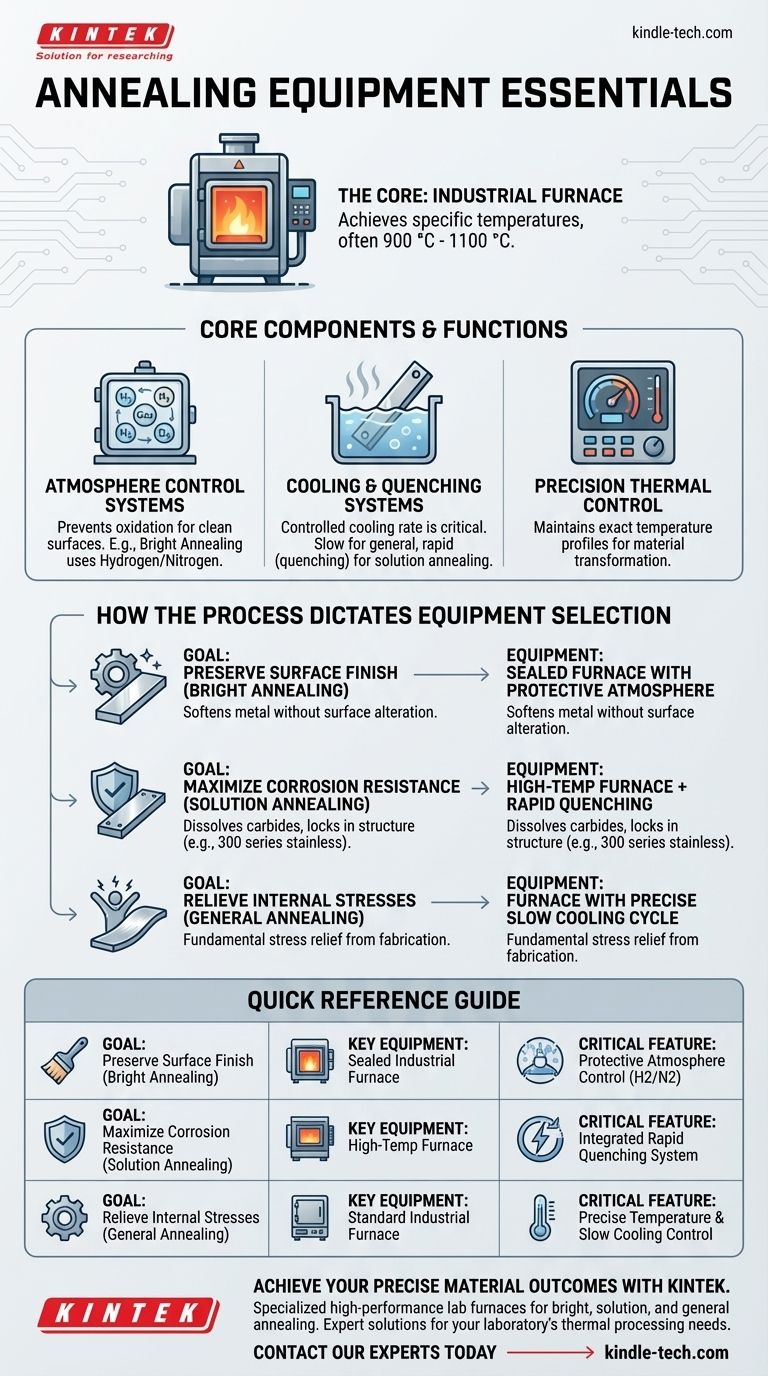
The primary equipment used in annealing is a specialized industrial furnace. The specific type and features of this furnace, such as its ability to control the atmosphere or facilitate rapid cooling, are determined by the material being treated and the precise goal of the heat treatment process.
The term "annealing" covers a range of heat treatment processes, so the equipment is not one-size-fits-all. The critical factor is that the equipment—a high-temperature furnace—must be chosen based on the specific type of annealing required, such as bright annealing or solution annealing.

The Core Components of Annealing Equipment
At its heart, any annealing operation relies on a furnace capable of precise thermal control. However, the complexity of the equipment extends beyond simple heating.
