grain," of a metal dictates its strength and toughness. Cold working can distort these grains. The controlled heating and cooling cycle of annealing allows new, strain-free grains to form, resulting in a more uniform and refined internal structure that improves overall performance.
How an Annealing Furnace Achieves This
An annealing furnace is far more sophisticated than a simple oven. Its design is focused on absolute control over the entire thermal cycle to guarantee a predictable and repeatable outcome.
Precise Temperature Control
The furnace's control system is its most critical component. It allows operators to set exact temperatures, with modern systems achieving automatic control precision as tight as ±1°C. This ensures the material reaches the exact temperature required for its specific alloy and desired outcome.
Controlled Heating and Cooling
Annealing is a three-part process: heating to a specific temperature, "soaking" or holding at that temperature, and finally, cooling at a specific rate. The furnace manages this entire cycle, often using piecewise program controllers to execute complex thermal profiles automatically.
The Role of a Protective Atmosphere
Heating metal to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen causes oxidation (rust or scale), which damages the surface finish and can compromise the part's integrity. To prevent this, annealing furnaces operate with a controlled atmosphere.
This is often a vacuum, which removes reactive gases entirely. Alternatively, the furnace can be filled with a protective gas, such as hydrogen or a hydrogen-nitrogen mixture, which displaces oxygen and prevents unwanted chemical reactions on the material's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
The choice of annealing furnace and process depends on the material, the desired outcome, and operational constraints.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
A vacuum furnace is ideal for high-precision components or materials that are extremely sensitive to surface contamination, such as medical implants or aerospace parts. It provides the highest level of purity.
A protective atmosphere furnace, like a hydrogen furnace, is more versatile and can often process larger batches more quickly. However, it requires careful management of flammable gases and may not be suitable for the most reactive metals.
The Importance of Temperature Uniformity
A critical performance metric is temperature uniformity, often specified as a range like ±3°C to ±10°C. This measures how consistent the temperature is across the entire heating chamber. Poor uniformity means different parts of the material will have different properties, leading to inconsistent product quality.
Operational Complexity
These are not "set and forget" machines. They require sophisticated control systems with functions for fault alarms, temperature recording, and safety interlocks for pressure and electrical systems. Proper operation requires a deep understanding of metallurgy and the specific process parameters for each material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal annealing strategy is dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is a perfect surface finish and preventing all oxidation: A vacuum annealing furnace is the definitive choice, especially for high-value stainless steel or reactive alloy components.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing for a variety of parts: A protective atmosphere furnace offers excellent versatility for applications ranging from tool steel to brazing and ceramic sintering.
- If your primary focus is improving the mechanical performance after heavy fabrication: The key is a precisely controlled heating and cooling cycle to relieve stress and refine grain structure, achievable in either furnace type.
Ultimately, understanding the function of an annealing furnace empowers you to select not just a machine, but a process that ensures your material achieves the exact properties required for its final purpose.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Relieves Internal Stresses | Prevents warping, cracking, and premature failure |
| Increases Ductility & Softness | Makes materials easier to shape, machine, or weld |
| Refines Grain Structure | Improves material uniformity, strength, and toughness |
Ready to achieve precise material properties for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including annealing furnaces designed for exact temperature control and uniform heating. Whether you need to relieve stress in fabricated parts, improve machinability, or ensure a perfect surface finish, our solutions deliver reliable, repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material processing needs and discover the right annealing solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















