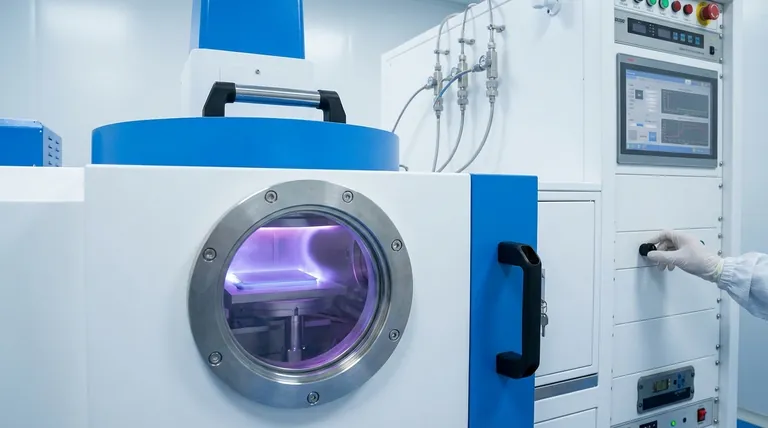
In industrial and material science processes, an inert gas serves two primary functions: it acts as a chemically stable medium to either apply immense physical pressure or to create a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere. This allows for the precise manipulation of materials at high temperatures and energies without causing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, which would compromise the final product's integrity.
The core purpose of using an inert gas is to isolate a process from chemical interference. Its non-reactivity is the key property that allows it to function as a pure physical agent—whether for applying pressure, forming a plasma, or carrying away byproducts—without altering the material's composition.

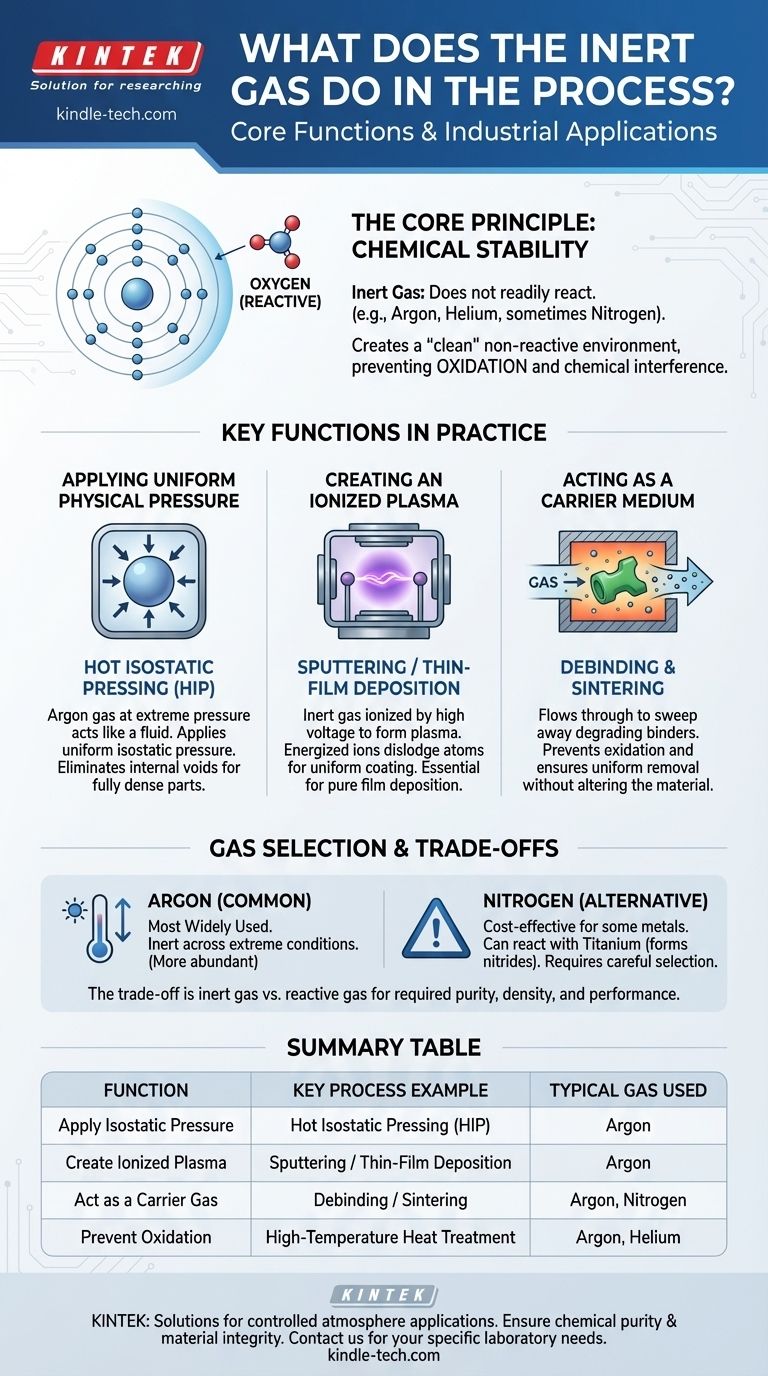
The Core Principle: Chemical Stability
Before examining its specific roles, it's crucial to understand why the "inert" quality is so important.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
An inert gas is one that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other substances. The noble gases, such as argon (Ar) and helium (He), are the most common examples due to their stable electron configurations.