The Industrial Furnace
The furnace is the central piece of equipment. It must be capable of reaching and maintaining the specific temperatures required for the material, often between 900 °C and 1100 °C for processes like solution annealing.
Atmosphere Control Systems
For certain processes, controlling the atmosphere inside the furnace is critical. This prevents oxidation and other surface reactions that can tarnish the material.
A prime example is the bright annealing furnace, which uses a protective atmosphere (like hydrogen or nitrogen) to heat treat finished stainless steel products, ensuring they maintain a clean, "bright" surface.
Cooling and Quenching Systems
The rate of cooling is just as important as the heating cycle. Some processes require slow, controlled cooling within the furnace, while others demand rapid cooling, or quenching, to lock in a specific material structure.
How the Process Dictates the Equipment
The specific purpose of the annealing treatment directly influences the selection of the furnace and its associated systems.
For Surface Finish: Bright Annealing
The goal of bright annealing is to soften the metal and relieve stress without altering its surface appearance.
The equipment must be a sealed furnace with a controlled, protective atmosphere. This prevents the oxidation that would otherwise occur at high temperatures, preserving the material's finish.
For Material Properties: Solution Annealing
Solution annealing is a specific process used primarily for 300 series (austenitic) stainless steels. Its purpose is to improve ductility and corrosion resistance.
This process involves heating the steel to dissolve carbides and then cooling it rapidly to prevent them from re-forming. The equipment must therefore include not only a high-temperature furnace but also an integrated or adjacent system for quenching, such as a water or polymer bath.
For Internal Stress: General Annealing
The most fundamental goal of annealing is to relieve internal stresses induced during manufacturing processes like casting or cold working.
For this purpose, the essential equipment is a furnace with precise temperature controls that can execute a specific heating and, crucially, a slow, controlled cooling cycle. Atmosphere control may be less critical if a final surface finishing step is planned.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct annealing equipment is a function of your end goal and the material you are working with.
- If your primary focus is preserving a pristine surface finish: You require a bright annealing furnace with robust atmosphere controls.
- If your primary focus is maximizing corrosion resistance in austenitic steel: You need a high-temperature furnace paired with a rapid quenching system for solution annealing.
- If your primary focus is simply relieving internal fabrication stresses: A standard industrial furnace with precise temperature and cooling-rate controls will be sufficient.
Ultimately, defining the desired material outcome is the first and most critical step in specifying the right annealing equipment.
Summary Table:
| Annealing Goal | Key Equipment Needed | Critical Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Preserve Surface Finish (Bright Annealing) | Sealed Industrial Furnace | Protective Atmosphere Control (e.g., Hydrogen/Nitrogen) |
| Maximize Corrosion Resistance (Solution Annealing) | High-Temperature Furnace | Integrated Rapid Quenching System |
| Relieve Internal Stresses (General Annealing) | Standard Industrial Furnace | Precise Temperature & Slow Cooling Control |
Achieve your precise material outcomes with the right annealing equipment.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab furnaces and consumables tailored to your specific annealing process, whether you require precise atmosphere control for bright annealing or rapid quenching capabilities for solution annealing. Our expertise ensures you get the exact thermal processing solution your laboratory needs for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect furnace for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature furnaces affect bio-oil yield? Optimize Pyrolysis with Precision Control
- Are steel containing carbon used for carburizing? The Right Steel for a Hard Surface & Tough Core
- Why is a vacuum drying oven preferred for drying ceramic slurries? Prevent Oxidation & Ensure Chemical Purity
- Is annealing a slow process? The Critical Role of Controlled Cooling in Heat Treatment
- What role do industrial-grade high-temperature sintering furnaces play in the final formation of Lanthanum Zirconate?
- How does a plasma arc furnace work? Harness a Superheated Plasma Jet for Intense Melting
- What is high vacuum used for? Essential for Particle Beams and Advanced Lab Instruments
- Why is a multi-stage aging furnace required for gamma prime phase control in superalloys? Expert Insights.



