In some contexts, less reactive gases like nitrogen (N₂) are also used, though their suitability depends on the specific materials and temperatures involved.
Why Non-Reactivity is Mission-Critical
Many advanced processes operate under extreme heat and energy. Introducing a reactive gas like oxygen (present in air) would cause immediate and catastrophic oxidation (rusting, on a microscopic level) or other chemical changes.
Using an inert gas creates a "clean" environment, ensuring the material retains its desired chemical properties and integrity from start to finish.
Key Functions in Practice
The non-reactive nature of inert gas allows it to perform several distinct physical tasks across different applications.
Applying Uniform Physical Pressure
In Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), argon gas is heated and pressurized to extreme levels inside a sealed vessel.
This high-pressure gas acts like a fluid, applying uniform, or isostatic, pressure to a part from all directions simultaneously. This immense, even pressure makes the material plastic, causing internal voids and pores to collapse and diffusion bond shut.
The result is a fully dense part with superior mechanical properties, a feat impossible to achieve with a gas that would react with the hot metal.
Creating an Ionized Plasma
In thin-film deposition processes like sputtering, a vacuum chamber is first evacuated and then backfilled with a small amount of inert gas, typically argon.
High voltage is applied, which strips electrons from the argon atoms and creates a plasma—a glowing, ionized gas. These energized ions are then accelerated into a target material, dislodging atoms that then deposit as a thin, uniform coating on a substrate.
The inert gas is essential because it forms the plasma without chemically bonding to the target or the substrate.
Acting as a Carrier Medium
During processes like debinding, where polymer binders must be removed from a "green" part, an inert gas serves a different role.
It acts as a carrier, flowing through the furnace to sweep away the degrading binder components. This prevents oxidation on the metal surface and ensures the binders are removed uniformly from the entire part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Gas Selection
The choice of inert gas is not arbitrary and depends on the specific process and material.
Why Argon is So Common
Argon is the most widely used inert gas. It is significantly more abundant (and thus less expensive) than other noble gases like helium, and it remains inert across an extremely wide range of temperatures and pressures.
When Other Gases Are Used
For some materials, like certain stainless steels during debinding, nitrogen can be a cost-effective alternative.
However, nitrogen can react with other materials, such as titanium, to form nitrides. For these reactive alloys, the superior inertness of argon is mandatory to prevent unwanted chemical changes.
The Impact on Process Control
The primary trade-off is not between different inert gases but between using an inert gas versus a reactive one (or simply air). While operating in an inert atmosphere is more complex and costly, it is the only way to achieve the required purity, density, and performance in high-specification components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The function of the inert gas is directly tied to the desired outcome of the process.
- If your primary focus is densification and defect removal: You need an inert gas like argon to apply high isostatic pressure without chemical reaction, as seen in Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP).
- If your primary focus is thin-film deposition: You need an inert gas to be efficiently ionized into a plasma for sputtering, ensuring the deposited film is chemically pure.
- If your primary focus is material purification or debinding: You need an inert gas to act as a clean carrier, flushing away contaminants without causing surface oxidation or reduction.
Ultimately, using an inert gas ensures that the only changes made to your material are the physical and structural ones you intend.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Process Example | Typical Gas Used |
|---|---|---|
| Apply Isostatic Pressure | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Argon |
| Create Ionized Plasma | Sputtering / Thin-Film Deposition | Argon |
| Act as a Carrier Gas | Debinding / Sintering | Argon, Nitrogen |
| Prevent Oxidation | High-Temperature Heat Treatment | Argon, Helium |
Need to ensure chemical purity and material integrity in your process? KINTEK's expertise in providing lab equipment and consumables for controlled atmosphere applications can help you achieve superior results. Whether you require a system for sputtering, HIP, or high-temperature sintering, our solutions are designed for precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Super Negative Oxygen Ion Generator Machine for Air Purification
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems







